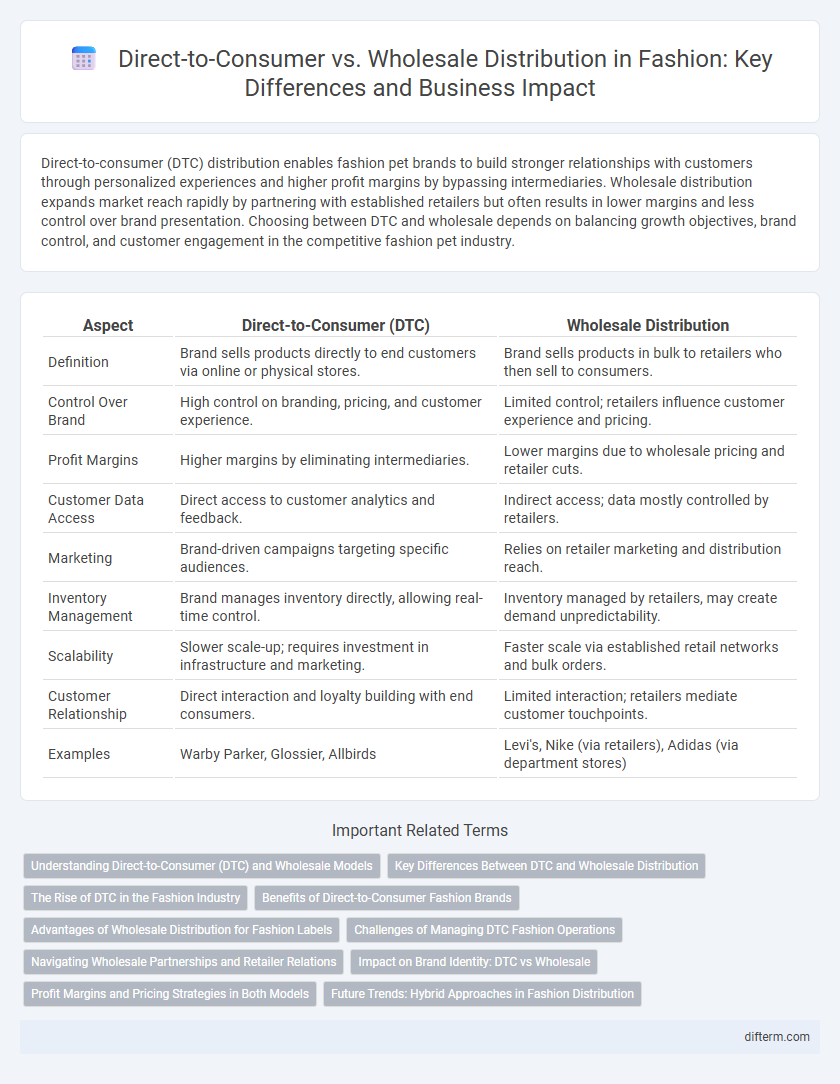
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) distribution enables fashion pet brands to build stronger relationships with customers through personalized experiences and higher profit margins by bypassing intermediaries. Wholesale distribution expands market reach rapidly by partnering with established retailers but often results in lower margins and less control over brand presentation. Choosing between DTC and wholesale depends on balancing growth objectives, brand control, and customer engagement in the competitive fashion pet industry.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) | Wholesale Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Brand sells products directly to end customers via online or physical stores. | Brand sells products in bulk to retailers who then sell to consumers. |
| Control Over Brand | High control on branding, pricing, and customer experience. | Limited control; retailers influence customer experience and pricing. |
| Profit Margins | Higher margins by eliminating intermediaries. | Lower margins due to wholesale pricing and retailer cuts. |
| Customer Data Access | Direct access to customer analytics and feedback. | Indirect access; data mostly controlled by retailers. |
| Marketing | Brand-driven campaigns targeting specific audiences. | Relies on retailer marketing and distribution reach. |
| Inventory Management | Brand manages inventory directly, allowing real-time control. | Inventory managed by retailers, may create demand unpredictability. |
| Scalability | Slower scale-up; requires investment in infrastructure and marketing. | Faster scale via established retail networks and bulk orders. |
| Customer Relationship | Direct interaction and loyalty building with end consumers. | Limited interaction; retailers mediate customer touchpoints. |
| Examples | Warby Parker, Glossier, Allbirds | Levi's, Nike (via retailers), Adidas (via department stores) |
Understanding Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) and Wholesale Models
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) fashion brands sell products directly to customers through online platforms or brand-owned stores, allowing for greater control over brand experience, pricing, and customer data. Wholesale distribution involves selling products in bulk to retailers, which then handle sales to end consumers, offering broader market reach but reduced control over brand presentation. Understanding these models helps fashion companies optimize supply chains, enhance customer engagement, and balance profit margins effectively.
Key Differences Between DTC and Wholesale Distribution
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) distribution allows fashion brands to sell products directly to customers through online stores, creating personalized shopping experiences and higher profit margins. Wholesale distribution involves selling large quantities of products to retailers or boutiques, enabling broader market reach but with reduced control over pricing and customer engagement. Key differences include inventory management, brand control, and profit margins, where DTC offers direct customer insights and higher margins, while wholesale prioritizes volume sales and partner relationships.
The Rise of DTC in the Fashion Industry
The rise of direct-to-consumer (DTC) distribution in the fashion industry has transformed traditional wholesale models by enabling brands like Warby Parker and Everlane to build stronger customer relationships and collect valuable data. DTC allows fashion companies to maintain complete control over branding, pricing, and customer experience, resulting in higher profit margins and faster market responsiveness. This shift is driven by increased online shopping, social media engagement, and consumer demand for personalized, transparent, and sustainable fashion products.
Benefits of Direct-to-Consumer Fashion Brands
Direct-to-consumer fashion brands benefit from higher profit margins by eliminating middlemen and controlling pricing strategies. They gain valuable customer data enabling personalized marketing, improved product development, and enhanced customer loyalty. Direct engagement fosters brand authenticity and agility in responding to trends, outperforming traditional wholesale distribution models.
Advantages of Wholesale Distribution for Fashion Labels
Wholesale distribution offers fashion labels the advantage of rapid market penetration by leveraging established retail networks, enabling higher volume sales and consistent revenue streams. This model reduces marketing and distribution costs, allowing brands to focus on product design and innovation while tapping into the retailer's customer base. Furthermore, wholesale partnerships provide valuable industry insights and foster long-term relationships that can enhance brand credibility and market reach.
Challenges of Managing DTC Fashion Operations
Managing direct-to-consumer (DTC) fashion operations presents challenges such as inventory management complexities, high customer acquisition costs, and the need for seamless omnichannel customer experiences. Brands must invest heavily in digital marketing, technology infrastructure, and supply chain agility to meet fast-changing consumer demands while maintaining profitability. Efficient handling of logistics, returns, and personalized customer service remains critical to sustaining competitive advantage in the DTC fashion market.
Navigating Wholesale Partnerships and Retailer Relations
Navigating wholesale partnerships requires clear communication of brand values and product uniqueness to align with retailer expectations and target audiences. Establishing transparent terms and consistent supply chain management fosters trust and long-term collaboration critical for fashion brand growth. Prioritizing retailer support with marketing resources and inventory flexibility enhances wholesale relationships and expands market reach effectively.
Impact on Brand Identity: DTC vs Wholesale
Direct-to-consumer distribution strengthens brand identity by enabling personalized customer experiences, consistent messaging, and direct feedback channels that foster brand loyalty. Wholesale distribution often dilutes brand messaging due to third-party retail involvement, reducing control over pricing, presentation, and customer interaction. Maintaining a strong brand identity is more achievable through DTC, where brands curate every touchpoint to align closely with their core values and aesthetic.
Profit Margins and Pricing Strategies in Both Models
Direct-to-consumer (DTC) fashion brands typically enjoy higher profit margins by eliminating intermediaries, allowing for more control over pricing strategies and direct customer engagement. Wholesale distribution often involves lower margins due to retailer discounts and bulk pricing, but it enables broader market reach and faster inventory turnover. Pricing in DTC focuses on value-based pricing tailored to customer insights, whereas wholesale pricing relies on competitive wholesale rates to attract retailers while maintaining profitability.
Future Trends: Hybrid Approaches in Fashion Distribution
Future trends in fashion distribution reveal a growing shift toward hybrid approaches that combine direct-to-consumer (DTC) and wholesale channels for optimized market reach. Brands leverage data-driven insights from DTC sales while maintaining wholesale partnerships to expand physical presence and scale efficiently. Integrating omnichannel strategies enhances customer experience, enabling seamless interaction across digital platforms and brick-and-mortar stores.
Direct-to-consumer vs Wholesale distribution Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com