Stand-up comedy delivers polished, scripted routines emphasizing individual performance and timing, generating laughter through clever jokes and personal anecdotes. Improv comedy thrives on spontaneous, unscripted interactions, requiring quick thinking and collaboration among performers to create humor in real-time. Both forms engage audiences uniquely, with stand-up offering refined storytelling and improv showcasing dynamic creativity and unpredictability.
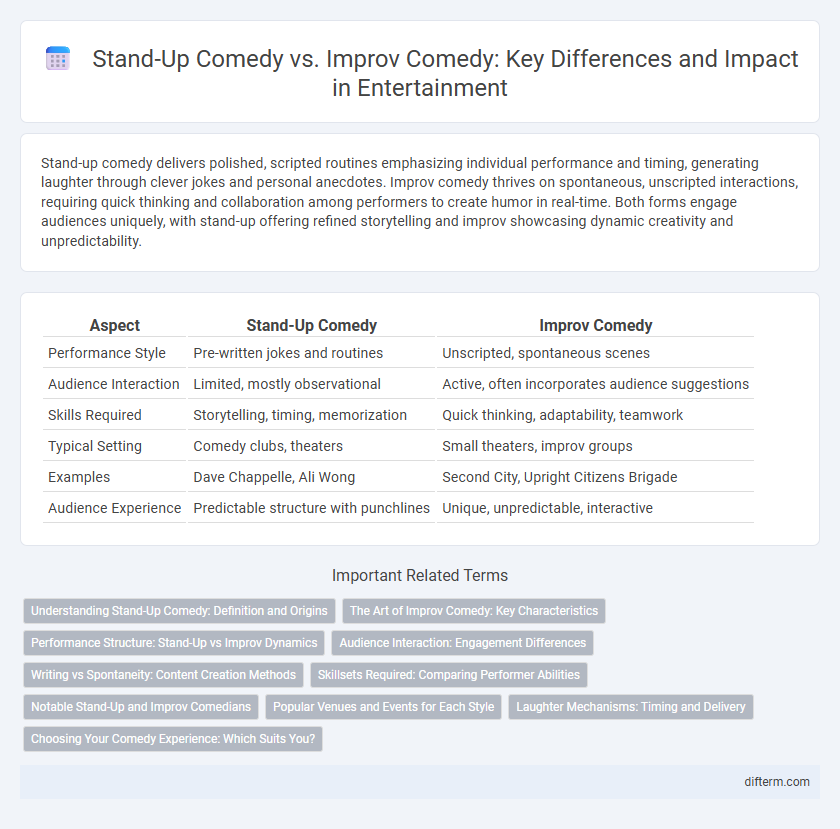
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stand-Up Comedy | Improv Comedy |
|---|---|---|
| Performance Style | Pre-written jokes and routines | Unscripted, spontaneous scenes |
| Audience Interaction | Limited, mostly observational | Active, often incorporates audience suggestions |
| Skills Required | Storytelling, timing, memorization | Quick thinking, adaptability, teamwork |
| Typical Setting | Comedy clubs, theaters | Small theaters, improv groups |
| Examples | Dave Chappelle, Ali Wong | Second City, Upright Citizens Brigade |
| Audience Experience | Predictable structure with punchlines | Unique, unpredictable, interactive |
Understanding Stand-Up Comedy: Definition and Origins
Stand-up comedy is a form of entertainment where a solo performer delivers humorous monologues directly to an audience, often reflecting personal experiences and social commentary. Originating in the vaudeville era of the late 19th century, stand-up evolved through the mid-20th century with figures like Lenny Bruce and Richard Pryor, who shaped its modern style. This genre emphasizes scripted jokes and timing, distinguishing it from the spontaneous, interactive nature of improv comedy.
The Art of Improv Comedy: Key Characteristics
Improv comedy thrives on spontaneous creativity, requiring performers to craft humorous scenes without scripts, relying heavily on quick thinking and audience interaction. Key characteristics include collaborative storytelling, real-time problem solving, and the "Yes, and" principle, which builds momentum by accepting and expanding on partners' ideas. This dynamic format demands adaptability and heightened awareness, distinguishing it from scripted stand-up comedy by its unpredictable and communal nature.
Performance Structure: Stand-Up vs Improv Dynamics
Stand-up comedy features a scripted solo performance where the comedian delivers pre-written jokes and anecdotes with a clear narrative arc, emphasizing timing and punchlines. Improv comedy relies on spontaneous, unscripted interactions among a group of performers, creating scenes and humor dynamically based on audience suggestions, highlighting quick thinking and collaboration. The structured nature of stand-up contrasts with the fluid, unpredictable flow of improv, making each style distinct in audience engagement and comedic rhythm.
Audience Interaction: Engagement Differences
Stand-up comedy relies on a scripted routine where audience interaction is minimal and mostly reactive, allowing the comedian to maintain control over timing and content. Improv comedy thrives on spontaneous audience engagement, often incorporating suggestions and immediate feedback to shape the performance in real-time. This dynamic interaction creates a unique, unpredictable experience that strengthens the connection between performers and spectators.
Writing vs Spontaneity: Content Creation Methods
Stand-up comedy relies heavily on carefully crafted scripts, with comedians writing and refining jokes to deliver precise punchlines and structured narratives. Improv comedy, in contrast, thrives on spontaneity, where performers create humor in real-time by reacting to audience suggestions and fellow actors' cues, fostering unpredictable and dynamic content. This fundamental difference highlights stand-up's dependency on premeditated content versus improv's emphasis on in-the-moment creativity and collaboration.
Skillsets Required: Comparing Performer Abilities
Stand-up comedy demands sharp storytelling, precise timing, and strong solo stage presence to deliver rehearsed material effectively. Improv comedy requires quick thinking, adaptability, and collaborative skills to create spontaneous humor in response to audience and fellow performers. Both styles cultivate unique performer abilities essential for engaging live entertainment.
Notable Stand-Up and Improv Comedians
Notable stand-up comedians such as Richard Pryor, George Carlin, and Dave Chappelle are celebrated for their solo performances filled with sharp wit and personal storytelling. In contrast, improv comedy icons like Tina Fey, Amy Poehler, and Keegan-Michael Key excel in unscripted, collaborative scenes that rely heavily on audience interaction and quick thinking. Both forms showcase comedic talent but differ significantly in style and audience engagement.
Popular Venues and Events for Each Style
Stand-up comedy thrives in iconic venues like The Comedy Cellar in New York and The Laugh Factory in Los Angeles, attracting headliners for solo performances. Improv comedy is celebrated in dedicated spaces such as The Second City in Chicago and Upright Citizens Brigade in New York, renowned for interactive and ensemble-driven shows. Major events like the Just for Laughs Festival in Montreal feature both styles, showcasing diverse comedic talents and drawing large audiences globally.
Laughter Mechanisms: Timing and Delivery
Stand-up comedy relies on meticulously crafted jokes with precise timing, where punchlines are delivered for maximum impact, creating laughter through anticipation and surprise. Improv comedy generates humor spontaneously, depending on quick thinking and interactive delivery, which fosters laughter by embracing unpredictability and audience engagement. Both forms utilize timing and delivery virtuously, yet stand-up focuses on rehearsed precision while improv thrives on real-time responsiveness.
Choosing Your Comedy Experience: Which Suits You?
Stand-up comedy offers a structured routine with polished jokes delivering consistent laughs, ideal for audiences seeking sharp, rehearsed humor. Improv comedy thrives on spontaneous, unscripted performances, engaging viewers who enjoy unpredictable, interactive entertainment. Select stand-up for clear punchlines and solo storytelling, or choose improv for dynamic group interactions and real-time creativity.
stand-up comedy vs improv comedy Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com