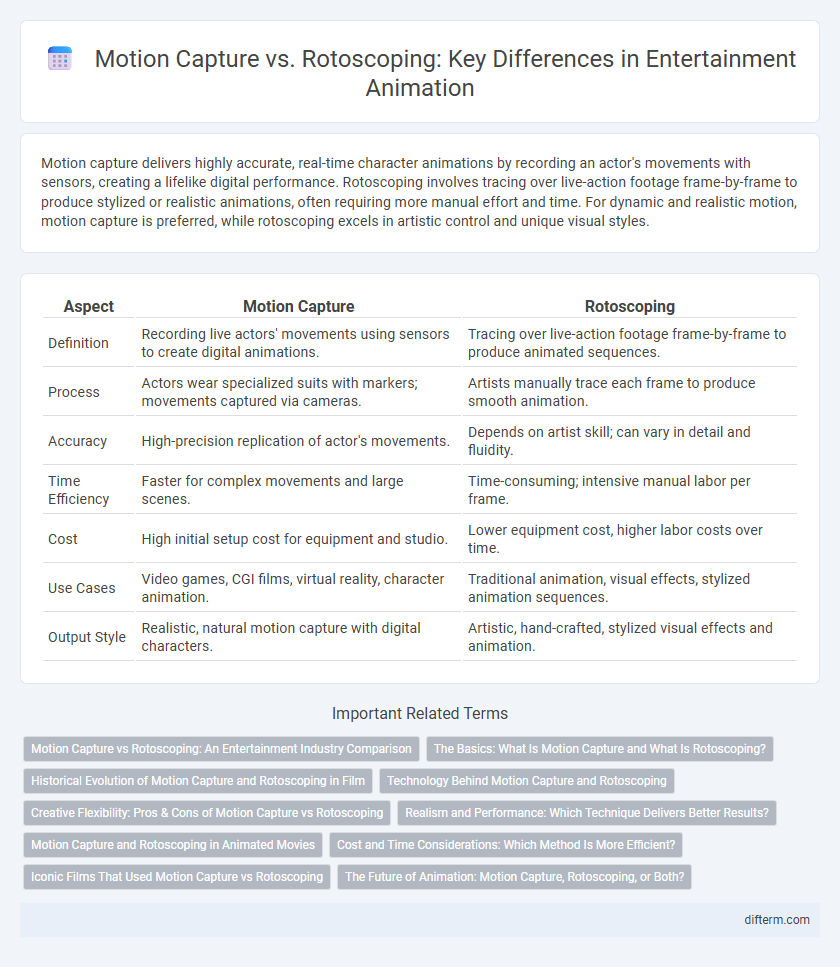
Motion capture delivers highly accurate, real-time character animations by recording an actor's movements with sensors, creating a lifelike digital performance. Rotoscoping involves tracing over live-action footage frame-by-frame to produce stylized or realistic animations, often requiring more manual effort and time. For dynamic and realistic motion, motion capture is preferred, while rotoscoping excels in artistic control and unique visual styles.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Motion Capture | Rotoscoping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recording live actors' movements using sensors to create digital animations. | Tracing over live-action footage frame-by-frame to produce animated sequences. |
| Process | Actors wear specialized suits with markers; movements captured via cameras. | Artists manually trace each frame to produce smooth animation. |
| Accuracy | High-precision replication of actor's movements. | Depends on artist skill; can vary in detail and fluidity. |
| Time Efficiency | Faster for complex movements and large scenes. | Time-consuming; intensive manual labor per frame. |
| Cost | High initial setup cost for equipment and studio. | Lower equipment cost, higher labor costs over time. |
| Use Cases | Video games, CGI films, virtual reality, character animation. | Traditional animation, visual effects, stylized animation sequences. |
| Output Style | Realistic, natural motion capture with digital characters. | Artistic, hand-crafted, stylized visual effects and animation. |
Motion Capture vs Rotoscoping: An Entertainment Industry Comparison
Motion capture captures realistic human movements using sensors and cameras to translate live performances into digital animations, widely used in video games and films for lifelike character actions. Rotoscoping involves tracing over live-action footage frame-by-frame to create stylized or traditional animations, commonly employed in visual effects and animated sequences. Motion capture offers efficiency and precise motion replication, whereas rotoscoping provides artistic control and unique visual styles, making each technique valuable depending on the entertainment project's goals.
The Basics: What Is Motion Capture and What Is Rotoscoping?
Motion capture involves recording the movement of objects or people to create realistic animations by capturing physical performances through sensors or cameras. Rotoscoping is an animation technique where animators trace over live-action footage frame by frame to produce lifelike motion and detail. Both methods are essential in entertainment for creating immersive visual effects and character animations, with motion capture emphasizing real-time performance data and rotoscoping focusing on detailed artistic interpretation.
Historical Evolution of Motion Capture and Rotoscoping in Film
Motion capture emerged in the late 1970s with pioneering projects like "Star Wars: Return of the Jedi," revolutionizing performance recording by capturing actors' movements digitally. Rotoscoping, invented in 1915 by Max Fleischer, allowed animators to trace live-action footage frame-by-frame to create realistic animations in iconic films such as "Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs" (1937). The transition from traditional rotoscoping to advanced motion capture technology reflects significant technological advancements in film production, enhancing both animation accuracy and creative possibilities.
Technology Behind Motion Capture and Rotoscoping
Motion capture technology employs sensors and cameras to record real-time human movements, translating them into digital animations with high precision and realism. Rotoscoping relies on manually tracing over live-action footage frame-by-frame, allowing animators to create lifelike sequences but requiring extensive labor and time. Advanced motion capture systems integrate inertial measurement units and optical markers, offering superior data accuracy compared to the traditional frame-by-frame process used in rotoscoping.
Creative Flexibility: Pros & Cons of Motion Capture vs Rotoscoping
Motion capture offers high creative flexibility by capturing authentic human movements in real time, allowing animators to easily manipulate 3D models for realistic character expressions and actions. Rotoscoping provides precise control over frame-by-frame animation, enabling stylistic choices and artistic interpretations that motion capture cannot replicate. However, motion capture requires specialized equipment and may limit exaggerated or non-human movements, while rotoscoping is labor-intensive but excels in creating unique visual styles.
Realism and Performance: Which Technique Delivers Better Results?
Motion capture captures authentic actor movements by recording real-time physical performances, resulting in highly realistic animation suitable for dynamic character actions. Rotoscoping involves manually tracing over footage to create stylized animation, offering control over artistic interpretation but potentially sacrificing natural fluidity. In terms of realism and performance fidelity, motion capture generally delivers superior results by preserving subtle nuances of human motion.
Motion Capture and Rotoscoping in Animated Movies
Motion capture technology captures real human movements using sensors to create highly realistic animations, significantly enhancing character authenticity in animated movies. Rotoscoping involves tracing over live-action footage frame by frame, allowing for stylized animation that retains lifelike motion but requires intensive manual labor. Both techniques play crucial roles in animation, with motion capture favored for dynamic action sequences and rotoscoping employed for artistic visual effects and detailed character expressions.
Cost and Time Considerations: Which Method Is More Efficient?
Motion capture offers faster production times by capturing real-time performances, reducing the need for extensive frame-by-frame animation, making it cost-efficient for large-scale projects. Rotoscoping demands meticulous hand-drawing over live-action footage, resulting in higher labor costs and longer timelines, particularly for detailed scenes. Studios choose motion capture when budgets and deadlines are tight, while rotoscoping is preferred for stylistic control despite its higher expense and time investment.
Iconic Films That Used Motion Capture vs Rotoscoping
Iconic films like "Avatar" and "The Lord of the Rings" trilogy showcase the groundbreaking use of motion capture to create lifelike digital characters with realistic movements. In contrast, classics such as "The Out of this World" and "Batman" (1989) employed rotoscoping to trace live-action footage frame-by-frame, achieving unique visual effects and animation styles. These distinct techniques highlight the evolution of visual storytelling in cinema, with motion capture enabling more immersive CGI experiences while rotoscoping offers stylized, hand-crafted animation aesthetics.
The Future of Animation: Motion Capture, Rotoscoping, or Both?
Motion capture technology offers unparalleled realism by capturing detailed human movement, while rotoscoping provides stylistic control by tracing live-action footage frame-by-frame. The future of animation likely involves a hybrid approach, leveraging motion capture's precision with rotoscoping's artistic flexibility to create immersive, visually compelling content. Integrating both techniques can optimize production efficiency and deliver innovative storytelling experiences in film, gaming, and virtual reality.
motion capture vs rotoscoping Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com