Live service games continuously deliver fresh content, events, and updates to keep players engaged over time, fostering a dynamic and evolving gaming experience. Buy-to-play titles offer a complete game upon purchase, providing a fixed amount of content without the need for ongoing payments or subscriptions. Players seeking long-term engagement and social interaction often prefer live service models, while those valuing upfront ownership and no recurring costs lean toward buy-to-play options.
Table of Comparison
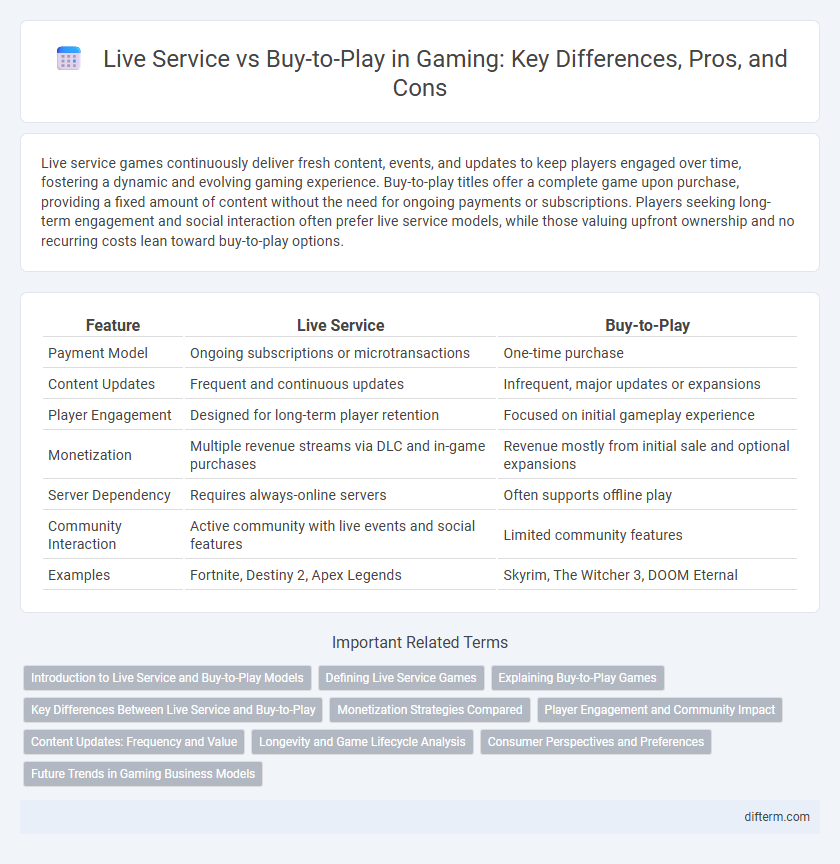
| Feature | Live Service | Buy-to-Play |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Model | Ongoing subscriptions or microtransactions | One-time purchase |
| Content Updates | Frequent and continuous updates | Infrequent, major updates or expansions |
| Player Engagement | Designed for long-term player retention | Focused on initial gameplay experience |
| Monetization | Multiple revenue streams via DLC and in-game purchases | Revenue mostly from initial sale and optional expansions |
| Server Dependency | Requires always-online servers | Often supports offline play |
| Community Interaction | Active community with live events and social features | Limited community features |
| Examples | Fortnite, Destiny 2, Apex Legends | Skyrim, The Witcher 3, DOOM Eternal |
Introduction to Live Service and Buy-to-Play Models
Live service games provide ongoing content updates and community engagement, generating revenue through subscriptions, microtransactions, and seasonal passes. Buy-to-play titles require a one-time purchase, granting full access to the game without mandatory additional spending, often supplemented by optional expansions or DLCs. These models shape player experience, monetization strategies, and game longevity in the gaming industry.
Defining Live Service Games
Live service games continuously deliver new content, events, and updates to engage players over extended periods, often using seasonal models and in-game purchases to sustain revenue. These games emphasize community interaction and evolving gameplay experiences rather than a one-time purchase. Popular examples include Fortnite and Destiny 2, which thrive on persistent online worlds and regular content drops.
Explaining Buy-to-Play Games
Buy-to-play games require a one-time purchase fee, granting players full access without ongoing subscription costs. These titles often receive periodic updates or expansions but do not rely on continuous microtransactions or seasonal passes for core content. This model offers a straightforward gaming experience with ownership guaranteed after the initial buy-in.
Key Differences Between Live Service and Buy-to-Play
Live Service games continuously deliver new content, updates, and events to keep players engaged over time, often supported by microtransactions and subscriptions. Buy-to-Play titles require a one-time purchase, granting full access without mandatory ongoing payments, emphasizing complete gameplay upfront. The key difference lies in Live Service's evolving, dynamic experience versus Buy-to-Play's static, complete package model.
Monetization Strategies Compared
Live Service games generate continuous revenue through microtransactions, battle passes, and seasonal content, ensuring long-term player engagement and steady cash flow. Buy-to-Play models rely on upfront purchases and occasional downloadable content (DLC) sales, limiting monetization opportunities to initial and periodic transactions. Live Service monetization leverages recurring spending patterns, while Buy-to-Play depends more on one-time payments and expansions to sustain profitability.
Player Engagement and Community Impact
Live Service games maintain continuous player engagement through regular content updates, seasonal events, and dynamic in-game experiences that foster active communities and long-term retention. Buy-to-Play titles offer a complete game experience upfront, often promoting deeper narrative immersion but with less ongoing interaction and fewer community-driven updates. The sustained engagement in Live Service models typically cultivates more vibrant, evolving player communities compared to the more static social environments of Buy-to-Play games.
Content Updates: Frequency and Value
Live Service games deliver frequent, often weekly or monthly, content updates that maintain player engagement through continuous new challenges, events, and story expansions. Buy-to-Play titles typically offer fewer but more substantial content updates, focusing on major expansions or DLCs that add significant value and depth over time. The steady cadence of Live Service updates promotes ongoing community interaction, while Buy-to-Play updates emphasize quality and lasting gameplay enhancement.
Longevity and Game Lifecycle Analysis
Live service games extend longevity through continuous content updates, seasonal events, and community engagement, fostering sustained player retention and evolving narratives. Buy-to-play models offer a complete experience upfront but often rely on expansions or sequels for lifecycle extension, which can limit long-term engagement. Analyzing player retention metrics and revenue streams reveals live service models generally sustain higher long-term activity and profitability compared to traditional buy-to-play games.
Consumer Perspectives and Preferences
Consumers favor Live Service games for their continuous content updates and evolving gameplay experiences, which enhance long-term engagement and value. Buy-to-Play titles attract players who prefer one-time purchases without recurring fees, offering a complete experience upfront and avoiding potential subscription fatigue. Player preferences often hinge on gameplay style, budget flexibility, and desire for community interaction or standalone narrative.
Future Trends in Gaming Business Models
Live service games increasingly dominate the market by generating continuous revenue through microtransactions and seasonal content updates, enhancing player retention and long-term engagement. Buy-to-play models maintain relevance by offering one-time purchase experiences with expansive single-player campaigns or multiplayer modes, attracting players seeking ownership without ongoing costs. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach, integrating live service elements into buy-to-play titles to balance monetization and player satisfaction while leveraging cloud gaming and AI-driven content personalization.
Live Service vs Buy-to-Play Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com