Web series offer greater creative freedom and diverse storytelling compared to traditional television series, appealing to niche audiences with tailored content. They often feature shorter episodes and flexible release schedules, enhancing viewer convenience and engagement. Television series maintain broader reach and higher production budgets, delivering polished visuals and mass-market appeal.
Table of Comparison
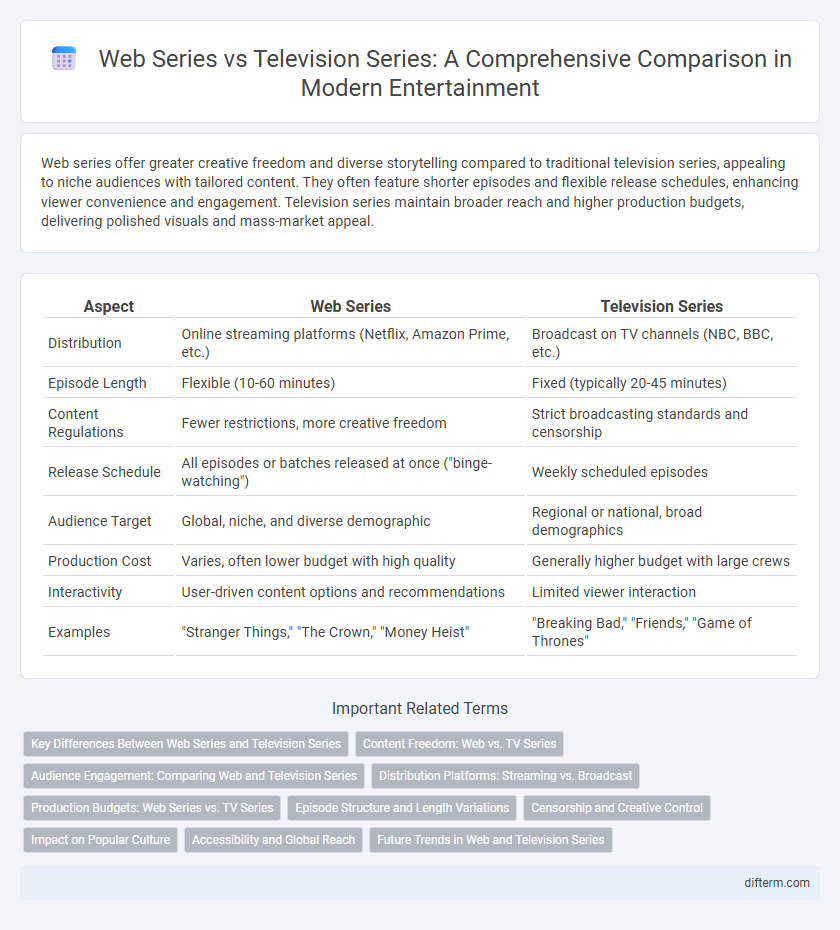
| Aspect | Web Series | Television Series |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Online streaming platforms (Netflix, Amazon Prime, etc.) | Broadcast on TV channels (NBC, BBC, etc.) |
| Episode Length | Flexible (10-60 minutes) | Fixed (typically 20-45 minutes) |
| Content Regulations | Fewer restrictions, more creative freedom | Strict broadcasting standards and censorship |
| Release Schedule | All episodes or batches released at once ("binge-watching") | Weekly scheduled episodes |
| Audience Target | Global, niche, and diverse demographic | Regional or national, broad demographics |
| Production Cost | Varies, often lower budget with high quality | Generally higher budget with large crews |
| Interactivity | User-driven content options and recommendations | Limited viewer interaction |
| Examples | "Stranger Things," "The Crown," "Money Heist" | "Breaking Bad," "Friends," "Game of Thrones" |
Key Differences Between Web Series and Television Series
Web series often feature shorter episodes and flexible release schedules, targeting online streaming platforms, whereas television series follow fixed broadcast times and longer episodes tailored for network airing. Audience interaction and niche content experimentation are more prominent in web series, benefiting from digital analytics and viewer feedback, unlike traditional television series constrained by regulatory guidelines and advertising formats. Production budgets vary significantly, with television series generally having higher financing, while web series leverage lower costs and creative freedom for diverse storytelling.
Content Freedom: Web vs. TV Series
Web series often benefit from greater content freedom compared to television series due to fewer censorship restrictions and platform-specific guidelines. Streaming platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime allow creators to explore mature themes, explicit language, and unconventional narratives, which traditional TV networks may avoid to comply with broadcast standards and advertiser preferences. This increased flexibility in web series production fosters innovative storytelling and diverse representation not always achievable on broadcast television.
Audience Engagement: Comparing Web and Television Series
Web series leverage interactive features and on-demand accessibility to boost audience engagement, allowing viewers to watch episodes anytime and participate through social media discussions. Television series maintain engagement through scheduled broadcasts and broader reach, often attracting viewers with high production values and network promotions. Streaming platforms report higher engagement rates for web series, particularly among younger demographics who prefer personalized viewing experiences.
Distribution Platforms: Streaming vs. Broadcast
Streaming platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Hulu offer on-demand access to web series, allowing viewers to watch episodes anytime, enhancing convenience and binge-watching capabilities. Broadcast television relies on scheduled programming, limiting viewer flexibility but reaching a broader audience through traditional cable and satellite networks. The shift towards streaming services has transformed content distribution, enabling global access and personalized viewing experiences compared to conventional broadcast constraints.
Production Budgets: Web Series vs. TV Series
Production budgets for web series typically range from $100,000 to $500,000 per season, significantly lower than traditional television series, which often exceed $2 million per episode. Television productions allocate substantial funds toward high-end set designs, star-studded casts, and extensive marketing campaigns that surpass most digital streaming projects. This budget disparity influences overall production quality, with TV series delivering cinematic visuals and complex storytelling supported by larger financial resources.
Episode Structure and Length Variations
Web series typically feature shorter episodes ranging from 10 to 30 minutes, allowing for concise storytelling and rapid plot development, whereas television series often have longer episodes between 30 to 60 minutes, enabling more in-depth character arcs and subplots. The episodic structure in web series is more flexible, frequently adopting non-linear narratives and varying episode lengths to suit digital consumption habits, unlike traditional television series which follow a consistent runtime dictated by broadcast schedules. These variations influence viewer engagement, with web series catering to on-the-go audiences through bite-sized content, while television series provide extended viewing experiences ideal for scheduled programming.
Censorship and Creative Control
Web series often experience less censorship compared to television series, allowing creators greater freedom to explore diverse themes and mature content. Television series typically face stricter regulatory standards imposed by broadcasting authorities, which can limit creative expression and narrative complexity. This difference in censorship directly influences the level of creative control, with web series creators enjoying more autonomy to push boundaries and experiment with storytelling formats.
Impact on Popular Culture
Web series have revolutionized popular culture by offering diverse storytelling formats and reaching global audiences through digital platforms, significantly influencing viewing habits and fandom communities. Television series traditionally established cultural norms and mainstream trends, but the rise of web series has democratized content creation, allowing niche genres and underrepresented voices to shape cultural narratives. The interactive and binge-friendly nature of web series has accelerated the formation of dedicated fan bases, thereby intensifying their impact on social media and modern pop culture discourse.
Accessibility and Global Reach
Web series offer unparalleled accessibility through on-demand streaming across multiple devices, enabling viewers to watch content anytime and anywhere, unlike traditional television series confined to scheduled broadcasts. Platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and YouTube facilitate global reach, breaking geographical barriers and attracting diverse audiences worldwide. Television series, while maintaining strong regional followings, often face limitations due to broadcast restrictions and time zones, reducing their potential for international viewership.
Future Trends in Web and Television Series
Web series are rapidly evolving with personalized content driven by artificial intelligence, enhanced interactivity, and global accessibility on streaming platforms, reshaping viewer engagement. Television series continue to integrate advanced production technologies like virtual reality and augmented reality to deliver immersive storytelling experiences. The future landscape will likely see a convergence of web and television series formats, leveraging data analytics and cross-platform distribution to maximize audience reach and retention.
Web series vs Television series Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com