Cabinet government centralizes executive power within the legislature, where the Prime Minister and cabinet members are directly accountable to Parliament, ensuring collective responsibility and political stability. The presidential system separates executive and legislative branches, with a President elected independently of the legislature, allowing for checks and balances but potential gridlock. Both systems shape how government policies are developed and implemented, reflecting different approaches to authority and accountability.
Table of Comparison
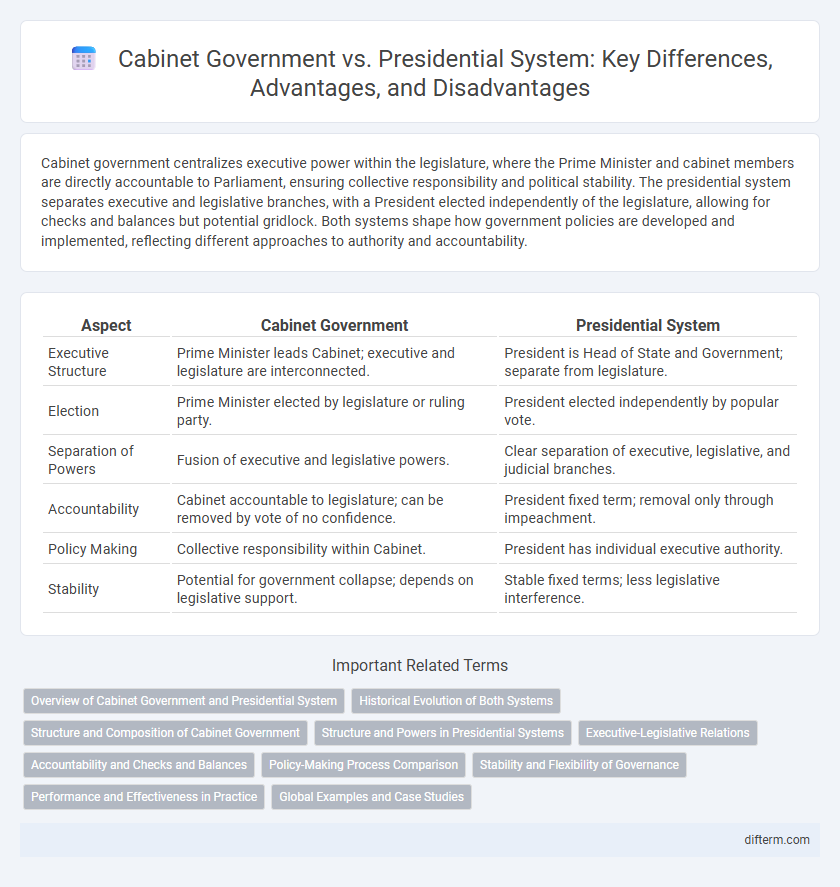
| Aspect | Cabinet Government | Presidential System |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Structure | Prime Minister leads Cabinet; executive and legislature are interconnected. | President is Head of State and Government; separate from legislature. |
| Election | Prime Minister elected by legislature or ruling party. | President elected independently by popular vote. |
| Separation of Powers | Fusion of executive and legislative powers. | Clear separation of executive, legislative, and judicial branches. |
| Accountability | Cabinet accountable to legislature; can be removed by vote of no confidence. | President fixed term; removal only through impeachment. |
| Policy Making | Collective responsibility within Cabinet. | President has individual executive authority. |
| Stability | Potential for government collapse; depends on legislative support. | Stable fixed terms; less legislative interference. |
Overview of Cabinet Government and Presidential System
The Cabinet Government system features a collective executive authority where the prime minister and cabinet members, drawn from the legislature, share decision-making responsibilities, promoting interdependence between branches. In contrast, the Presidential System separates executive and legislative powers, with a president elected independently, allowing for distinct checks and balances. The Cabinet Government often leads to greater legislative cohesion, while the Presidential System emphasizes individual leadership and fixed terms.
Historical Evolution of Both Systems
The Cabinet Government system evolved primarily in the United Kingdom during the 18th century, emphasizing collective decision-making by ministers accountable to Parliament, reflecting the gradual shift from absolute monarchy to constitutional democracy. The Presidential System, established notably in the United States with the 1787 Constitution, introduced a clear separation of powers between the executive and legislative branches, ensuring checks and balances and direct election of the president. These historical developments highlight the contrasting foundations: Cabinet Government's parliamentary sovereignty versus the Presidential System's federalism and institutional independence.
Structure and Composition of Cabinet Government
Cabinet government features a collective executive body composed of members of the legislature, typically headed by a prime minister who is accountable to the parliament. This structure integrates the executive and legislative branches, allowing the cabinet to formulate and implement policies through majority support within the legislature. The composition of the cabinet reflects political party alignments and coalition agreements, promoting collaborative decision-making and shared responsibility among ministers.
Structure and Powers in Presidential Systems
In presidential systems, the structure centralizes executive power in a separately elected president who serves as both head of state and government, ensuring distinct separation from the legislature. The president holds significant constitutional authority, including veto power, command of the armed forces, and appointment of cabinet officials without requiring legislative approval for the executive branch's formation. This framework contrasts with cabinet government systems where executive power is derived from and accountable to the legislature, highlighting the independence and concentrated powers embedded in presidential systems.
Executive-Legislative Relations
The Cabinet Government system features a fusion of executive and legislative powers, where the executive branch is derived from and accountable to the legislature, allowing for more collaborative policy-making and easier passage of laws. In contrast, the Presidential System maintains a clear separation of powers, with the executive independently elected and separate from the legislature, which can lead to checks and balances but also potential legislative gridlock. Executive-legislative relations in Cabinet Government tend to be more integrated and cooperative, while in the Presidential System, they are more adversarial and distinct, impacting governance efficiency and political stability.
Accountability and Checks and Balances
In a Cabinet Government, accountability is concentrated within the executive branch where the Prime Minister and cabinet members are collectively responsible to the legislature, enabling direct parliamentary scrutiny and potential dismissal through votes of no confidence. The Presidential System features a separation of powers with independent executive and legislative branches, ensuring checks and balances via veto powers, legislative oversight, and judicial review to prevent executive overreach. This structural distinction shapes the mechanisms for maintaining government accountability and balancing institutional powers within democratic governance.
Policy-Making Process Comparison
The Cabinet Government system centralizes policy-making within a collective cabinet led by the Prime Minister, enabling swift consensus and unified executive decisions. In contrast, the Presidential System disperses policy authority across independently elected executive and legislative branches, often resulting in slower, more deliberative policy development due to checks and balances. This structural difference critically impacts the efficiency and coordination of policy formulation and implementation in governance.
Stability and Flexibility of Governance
Cabinet government systems offer greater flexibility by allowing the executive branch to be directly accountable to the legislature, enabling swift policy adjustments and coalition formations. Presidential systems provide stability through a fixed term and a clear separation of powers, reducing the risk of abrupt governmental collapse. The balance between flexibility and stability is crucial in determining effective governance and responsiveness to political dynamics.
Performance and Effectiveness in Practice
Cabinet governments often demonstrate higher policy coherence and adaptability due to collective decision-making and party discipline, leading to more consistent legislative output. Presidential systems provide stability through fixed terms and clear separation of powers, but may face gridlock and slower decision-making processes during political stalemates. Comparative studies indicate cabinet governments excel in rapid policy implementation, whereas presidential systems offer stronger checks and balances, influencing overall government performance and effectiveness.
Global Examples and Case Studies
The Cabinet Government system, exemplified by the United Kingdom and India, features collective executive responsibility where the Prime Minister and cabinet members are drawn from the legislature, ensuring parliamentary accountability. In contrast, the Presidential System, as seen in the United States and Brazil, separates executive and legislative powers with a directly elected president serving as both head of state and government, providing checks and balances through fixed terms. Case studies highlight that Cabinet Governments tend to enable quicker legislative consensus, while Presidential Systems emphasize stability and separation of powers to prevent authoritarian rule.
Cabinet Government vs Presidential System Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com