Eco-fashion prioritizes environmental impact reduction by using organic or recycled materials and minimizing waste, while sustainable fashion encompasses a broader commitment to ethical production, fair labor practices, and long-term ecological balance. In the pet fashion industry, integrating sustainable fashion means ensuring that pet clothing and accessories are made not only from eco-friendly materials but also produced under conditions that support workers' rights and animal welfare. Choosing sustainable pet fashion helps reduce carbon footprints and promotes responsible consumption, benefiting pets, people, and the planet alike.
Table of Comparison
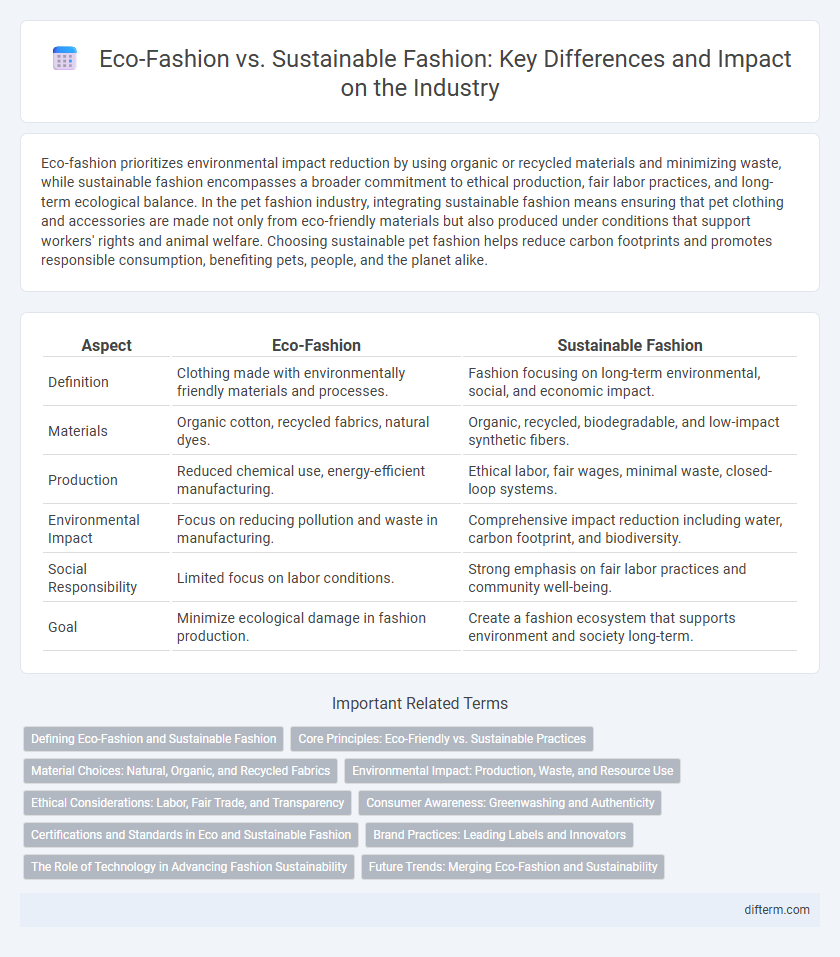
| Aspect | Eco-Fashion | Sustainable Fashion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clothing made with environmentally friendly materials and processes. | Fashion focusing on long-term environmental, social, and economic impact. |
| Materials | Organic cotton, recycled fabrics, natural dyes. | Organic, recycled, biodegradable, and low-impact synthetic fibers. |
| Production | Reduced chemical use, energy-efficient manufacturing. | Ethical labor, fair wages, minimal waste, closed-loop systems. |
| Environmental Impact | Focus on reducing pollution and waste in manufacturing. | Comprehensive impact reduction including water, carbon footprint, and biodiversity. |
| Social Responsibility | Limited focus on labor conditions. | Strong emphasis on fair labor practices and community well-being. |
| Goal | Minimize ecological damage in fashion production. | Create a fashion ecosystem that supports environment and society long-term. |
Defining Eco-Fashion and Sustainable Fashion
Eco-fashion emphasizes the use of environmentally friendly materials and processes, reducing pollution and waste throughout the design and production stages. Sustainable fashion extends beyond eco-conscious materials, incorporating ethical labor practices, resource efficiency, and long-term environmental impact reduction across the entire supply chain. Both approaches aim to minimize the fashion industry's negative effects but sustainable fashion integrates broader social and economic dimensions.
Core Principles: Eco-Friendly vs. Sustainable Practices
Eco-fashion emphasizes the use of eco-friendly materials and processes that reduce environmental impact, such as organic fabrics and non-toxic dyes. Sustainable fashion incorporates broader principles, including ethical labor practices, circular design, and long-term resource conservation to ensure social and environmental responsibility. Both approaches prioritize minimizing waste and carbon footprint, but sustainable fashion adopts a holistic framework encompassing economic and social equity alongside ecological concerns.
Material Choices: Natural, Organic, and Recycled Fabrics
Eco-fashion emphasizes the use of natural, organic, and recycled fabrics to minimize environmental impact, often prioritizing materials like organic cotton, hemp, and recycled polyester. Sustainable fashion incorporates these material choices as part of a broader strategy that also addresses ethical production, waste reduction, and lifecycle longevity. Both approaches promote eco-friendly textiles, but sustainable fashion integrates material innovation with social responsibility and circular economy principles.
Environmental Impact: Production, Waste, and Resource Use
Eco-fashion emphasizes the use of organic materials and low-impact dyes to minimize chemical pollution during production, whereas sustainable fashion integrates circular design principles to reduce waste through recycling and upcycling. Sustainable fashion prioritizes efficient resource use, such as water and energy conservation, reducing the carbon footprint throughout the supply chain. Both approaches aim to mitigate environmental degradation but sustainable fashion offers a more comprehensive strategy for long-term ecological balance.
Ethical Considerations: Labor, Fair Trade, and Transparency
Eco-fashion emphasizes using environmentally friendly materials and processes, whereas sustainable fashion integrates ethical considerations such as fair labor practices, fair trade certification, and supply chain transparency. Fair trade ensures that workers receive fair wages and safe working conditions, addressing labor rights and social justice within the fashion industry. Transparency in sourcing and manufacturing allows consumers to make informed choices, holding brands accountable for ethical labor standards.
Consumer Awareness: Greenwashing and Authenticity
Consumer awareness in eco-fashion versus sustainable fashion is crucial due to prevalent greenwashing tactics that mislead buyers with false environmental claims. Authenticity in sustainable fashion brands relies on transparent sourcing, ethical labor practices, and verified eco-friendly certifications. Informed consumers prioritize verifiable sustainability efforts over marketing buzz, driving demand for genuinely impactful fashion choices.
Certifications and Standards in Eco and Sustainable Fashion
Certifications such as GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) and OEKO-TEX play a crucial role in verifying eco-fashion claims by ensuring organic materials and chemical safety. Sustainable fashion standards often incorporate certifications like Fair Trade and B Corp to emphasize ethical labor practices alongside environmental impact. These certifications provide transparent benchmarks, helping consumers differentiate between eco-friendly processes and broader sustainability commitments in the fashion industry.
Brand Practices: Leading Labels and Innovators
Leading labels like Stella McCartney and Patagonia exemplify eco-fashion by prioritizing organic materials, reducing waste, and employing renewable resources in their collections. Sustainable fashion innovators such as Eileen Fisher and Reformation emphasize circular economy principles, including garment recycling, fair labor practices, and transparency throughout their supply chains. Both approaches drive industry-wide shifts, merging eco-consciousness with ethical production to reshape brand practices and consumer expectations.
The Role of Technology in Advancing Fashion Sustainability
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing fashion sustainability by enabling eco-fashion practices such as the development of biodegradable fabrics and waterless dyeing techniques. Sustainable fashion benefits from innovations like blockchain for transparent supply chains and AI-driven design to reduce waste and optimize resource use. These technological advancements accelerate the shift from traditional production methods to environmentally responsible fashion that minimizes carbon footprints and supports circular economy principles.
Future Trends: Merging Eco-Fashion and Sustainability
Emerging trends in fashion emphasize the convergence of eco-fashion and sustainable fashion, driven by innovative materials like biodegradable fabrics and advanced recycling technologies. Brands increasingly adopt circular economy models that minimize waste and promote resource efficiency, ensuring long-term environmental impact reduction. Consumer demand for transparency and ethical production fuels investment in sustainable supply chains and green manufacturing practices, shaping the industry's future landscape.
eco-fashion vs sustainable fashion Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com