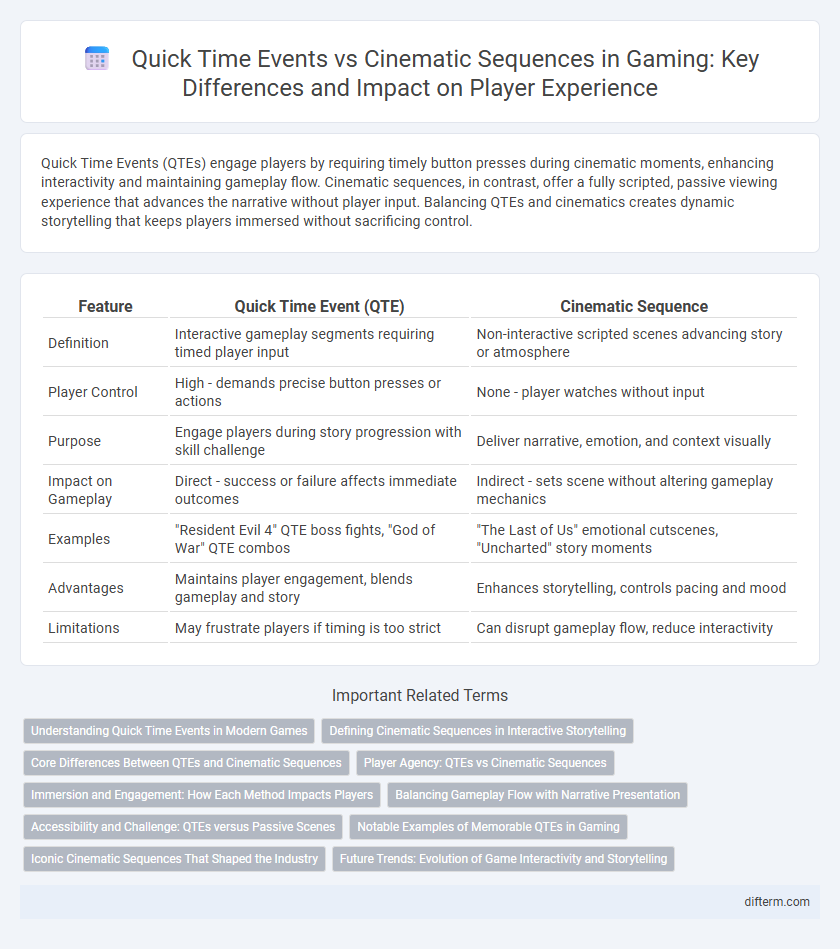
Quick Time Events (QTEs) engage players by requiring timely button presses during cinematic moments, enhancing interactivity and maintaining gameplay flow. Cinematic sequences, in contrast, offer a fully scripted, passive viewing experience that advances the narrative without player input. Balancing QTEs and cinematics creates dynamic storytelling that keeps players immersed without sacrificing control.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Quick Time Event (QTE) | Cinematic Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interactive gameplay segments requiring timed player input | Non-interactive scripted scenes advancing story or atmosphere |
| Player Control | High - demands precise button presses or actions | None - player watches without input |
| Purpose | Engage players during story progression with skill challenge | Deliver narrative, emotion, and context visually |
| Impact on Gameplay | Direct - success or failure affects immediate outcomes | Indirect - sets scene without altering gameplay mechanics |
| Examples | "Resident Evil 4" QTE boss fights, "God of War" QTE combos | "The Last of Us" emotional cutscenes, "Uncharted" story moments |
| Advantages | Maintains player engagement, blends gameplay and story | Enhances storytelling, controls pacing and mood |
| Limitations | May frustrate players if timing is too strict | Can disrupt gameplay flow, reduce interactivity |
Understanding Quick Time Events in Modern Games
Quick Time Events (QTEs) in modern games enhance player immersion by requiring real-time button presses during cinematic sequences to influence outcomes, blending interactive gameplay with storytelling. Unlike passive cinematic sequences, QTEs actively engage players, creating tension and a sense of agency within the narrative flow. Developers use QTEs strategically to maintain gameplay momentum while delivering visually dramatic moments that keep players invested.
Defining Cinematic Sequences in Interactive Storytelling
Cinematic sequences in interactive storytelling are scripted, non-interactive moments designed to advance the narrative and deepen emotional engagement through visually immersive and carefully directed scenes. These sequences often use high-quality animations and voice acting to create a film-like experience, contrasting with quick time events that require player input to influence outcomes. By controlling pacing and emphasizing story beats, cinematic sequences enhance the storytelling depth without interrupting player immersion.
Core Differences Between QTEs and Cinematic Sequences
Quick Time Events (QTEs) require player interaction through timed button presses to influence gameplay outcomes, creating an active engagement moment during scripted sequences. Cinematic sequences are non-interactive story-driven cutscenes designed to advance the narrative without player control. The core difference lies in QTEs blending gameplay with storytelling via interactivity, while cinematic sequences prioritize passive narrative delivery.
Player Agency: QTEs vs Cinematic Sequences
Quick Time Events (QTEs) enhance player agency by requiring timely input, creating an interactive experience that impacts the outcome, unlike cinematic sequences where players passively watch predetermined events unfold. QTEs maintain engagement through skill-based challenges, reinforcing a sense of control, while cinematic sequences prioritize storytelling and immersion with limited player interaction. Balancing these elements is crucial in game design to optimize narrative flow without sacrificing player involvement.
Immersion and Engagement: How Each Method Impacts Players
Quick Time Events (QTEs) actively engage players by requiring timely input, creating a sense of immersion through interactive storytelling that blends gameplay and narrative. Cinematic Sequences provide a visually rich, passive experience that enhances emotional impact and world-building but can reduce player agency. Balancing these elements influences how deeply players connect with the game environment and remain engaged throughout the storyline.
Balancing Gameplay Flow with Narrative Presentation
Quick Time Events (QTEs) engage players by requiring timely input during cinematic sequences, maintaining interactive gameplay while advancing the narrative. Cinematic sequences provide rich storytelling and emotional depth without player control, often enhancing immersion but potentially disrupting gameplay flow. Balancing QTEs and cinematic sequences ensures players remain active participants, preserving pacing and narrative impact in gaming experiences.
Accessibility and Challenge: QTEs versus Passive Scenes
Quick Time Events (QTEs) enhance accessibility by actively engaging players through timely button presses, offering a dynamic challenge that tests reflexes and decision-making skills. In contrast, cinematic sequences provide passive narrative delivery, ensuring inclusivity for players with varying physical abilities but reducing interactive difficulty. Balancing QTEs with well-integrated cinematics can enrich gameplay by catering to diverse player preferences and accessibility needs.
Notable Examples of Memorable QTEs in Gaming
Notable examples of memorable Quick Time Events (QTEs) in gaming include the intense sequences in "Resident Evil 4," where timely button presses during boss fights heighten suspense and immersion. "Heavy Rain" utilizes QTEs extensively to shape narrative outcomes, making player input crucial for character survival and emotional impact. The climactic escape scenes in "God of War" showcase QTEs to deliver cinematic thrills while maintaining interactive engagement.
Iconic Cinematic Sequences That Shaped the Industry
Iconic cinematic sequences like the intense opening of "Metal Gear Solid 2" and the emotional ending of "The Last of Us" redefined storytelling in gaming by blending narrative depth with visual spectacle. These sequences elevate player immersion beyond Quick Time Events (QTEs), which often rely on timed button presses to engage users without fully developing emotional connections. The impact of cinematic sequences in games has set new standards for narrative delivery, influencing game design and player expectations worldwide.
Future Trends: Evolution of Game Interactivity and Storytelling
Quick Time Events (QTEs) and cinematic sequences are evolving with increasing player agency and immersive technologies like VR and AI-driven narratives. Future trends emphasize seamless integration of interactive storytelling where player choices dynamically influence cinematic outcomes and gameplay flow. Advances in procedural generation and motion capture enhance real-time adaptability, creating more personalized and engaging gaming experiences.
Quick Time Event vs Cinematic Sequence Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com