Digital fashion offers limitless creativity and instant customization without environmental impact, revolutionizing how pets can showcase style. Physical fashion provides tactile comfort and durability, allowing pets to experience real textures and protection. Combining both trends enhances pet fashion by blending innovation with practicality for every occasion.
Table of Comparison
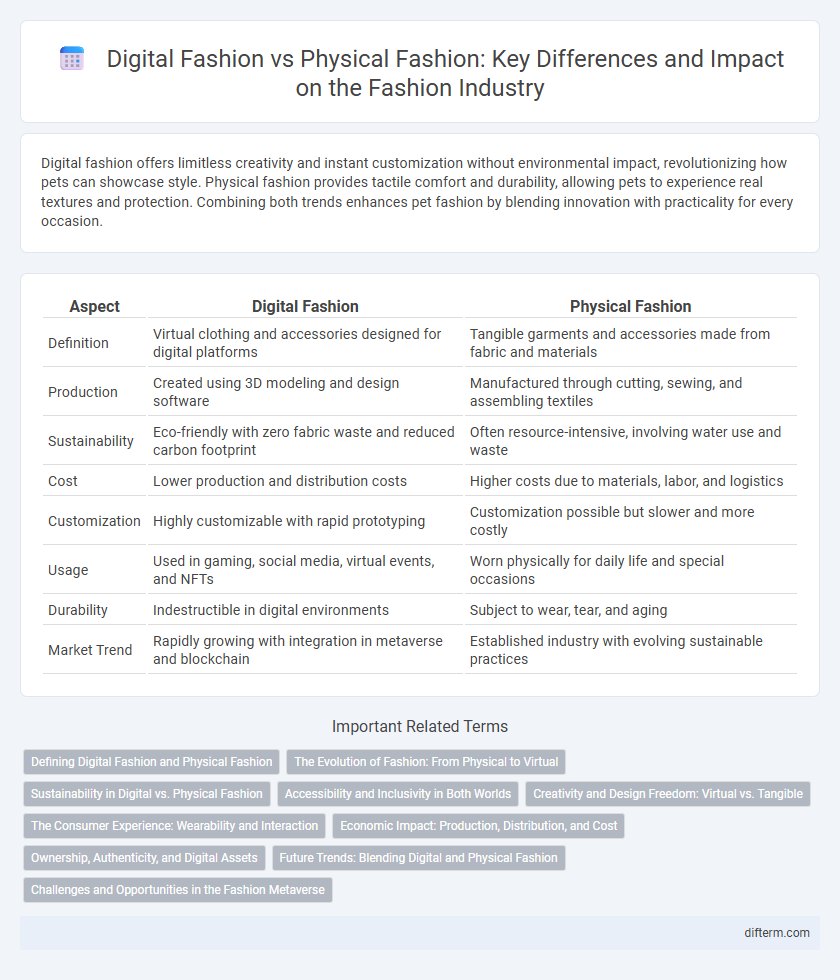
| Aspect | Digital Fashion | Physical Fashion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual clothing and accessories designed for digital platforms | Tangible garments and accessories made from fabric and materials |
| Production | Created using 3D modeling and design software | Manufactured through cutting, sewing, and assembling textiles |
| Sustainability | Eco-friendly with zero fabric waste and reduced carbon footprint | Often resource-intensive, involving water use and waste |
| Cost | Lower production and distribution costs | Higher costs due to materials, labor, and logistics |
| Customization | Highly customizable with rapid prototyping | Customization possible but slower and more costly |
| Usage | Used in gaming, social media, virtual events, and NFTs | Worn physically for daily life and special occasions |
| Durability | Indestructible in digital environments | Subject to wear, tear, and aging |
| Market Trend | Rapidly growing with integration in metaverse and blockchain | Established industry with evolving sustainable practices |
Defining Digital Fashion and Physical Fashion
Digital fashion refers to apparel and accessories created using computer-generated imagery (CGI) and augmented reality technologies, designed specifically for virtual environments or digital avatars. Physical fashion encompasses tangible clothing produced from fabrics and materials, intended for real-world wear and sensory interaction. Both forms influence contemporary style, with digital fashion emphasizing innovation and sustainability, while physical fashion upholds tradition and material craftsmanship.
The Evolution of Fashion: From Physical to Virtual
Fashion evolution has shifted from traditional physical garments to immersive digital apparel, transforming how consumers engage with style. Virtual fashion leverages augmented reality (AR) and blockchain technology, enabling unique, customizable, and sustainable designs without material waste. This digital shift enhances creativity, expands accessibility, and introduces new revenue streams through NFTs and metaverse experiences.
Sustainability in Digital vs. Physical Fashion
Digital fashion significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste, water consumption, and carbon emissions compared to traditional physical fashion production. Virtual garments eliminate the need for raw materials, dyes, and transportation, contributing to a more sustainable supply chain. Sustainable practices in physical fashion still face challenges like textile waste and resource-intensive manufacturing, positioning digital fashion as a greener alternative for eco-conscious consumers.
Accessibility and Inclusivity in Both Worlds
Digital fashion expands accessibility by enabling users worldwide to customize and wear virtual garments without geographic or economic barriers. Physical fashion increasingly embraces inclusivity through adaptive designs and diverse sizing, catering to various body types and abilities. Both realms leverage technology and innovation to democratize style, enhancing personal expression for traditionally underserved communities.
Creativity and Design Freedom: Virtual vs. Tangible
Digital fashion offers unparalleled design freedom, enabling creators to experiment with complex patterns, dynamic textures, and gravity-defying silhouettes impossible in physical garments. Virtual platforms support infinite customization and rapid prototyping, reducing material constraints and waste while expanding creative boundaries. Physical fashion remains rooted in textile innovation and tactile craftsmanship, providing sensory qualities and real-world wearability that digital counterparts cannot replicate fully.
The Consumer Experience: Wearability and Interaction
Digital fashion enhances consumer experience by offering customizable, interactive garments that adapt instantly to user preferences and environments, unlike physical fashion which relies on static designs and tangible materials. Virtual try-ons and augmented reality enable more precise fit visualization and innovative styling options, increasing engagement and reducing return rates. Consumers benefit from the seamless integration of technology, redefining wearability through virtual interaction and instant personalization.
Economic Impact: Production, Distribution, and Cost
Digital fashion significantly reduces production costs by eliminating material expenses and minimizing waste, streamlining distribution through virtual platforms that bypass traditional retail logistics. Physical fashion incurs higher expenses due to raw materials, manufacturing labor, and complex supply chains, impacting overall pricing and profit margins. The economic shift toward digital fashion fosters scalability and rapid market adaptation, challenging the traditional industry's cost structures and distribution models.
Ownership, Authenticity, and Digital Assets
Digital fashion offers enhanced ownership through blockchain technology, ensuring verifiable authenticity and unique digital assets that cannot be duplicated. Physical fashion relies on tangible ownership but faces challenges with counterfeit products and limited traceability. The integration of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) in digital fashion bridges the gap, providing consumers with provable scarcity and exclusive digital wardrobes.
Future Trends: Blending Digital and Physical Fashion
The future of fashion anticipates a seamless fusion of digital and physical elements, driven by innovations in augmented reality (AR) and blockchain technology for authenticating digital garments. Brands are leveraging virtual try-ons and NFT-based collections to create hybrid experiences that enhance consumer engagement and sustainability. This convergence not only transforms how fashion is designed and worn but also redefines ownership, personalization, and environmental impact in the industry.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Fashion Metaverse
The Fashion Metaverse presents challenges such as ensuring digital garment authenticity and overcoming technological barriers like 3D modeling complexity and platform interoperability. Opportunities abound with enhanced personalization, sustainable production through virtual apparel, and expanding global reach without physical inventory constraints. Brands leveraging blockchain for secure ownership and augmented reality for immersive experiences can redefine consumer engagement in digital fashion.
digital fashion vs physical fashion Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com