Achieving a caloric deficit is essential for weight loss, as it means consuming fewer calories than the body expends, forcing it to use stored fat for energy. Energy balance occurs when the number of calories consumed matches the calories burned, maintaining current body weight without fat gain or loss. Understanding the relationship between energy balance and caloric deficit is crucial for designing effective health and nutrition plans.
Table of Comparison
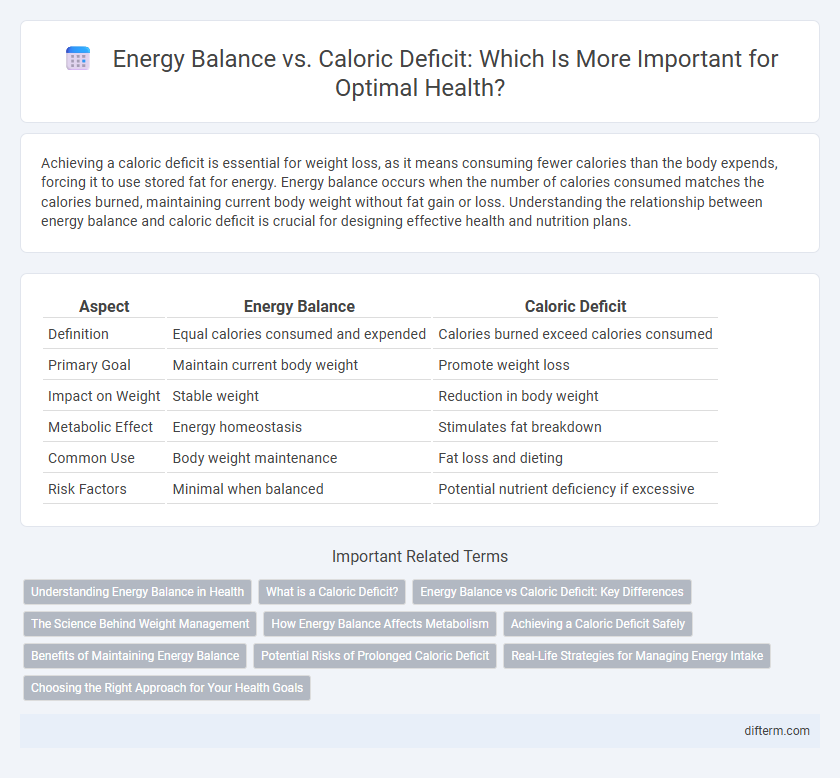
| Aspect | Energy Balance | Caloric Deficit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Equal calories consumed and expended | Calories burned exceed calories consumed |
| Primary Goal | Maintain current body weight | Promote weight loss |
| Impact on Weight | Stable weight | Reduction in body weight |
| Metabolic Effect | Energy homeostasis | Stimulates fat breakdown |
| Common Use | Body weight maintenance | Fat loss and dieting |
| Risk Factors | Minimal when balanced | Potential nutrient deficiency if excessive |
Understanding Energy Balance in Health
Energy balance is the relationship between calories consumed from food and beverages and calories expended through bodily functions and physical activity, crucial for maintaining, gaining, or losing weight. A positive energy balance occurs when calorie intake exceeds expenditure, leading to weight gain, while a caloric deficit arises when energy consumption is lower than energy use, promoting weight loss. Understanding energy balance helps optimize nutrition strategies for metabolic health, weight management, and overall well-being.
What is a Caloric Deficit?
A caloric deficit occurs when the number of calories consumed is less than the calories expended through basal metabolic rate and physical activity, prompting the body to use stored fat for energy. Maintaining a consistent caloric deficit is essential for weight loss and improving metabolic health. Understanding energy balance helps in creating effective diet plans to achieve and sustain this deficit.
Energy Balance vs Caloric Deficit: Key Differences
Energy balance occurs when the calories consumed equal the calories expended, maintaining stable body weight, while a caloric deficit happens when calorie expenditure surpasses intake, leading to weight loss. Understanding the key differences between energy balance and caloric deficit is crucial for designing effective nutrition and fitness plans. Managing these factors influences metabolism, fat loss, and overall health outcomes.
The Science Behind Weight Management
Energy balance, defined as the relationship between calories consumed and calories expended, plays a crucial role in weight management. A caloric deficit occurs when energy expenditure exceeds intake, prompting the body to utilize stored fat for fuel, leading to weight loss. Scientific studies highlight that maintaining a consistent caloric deficit is essential for effective and sustainable fat reduction while supporting metabolic health.
How Energy Balance Affects Metabolism
Energy balance directly influences metabolism by regulating how the body processes calories for energy storage or expenditure. A positive energy balance leads to increased fat storage, while a caloric deficit prompts the body to utilize stored fat, enhancing metabolic rate temporarily. Sustained caloric deficits can slow metabolism as the body adapts to conserve energy, highlighting the importance of balanced energy intake for optimal metabolic function.
Achieving a Caloric Deficit Safely
Achieving a caloric deficit safely involves consuming fewer calories than the body expends while maintaining adequate nutrient intake to support metabolic functions and overall health. Balancing macronutrients and incorporating regular physical activity helps preserve lean muscle mass and prevents metabolic slowdown commonly associated with extreme calorie restriction. Monitoring energy balance through tools like food diaries and wearable fitness trackers ensures a sustainable approach to weight loss without compromising essential physiological processes.
Benefits of Maintaining Energy Balance
Maintaining energy balance supports metabolic stability by ensuring calorie intake matches energy expenditure, which promotes weight maintenance and prevents nutrient deficiencies. This equilibrium enhances physical performance and supports hormonal regulation, contributing to overall health and reduced risk of chronic diseases. Consistent energy balance also aids in preserving lean muscle mass while optimizing recovery and immune function.
Potential Risks of Prolonged Caloric Deficit
Prolonged caloric deficit can lead to muscle loss, decreased metabolic rate, and nutrient deficiencies that impair overall health and recovery. Energy imbalance disrupts hormonal functions, increasing risks of fatigue, weakened immune response, and bone density reduction. Maintaining a moderate energy balance is crucial for sustainable weight management and optimal physiological function.
Real-Life Strategies for Managing Energy Intake
Managing energy intake through real-life strategies involves tracking portion sizes and prioritizing nutrient-dense foods to maintain a balanced caloric intake. Incorporating regular physical activity enhances energy expenditure, supporting a caloric deficit for weight management. Consistent meal timing and mindful eating practices improve satiety cues, helping prevent overeating and promote long-term energy balance.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Health Goals
Energy balance refers to the equilibrium between calories consumed and calories expended, essential for maintaining current weight and overall health. A caloric deficit, achieved by consuming fewer calories than the body uses, is critical for weight loss but requires mindful adjustment to avoid nutrient deficiencies and metabolic slowdown. Selecting the right approach depends on individual health goals, metabolic rate, activity level, and nutritional needs, ensuring sustainable progress and long-term wellness.
Energy balance vs Caloric deficit Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com