Landfills and incineration are two common waste management methods with distinct environmental impacts. Landfills can lead to soil and water contamination through leachate and generate methane, a potent greenhouse gas, while incineration reduces waste volume and can produce energy but releases pollutants and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Choosing between landfill and incineration requires balancing waste reduction, emissions control, and environmental health considerations for sustainable pet ownership waste disposal.
Table of Comparison
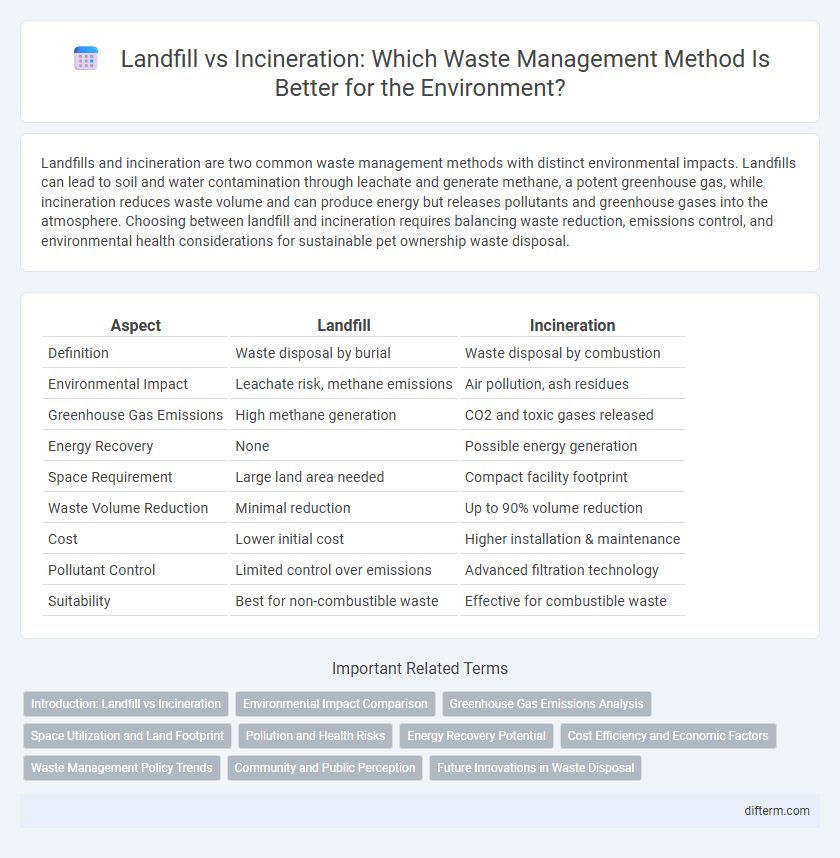
| Aspect | Landfill | Incineration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Waste disposal by burial | Waste disposal by combustion |
| Environmental Impact | Leachate risk, methane emissions | Air pollution, ash residues |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | High methane generation | CO2 and toxic gases released |
| Energy Recovery | None | Possible energy generation |
| Space Requirement | Large land area needed | Compact facility footprint |
| Waste Volume Reduction | Minimal reduction | Up to 90% volume reduction |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher installation & maintenance |
| Pollutant Control | Limited control over emissions | Advanced filtration technology |
| Suitability | Best for non-combustible waste | Effective for combustible waste |
Introduction: Landfill vs Incineration
Landfill and incineration are two primary waste management methods impacting environmental sustainability. Landfills store waste underground, often causing methane emissions and groundwater contamination, while incineration burns waste, reducing volume but emitting pollutants like dioxins and greenhouse gases. Evaluating their environmental footprints involves analyzing factors such as emissions, energy recovery, and long-term ecological consequences.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Landfills contribute significantly to methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas, while incineration releases carbon dioxide and potentially harmful pollutants if not properly managed. Landfills risk soil and groundwater contamination due to leachate, whereas modern incinerators with advanced filtration reduce toxic emissions but generate ash requiring safe disposal. Evaluating environmental impact involves considering greenhouse gases, toxic emissions, resource recovery potential, and long-term ecosystem effects.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Analysis
Landfills produce significant methane emissions, a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential over 25 times greater than CO2, due to anaerobic decomposition of organic waste. Incineration emits CO2 directly through combustion but significantly reduces methane output and volume of waste, potentially lowering overall greenhouse gas impact if energy recovery is implemented. Comprehensive life cycle assessments indicate incineration with energy recovery can result in lower net greenhouse gas emissions compared to unmanaged or poorly managed landfills.
Space Utilization and Land Footprint
Landfills require extensive land areas for waste disposal, often leading to significant land footprint and potential environmental contamination over time. Incineration drastically reduces the volume of waste, thereby minimizing space utilization and enabling more efficient land use. This reduction in physical waste storage allows for better land resource management, especially in urban settings where land availability is limited.
Pollution and Health Risks
Landfills release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, and leachate that contaminates soil and groundwater, posing significant environmental and health risks. Incineration emits toxic pollutants like dioxins and heavy metals, which can lead to respiratory problems and long-term health effects in nearby populations. Both waste management methods contribute to air and water pollution, but incineration's airborne toxins present more direct respiratory hazards compared to landfill emissions.
Energy Recovery Potential
Landfill gas captures methane generated from waste decomposition, enabling energy recovery but with lower efficiency compared to incineration. Incineration converts waste directly into heat for electricity and steam production, achieving higher energy recovery rates and reducing landfill volume. Technologies like waste-to-energy plants optimize combustion processes, maximizing energy output while minimizing environmental impact.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Factors
Landfill disposal generally incurs lower upfront costs compared to incineration, making it attractive for short-term waste management, but long-term expenses such as land acquisition, environmental monitoring, and potential remediation can escalate significantly. Incineration facilities require substantial capital investment and operational costs, but they offer energy recovery and volume reduction, which can translate into economic benefits through energy sales and reduced landfill fees. Evaluating cost efficiency depends on waste volume, local regulations, and potential revenues from energy generation or carbon credits linked to incineration.
Waste Management Policy Trends
Emerging waste management policy trends prioritize reducing landfill dependency by promoting incineration with energy recovery due to its capacity to decrease volume and generate electricity. Stringent regulations on landfill emissions, including methane capture mandates, are pushing municipalities to adopt advanced thermal treatment technologies. Policy frameworks increasingly support circular economy principles, incentivizing waste-to-energy solutions that align with decarbonization goals and resource recovery targets.
Community and Public Perception
Landfills often face community opposition due to concerns about odors, groundwater contamination, and decreased property values, which negatively impact public perception. Incineration plants are perceived as technologically advanced waste solutions but raise fears about air pollution and toxic emissions among residents. Effective communication and transparent environmental monitoring are essential to improve community trust and acceptance of both waste management methods.
Future Innovations in Waste Disposal
Future innovations in waste disposal emphasize the development of advanced landfill liners and bioreactor technologies to enhance waste containment and accelerate decomposition processes. Emerging incineration techniques focus on optimizing energy recovery through improved gasification and plasma arc technologies, reducing harmful emissions significantly. Integration of smart monitoring systems using IoT and AI aims to improve efficiency and environmental safety in both landfill and incineration methods.
landfill vs incineration Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com