Sustainable fabrics prioritize reducing environmental impact through eco-friendly production processes, often incorporating recycled or innovative materials. Organic fabrics are specifically grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, ensuring a chemical-free and natural fiber source. Both options support eco-conscious fashion choices, but sustainable fabrics offer a broader approach encompassing the entire lifecycle of textile production.
Table of Comparison
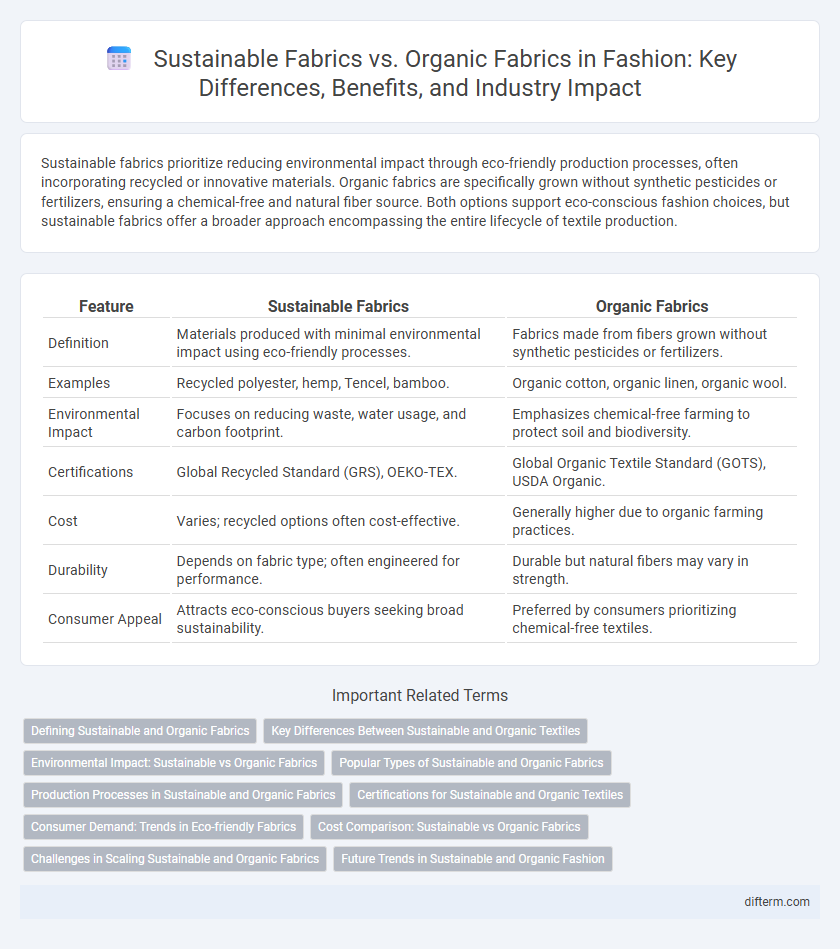
| Feature | Sustainable Fabrics | Organic Fabrics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Materials produced with minimal environmental impact using eco-friendly processes. | Fabrics made from fibers grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers. |
| Examples | Recycled polyester, hemp, Tencel, bamboo. | Organic cotton, organic linen, organic wool. |
| Environmental Impact | Focuses on reducing waste, water usage, and carbon footprint. | Emphasizes chemical-free farming to protect soil and biodiversity. |
| Certifications | Global Recycled Standard (GRS), OEKO-TEX. | Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), USDA Organic. |
| Cost | Varies; recycled options often cost-effective. | Generally higher due to organic farming practices. |
| Durability | Depends on fabric type; often engineered for performance. | Durable but natural fibers may vary in strength. |
| Consumer Appeal | Attracts eco-conscious buyers seeking broad sustainability. | Preferred by consumers prioritizing chemical-free textiles. |
Defining Sustainable and Organic Fabrics
Sustainable fabrics are materials produced through eco-friendly processes that minimize environmental impact by conserving resources and reducing emissions throughout their lifecycle. Organic fabrics specifically refer to textiles made from fibers grown without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms, ensuring chemical-free cultivation. Both terms emphasize environmental responsibility but differ in scope--sustainable fabrics cover broader ecological practices, while organic fabrics focus on raw material purity.
Key Differences Between Sustainable and Organic Textiles
Sustainable fabrics encompass a broad range of environmentally friendly materials manufactured through eco-conscious processes, while organic fabrics specifically derive from fibers grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, such as organic cotton or linen. Sustainable textiles prioritize the entire lifecycle impact, including water usage, energy consumption, and waste reduction, whereas organic textiles emphasize chemical-free cultivation methods to ensure soil health and reduce toxicity. Both approaches aim to minimize environmental harm, but sustainable fabrics integrate diverse practices beyond raw material origin, making them a more comprehensive category in eco-friendly fashion.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable vs Organic Fabrics
Sustainable fabrics encompass a broad range of materials designed to minimize environmental impact through resource efficiency and reduced waste, while organic fabrics specifically derive from crops grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, promoting soil health and biodiversity. Organic cotton, hemp, and linen often require less water and energy during cultivation compared to conventional counterparts, making them environmentally preferable within the sustainable fabric category. However, sustainable fabrics may also include recycled fibers and innovative materials, offering diverse eco-friendly benefits beyond organic certification alone.
Popular Types of Sustainable and Organic Fabrics
Sustainable fabrics include recycled polyester, Tencel, and hemp, offering eco-friendly alternatives by reducing waste and resource consumption. Organic fabrics primarily feature cotton, linen, and wool grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, ensuring lower environmental impact and better soil health. Combining sustainable and organic fabrics enhances fashion's contribution to environmental responsibility and ethical production.
Production Processes in Sustainable and Organic Fabrics
Sustainable fabrics emphasize eco-friendly production processes that minimize waste, reduce water usage, and avoid harmful chemicals, often incorporating recycled or low-impact materials. Organic fabrics are produced using strictly regulated methods that forbid synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, ensuring the cotton or fibers grow naturally and maintain soil health. Both prioritize environmental responsibility, but organic fabric production adheres to stricter certification standards, guaranteeing chemical-free cultivation and ethical farming practices.
Certifications for Sustainable and Organic Textiles
Sustainable fabrics often carry certifications such as Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), OEKO-TEX Standard 100, and Bluesign, which ensure environmentally responsible production and chemical safety. Organic fabrics specifically require certifications like USDA Organic or GOTS Organic, verifying the use of organic farming practices free from synthetic pesticides and genetically modified organisms. These certifications are crucial for consumer trust, guaranteeing adherence to strict environmental and social criteria throughout the textile supply chain.
Consumer Demand: Trends in Eco-friendly Fabrics
Consumer demand for sustainable fabrics has surged as awareness of environmental impact grows, with materials like recycled polyester and Tencel gaining popularity for their low carbon footprint and resource efficiency. Organic fabrics, such as certified organic cotton and hemp, attract eco-conscious buyers due to their chemical-free cultivation and biodegradability. Trends indicate a significant shift towards transparency and traceability in fabric sourcing, driving brands to prioritize sustainable and organic materials in their collections.
Cost Comparison: Sustainable vs Organic Fabrics
Sustainable fabrics often have a lower production cost due to the use of recycled or innovative materials, offering a more affordable option compared to organic fabrics. Organic fabrics, certified by standards such as GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard), typically incur higher costs related to farming practices, certification processes, and limited supply. Consumers seeking eco-friendly textiles should weigh the price differences alongside factors like environmental impact and fabric durability when choosing between sustainable and organic options.
Challenges in Scaling Sustainable and Organic Fabrics
Scaling sustainable and organic fabrics faces challenges such as limited availability of raw materials, higher production costs, and lack of infrastructure for large-scale manufacturing. The complexity of certification processes and inconsistent standards across regions further complicate market expansion. Consumer demand growth struggles to keep pace with supply chain constraints, hindering widespread adoption in the fashion industry.
Future Trends in Sustainable and Organic Fashion
Sustainable fabrics such as recycled polyester and Tencel are gaining traction alongside organic fabrics like certified organic cotton due to increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly materials. Innovations in bio-based textiles and closed-loop production systems are driving the future of sustainable and organic fashion, promoting reduced environmental impact and enhanced circularity. Brands investing in transparency and traceability are setting new industry standards, aligning with global sustainability goals and fostering long-term market growth.
Sustainable fabrics vs Organic fabrics Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com