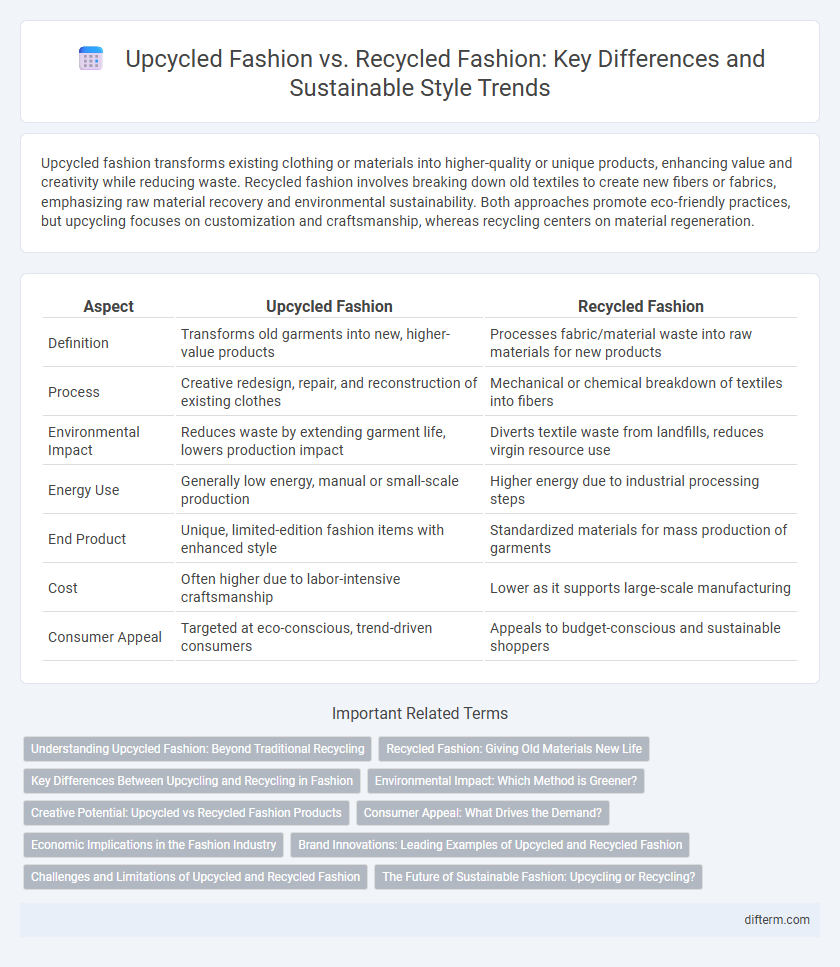
Upcycled fashion transforms existing clothing or materials into higher-quality or unique products, enhancing value and creativity while reducing waste. Recycled fashion involves breaking down old textiles to create new fibers or fabrics, emphasizing raw material recovery and environmental sustainability. Both approaches promote eco-friendly practices, but upcycling focuses on customization and craftsmanship, whereas recycling centers on material regeneration.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Upcycled Fashion | Recycled Fashion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transforms old garments into new, higher-value products | Processes fabric/material waste into raw materials for new products |
| Process | Creative redesign, repair, and reconstruction of existing clothes | Mechanical or chemical breakdown of textiles into fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste by extending garment life, lowers production impact | Diverts textile waste from landfills, reduces virgin resource use |
| Energy Use | Generally low energy, manual or small-scale production | Higher energy due to industrial processing steps |
| End Product | Unique, limited-edition fashion items with enhanced style | Standardized materials for mass production of garments |
| Cost | Often higher due to labor-intensive craftsmanship | Lower as it supports large-scale manufacturing |
| Consumer Appeal | Targeted at eco-conscious, trend-driven consumers | Appeals to budget-conscious and sustainable shoppers |
Understanding Upcycled Fashion: Beyond Traditional Recycling
Upcycled fashion transforms discarded materials or garments into new, higher-value pieces through creative redesign and craftsmanship, emphasizing originality and sustainability. This approach reduces waste by extending the life cycle of existing fabrics instead of breaking them down chemically, as in traditional recycling. By prioritizing quality and unique aesthetics, upcycled fashion offers an eco-friendly alternative that celebrates innovation and conscious consumerism in the apparel industry.
Recycled Fashion: Giving Old Materials New Life
Recycled fashion transforms discarded textiles and materials into new clothing, reducing waste and conserving resources by bypassing the need for virgin fibers. Innovative processes like fabric regeneration and fiber re-spinning enable high-quality garments with a lower environmental footprint. Brands adopting recycled fashion emphasize circular economy principles, promoting sustainability and reducing landfill contributions in the apparel industry.
Key Differences Between Upcycling and Recycling in Fashion
Upcycled fashion transforms existing garments or materials into new, higher-quality products, emphasizing creativity and design innovation, while recycled fashion breaks down textiles to create new fibers or fabrics, focusing on material recovery and sustainability. Upcycling preserves original fabric integrity and uniqueness, reducing waste by extending product life, whereas recycling often involves energy-intensive processes that can degrade material quality. Both methods contribute to eco-friendly fashion but serve different roles in reducing environmental impact within the industry.
Environmental Impact: Which Method is Greener?
Upcycled fashion reduces environmental impact by creatively repurposing existing garments, minimizing waste and lowering demand for new materials, which significantly cuts down water and energy consumption. Recycled fashion involves breaking down fibers to create new fabric but often requires intensive processing and chemical treatments that generate carbon emissions and pollution. Upcycling generally offers a greener alternative due to its lower resource use and contribution to waste reduction in the fashion industry.
Creative Potential: Upcycled vs Recycled Fashion Products
Upcycled fashion transforms existing garments or materials into unique, one-of-a-kind pieces, maximizing creative expression and design innovation. In contrast, recycled fashion typically breaks down fabrics into raw fibers, resulting in mass-produced fabrics with limited originality. Upcycling offers designers greater artistic freedom by retaining original textures and details, enhancing sustainability through creativity.
Consumer Appeal: What Drives the Demand?
Consumer appeal in upcycled fashion lies in its uniqueness and storytelling, as each piece is often handcrafted and carries an individual narrative that resonates with eco-conscious shoppers seeking authenticity. Recycled fashion attracts consumers driven by environmental impact, emphasizing sustainability through the transformation of materials like plastic and old textiles into new fabrics, appealing to those prioritizing circular economy principles. Both trends thrive on increasing awareness of environmental issues, but upcycled items offer exclusivity, while recycled fashion provides scalable solutions for sustainable apparel.
Economic Implications in the Fashion Industry
Upcycled fashion reduces production costs by transforming existing garments into new designs, stimulating niche markets and supporting local artisans, which can lead to increased economic resilience. Recycled fashion relies on industrial processes to break down textile fibers and create new fabrics, often requiring significant energy and infrastructure investments, influencing large-scale manufacturing economics. Both approaches contribute to sustainable growth by minimizing waste and encouraging circular economy models, impacting market demand and pricing strategies within the fashion industry.
Brand Innovations: Leading Examples of Upcycled and Recycled Fashion
Brand innovations in upcycled fashion showcase pioneers like Patagonia, which transforms discarded fishing nets into high-performance outerwear, blending sustainability with functionality. Recycled fashion leaders such as Adidas collaborate with Parley for the Oceans, producing sneakers with yarn made from ocean plastic waste, exemplifying circular economy principles. These brands highlight the intersection of creativity and eco-consciousness, driving industry-wide shifts towards minimizing textile waste.
Challenges and Limitations of Upcycled and Recycled Fashion
Upcycled fashion faces challenges such as inconsistent material supply and higher labor costs, limiting its scalability and market reach. Recycled fashion struggles with fiber degradation, which reduces fabric quality and durability, affecting consumer acceptance. Both methods encounter limitations in mass production and maintaining aesthetic appeal while meeting sustainability goals.
The Future of Sustainable Fashion: Upcycling or Recycling?
Upcycled fashion transforms existing garments into new, unique pieces by creatively repurposing materials, reducing waste and resource consumption more effectively than traditional recycling methods. Recycled fashion breaks down fibers to create new textiles, maintaining material value but often consuming more energy and producing lower-quality fabrics. The future of sustainable fashion leans toward upcycling as brands and consumers seek innovative, eco-friendly solutions that minimize environmental impact while promoting originality and longevity.
Upcycled Fashion vs Recycled Fashion Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com