The Blue Zones Diet emphasizes plant-based foods, whole grains, and legumes, mirroring the diets of communities with the longest lifespans, while limiting processed foods and animal products. The Mediterranean Diet also highlights fruits, vegetables, nuts, and olive oil, promoting heart health through moderate consumption of fish and dairy and minimal red meat. Both diets support longevity and well-being by focusing on nutrient-rich, minimally processed foods, but the Blue Zones Diet leans more heavily on plant-only meals and social eating habits.
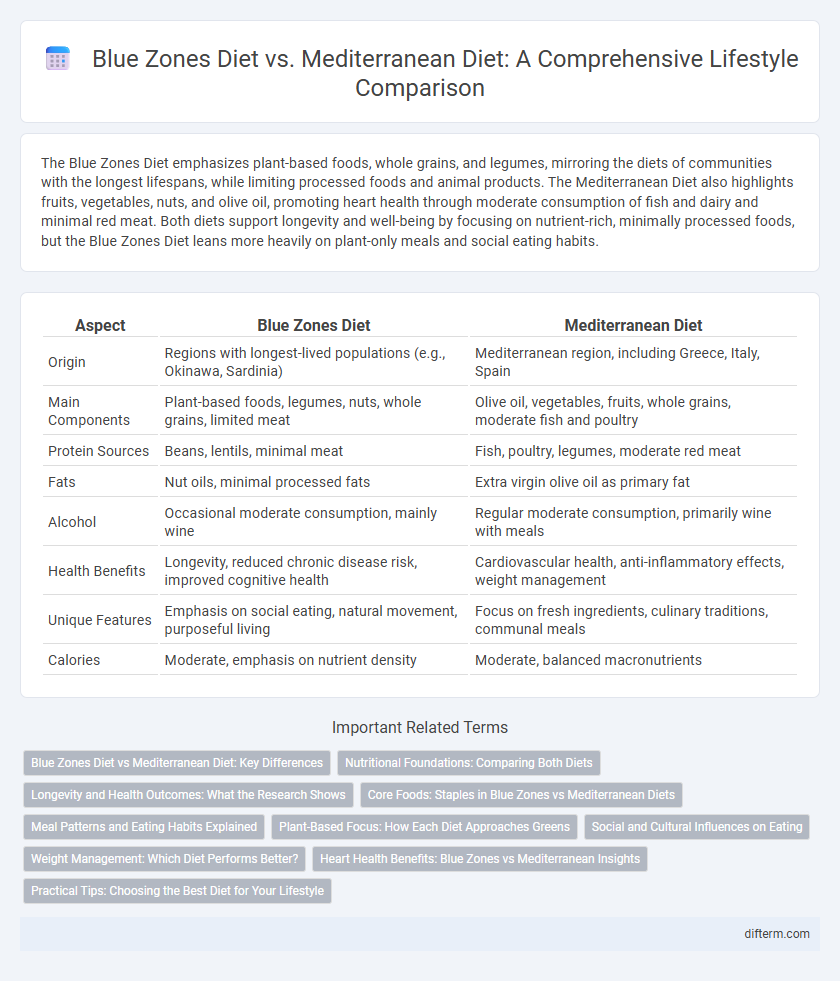
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blue Zones Diet | Mediterranean Diet |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Regions with longest-lived populations (e.g., Okinawa, Sardinia) | Mediterranean region, including Greece, Italy, Spain |
| Main Components | Plant-based foods, legumes, nuts, whole grains, limited meat | Olive oil, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, moderate fish and poultry |
| Protein Sources | Beans, lentils, minimal meat | Fish, poultry, legumes, moderate red meat |
| Fats | Nut oils, minimal processed fats | Extra virgin olive oil as primary fat |
| Alcohol | Occasional moderate consumption, mainly wine | Regular moderate consumption, primarily wine with meals |
| Health Benefits | Longevity, reduced chronic disease risk, improved cognitive health | Cardiovascular health, anti-inflammatory effects, weight management |
| Unique Features | Emphasis on social eating, natural movement, purposeful living | Focus on fresh ingredients, culinary traditions, communal meals |
| Calories | Moderate, emphasis on nutrient density | Moderate, balanced macronutrients |
Blue Zones Diet vs Mediterranean Diet: Key Differences
The Blue Zones Diet emphasizes plant-based foods, legumes, nuts, and limited animal protein, reflecting dietary patterns observed in regions with exceptional longevity, while the Mediterranean Diet highlights olive oil, moderate fish and wine consumption, and a higher intake of fruits and vegetables. Blue Zones Diet focuses on natural, minimally processed foods tied to cultural habits fostering longevity, whereas the Mediterranean Diet integrates heart-healthy fats and antioxidants known for cardiovascular benefits. Key differences include the strict vegetarian inclination of Blue Zones versus the Mediterranean Diet's inclusion of lean meats and seafood, alongside variations in fat sources and portion moderation.
Nutritional Foundations: Comparing Both Diets
The Blue Zones Diet emphasizes plant-based foods, legumes, nuts, whole grains, and limited animal products, promoting longevity through nutrient-dense, low-calorie intake. The Mediterranean Diet centers on olive oil, fruits, vegetables, fish, whole grains, and moderate wine consumption, offering heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and antioxidants. Both diets prioritize fresh, minimally processed foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, fostering improved metabolic health and reduced chronic disease risk.
Longevity and Health Outcomes: What the Research Shows
Research indicates that both the Blue Zones Diet and Mediterranean Diet significantly contribute to increased longevity and improved health outcomes, with the Blue Zones Diet emphasizing plant-based foods, legumes, and moderate caloric intake often linked to centenarian populations. The Mediterranean Diet, rich in olive oil, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins like fish, is associated with reduced risks of cardiovascular disease, cognitive decline, and metabolic disorders. Comparative studies reveal overlapping benefits such as anti-inflammatory effects and enhanced metabolic health, underscoring their roles in aging well and preventing chronic diseases.
Core Foods: Staples in Blue Zones vs Mediterranean Diets
Blue Zones diets emphasize core staples such as legumes, whole grains, nuts, and a variety of local vegetables, reflecting a plant-based focus rich in fiber and antioxidants. Mediterranean diets prioritize olive oil, fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and moderate fish and dairy, highlighting healthy fats and omega-3 fatty acids. Both diets share a reliance on nutrient-dense, minimally processed foods that support heart health and longevity.
Meal Patterns and Eating Habits Explained
The Blue Zones diet emphasizes plant-based meals rich in legumes, nuts, and whole grains, often accompanied by small portions of fish or meat consumed sparingly, reflecting a primarily vegetarian lifestyle with periodic fasting. In contrast, the Mediterranean diet features consistent intake of fruits, vegetables, olive oil, whole grains, fish, and moderate wine consumption, promoting balanced macronutrients and daily moderate eating habits. Both diets encourage mindful eating practices, such as eating with family, slow consumption, and portion control, which support longevity and overall health.
Plant-Based Focus: How Each Diet Approaches Greens
The Blue Zones Diet emphasizes a predominantly plant-based approach by prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense vegetables, beans, and leafy greens common in regions with exceptional longevity, such as Okinawa and Sardinia. The Mediterranean Diet also highlights plant-based foods but integrates a moderate amount of healthy fats like olive oil and includes seasonal vegetables, fruits, and legumes as staples to promote heart health. Both diets encourage minimizing processed foods and animal protein, yet Blue Zones lean more heavily on plant diversity and minimal meat consumption for optimal wellness.
Social and Cultural Influences on Eating
The Blue Zones Diet emphasizes plant-based foods rooted in traditional eating patterns of regions with high longevity, fostering communal meals that strengthen social bonds and cultural identity. The Mediterranean Diet, rich in olive oil, fruits, vegetables, and fish, reflects centuries-old culinary traditions that encourage family gatherings and shared dining experiences. Both diets highlight how social interactions and cultural heritage shape eating habits, promoting longevity and well-being through connected and mindful consumption.
Weight Management: Which Diet Performs Better?
The Blue Zones Diet emphasizes plant-based foods, legumes, and moderate portions, promoting sustainable weight management through natural calorie control and nutrient density. The Mediterranean Diet incorporates healthy fats like olive oil and omega-3-rich fish, offering metabolic benefits that support weight loss and cardiovascular health. Studies suggest both diets effectively aid weight management, with the Blue Zones Diet often excelling in long-term adherence and the Mediterranean Diet providing robust anti-inflammatory effects.
Heart Health Benefits: Blue Zones vs Mediterranean Insights
Both the Blue Zones Diet and Mediterranean Diet emphasize plant-based foods, healthy fats, and whole grains, contributing to improved cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation and cholesterol levels. Studies reveal the Blue Zones Diet, rich in legumes, nuts, and antioxidant-dense foods, promotes lower heart disease risk and increased longevity. In comparison, the Mediterranean Diet, abundant in olive oil, fish, and moderate wine consumption, supports heart health through enhanced artery function and reduced oxidative stress.
Practical Tips: Choosing the Best Diet for Your Lifestyle
The Blue Zones Diet emphasizes whole, plant-based foods with minimal processed ingredients, ideal for those seeking longevity and low environmental impact. The Mediterranean Diet incorporates healthy fats like olive oil, lean proteins, and moderate wine consumption, suited for heart health and flexible meal planning. Prioritize your dietary goals, accessibility to fresh ingredients, and cultural preferences when selecting the best diet for sustainable lifestyle changes.
Blue Zones Diet vs Mediterranean Diet Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com