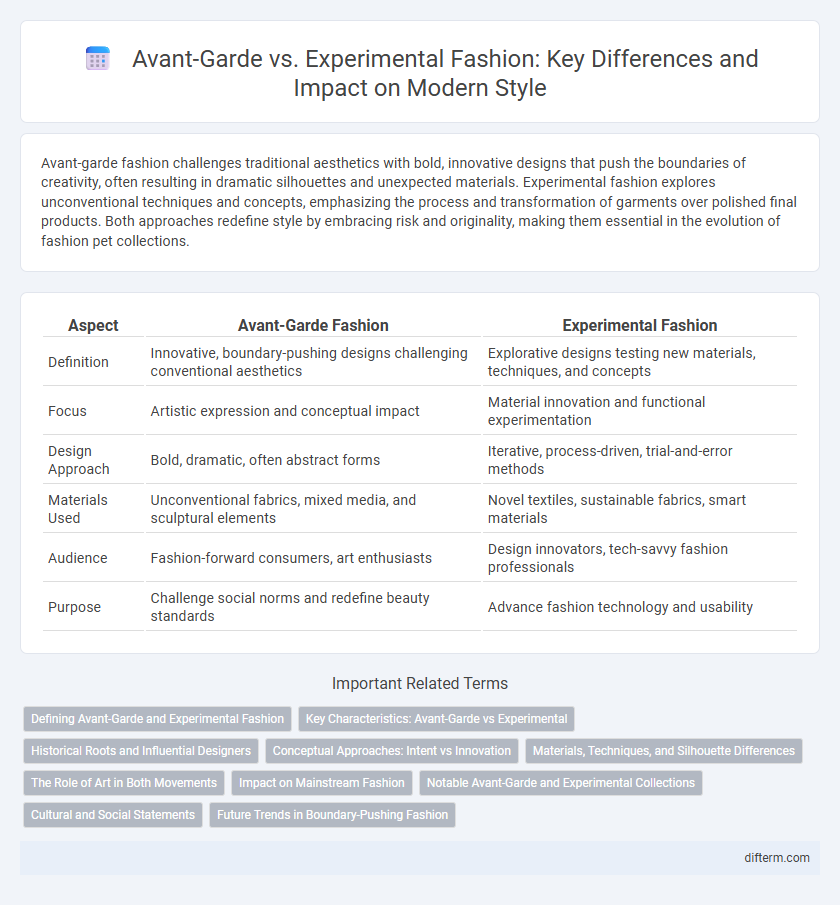
Avant-garde fashion challenges traditional aesthetics with bold, innovative designs that push the boundaries of creativity, often resulting in dramatic silhouettes and unexpected materials. Experimental fashion explores unconventional techniques and concepts, emphasizing the process and transformation of garments over polished final products. Both approaches redefine style by embracing risk and originality, making them essential in the evolution of fashion pet collections.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Avant-Garde Fashion | Experimental Fashion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Innovative, boundary-pushing designs challenging conventional aesthetics | Explorative designs testing new materials, techniques, and concepts |
| Focus | Artistic expression and conceptual impact | Material innovation and functional experimentation |
| Design Approach | Bold, dramatic, often abstract forms | Iterative, process-driven, trial-and-error methods |
| Materials Used | Unconventional fabrics, mixed media, and sculptural elements | Novel textiles, sustainable fabrics, smart materials |
| Audience | Fashion-forward consumers, art enthusiasts | Design innovators, tech-savvy fashion professionals |
| Purpose | Challenge social norms and redefine beauty standards | Advance fashion technology and usability |
Defining Avant-Garde and Experimental Fashion
Avant-garde fashion challenges traditional design norms by pushing boundaries with innovative shapes, materials, and concepts that often evoke artistic expression. Experimental fashion explores uncharted territories in garment construction and technology, aiming to discover new forms and functionalities beyond conventional wearability. Both styles prioritize creativity and future-forward thinking, but avant-garde leans heavily on conceptual art influences while experimental fashion emphasizes material innovation and technological integration.
Key Characteristics: Avant-Garde vs Experimental
Avant-garde fashion is defined by its radical designs that challenge traditional aesthetics, often incorporating unconventional materials and bold silhouettes to provoke thought and redefine style norms. Experimental fashion pushes the boundaries through innovative techniques, technology integration, and material exploration, emphasizing function and transformation alongside artistic expression. Both styles prioritize originality and risk-taking but differ in intent: avant-garde aims to disrupt cultural perceptions, while experimental focuses on testing new concepts and wearable innovations.
Historical Roots and Influential Designers
Avant-garde fashion traces its roots to early 20th-century movements like Dadaism and Surrealism, challenging traditional aesthetics and pushing boundaries through conceptual designs. Designers such as Elsa Schiaparelli and Rei Kawakubo pioneered this style by integrating art and innovation, reshaping fashion norms. Experimental fashion, closely related yet distinct, emphasizes material exploration and technology, exemplified by designers like Issey Miyake and Hussein Chalayan, who innovate fabrics and garment structures.
Conceptual Approaches: Intent vs Innovation
Avant-garde fashion challenges traditional aesthetics by prioritizing conceptual intent that pushes boundaries beyond wearability, often serving as a cultural or artistic statement. Experimental fashion embraces innovation through the use of new materials, technologies, and techniques, emphasizing functionality and the exploration of future possibilities. Both approaches redefine fashion norms but differ fundamentally in their focus on meaning versus material advancement.
Materials, Techniques, and Silhouette Differences
Avant-garde fashion emphasizes unconventional materials like metallic fabrics and plastics, employing techniques such as deconstruction and sculpting to create bold, futuristic silhouettes that challenge traditional norms. Experimental fashion explores innovative textiles like biofabricated leather and 3D-printed components, utilizing cutting-edge methods including laser cutting and digital knitting to craft fluid, asymmetrical shapes that blur the boundaries between art and wearability. Both styles redefine silhouettes, with avant-garde favoring dramatic, architectural forms and experimental fashion prioritizing adaptability and transformation through dynamic structures.
The Role of Art in Both Movements
Art serves as the foundational influence in both avant-garde and experimental fashion, shaping designers' approaches to innovation and expression. Avant-garde fashion integrates artistic concepts to challenge traditional aesthetics and provoke cultural dialogue, often blurring the lines between fashion and fine art. Experimental fashion pushes boundaries by using unconventional materials and techniques, transforming garments into sculptural art pieces that redefine wearability and visual impact.
Impact on Mainstream Fashion
Avant-garde fashion challenges traditional design norms, introducing bold silhouettes, unconventional materials, and innovative construction techniques that gradually influence mainstream trends. Experimental fashion pushes creative boundaries through technology integration and sustainability, inspiring widespread adoption of eco-friendly fabrics and smart clothing in everyday wear. These movements drive the evolution of fashion by transforming niche concepts into commercially viable designs embraced by global brands and consumers.
Notable Avant-Garde and Experimental Collections
Notable avant-garde collections by designers such as Rei Kawakubo of Comme des Garcons and Alexander McQueen challenge traditional silhouettes and materials, pushing boundaries with conceptual designs that often evoke emotional responses. Experimental fashion collections from brands like Iris van Herpen incorporate innovative technologies and unconventional textiles, blending art and science to create wearable sculptures. These influential collections redefine fashion norms, emphasizing creativity and futurism over commercial appeal.
Cultural and Social Statements
Avant-garde fashion challenges traditional aesthetics through bold, unconventional designs that often critique societal norms and cultural conventions. Experimental fashion pushes the boundaries of materials, technology, and form, creating innovative expressions that reflect contemporary social issues and identity politics. Both styles serve as powerful platforms for cultural dialogue, using clothing to question and redefine collective values and social hierarchies.
Future Trends in Boundary-Pushing Fashion
Avant-garde fashion challenges conventional design through innovative materials, futuristic silhouettes, and unconventional construction techniques, influencing future trends that blur the lines between art and wearable technology. Experimental fashion emphasizes sustainability, 3D printing, and smart textiles that respond to environmental changes, shaping a new wave of eco-conscious and tech-integrated apparel. These boundary-pushing movements drive the evolution of fashion by merging creativity with cutting-edge science, forecasting a transformative industry landscape.
avant-garde vs experimental fashion Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com