Method acting immerses actors deeply into their characters by drawing on personal emotions and memories to create authentic performances. Classical acting emphasizes control, technique, and adherence to scripted dialogue, often relying on external expression and physicality. Both approaches offer unique tools to achieve believable portrayals but differ in emotional engagement and preparation style.
Table of Comparison
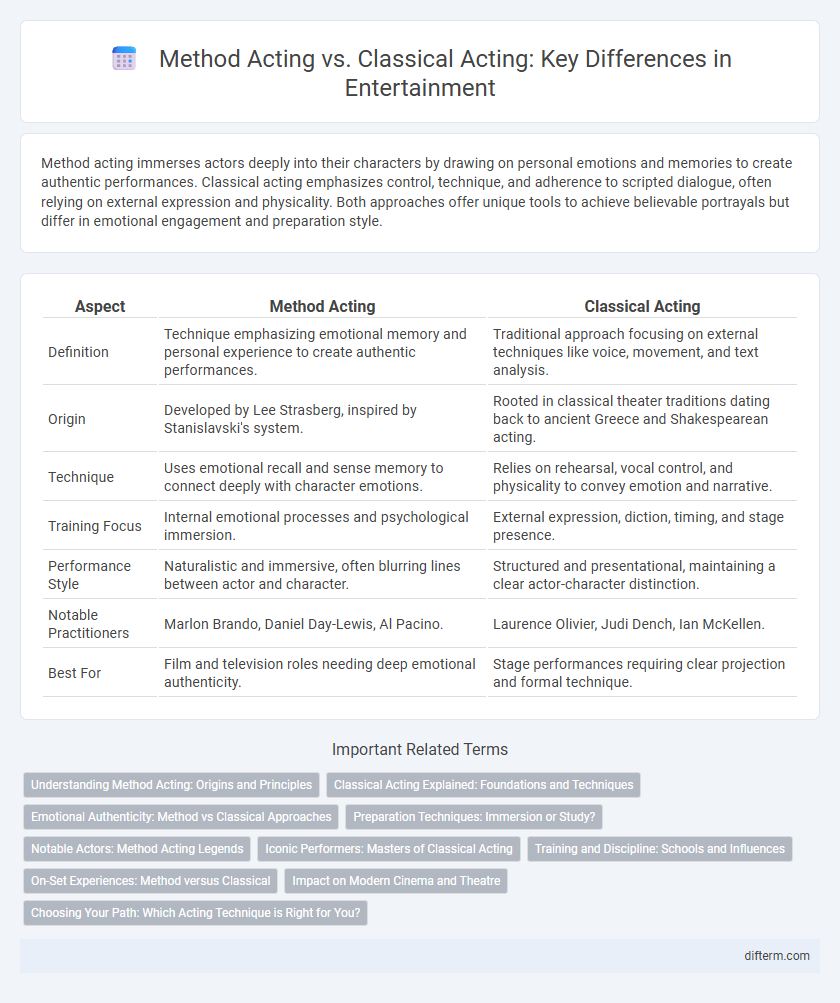
| Aspect | Method Acting | Classical Acting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technique emphasizing emotional memory and personal experience to create authentic performances. | Traditional approach focusing on external techniques like voice, movement, and text analysis. |
| Origin | Developed by Lee Strasberg, inspired by Stanislavski's system. | Rooted in classical theater traditions dating back to ancient Greece and Shakespearean acting. |
| Technique | Uses emotional recall and sense memory to connect deeply with character emotions. | Relies on rehearsal, vocal control, and physicality to convey emotion and narrative. |
| Training Focus | Internal emotional processes and psychological immersion. | External expression, diction, timing, and stage presence. |
| Performance Style | Naturalistic and immersive, often blurring lines between actor and character. | Structured and presentational, maintaining a clear actor-character distinction. |
| Notable Practitioners | Marlon Brando, Daniel Day-Lewis, Al Pacino. | Laurence Olivier, Judi Dench, Ian McKellen. |
| Best For | Film and television roles needing deep emotional authenticity. | Stage performances requiring clear projection and formal technique. |
Understanding Method Acting: Origins and Principles
Method acting, developed from the Stanislavski system by Lee Strasberg, emphasizes emotional authenticity by encouraging actors to draw on personal experiences to fully inhabit their characters. Rooted in psychological realism, this technique requires deep emotional recall and immersive character study to achieve genuine expression. Unlike classical acting, which prioritizes external techniques and script interpretation, method acting seeks an internal, transformative connection between actor and role.
Classical Acting Explained: Foundations and Techniques
Classical acting emphasizes mastery of voice control, precise physical expression, and rigorous interpretation of text, rooted in traditions established by Shakespeare and Stanislavski. Techniques such as breath regulation, articulation exercises, and disciplined rehearsal cultivate an actor's ability to convincingly portray complex characters on stage and screen. This method prioritizes external performance skills and faithful text realization, distinguishing it from the internal emotional focus characteristic of method acting.
Emotional Authenticity: Method vs Classical Approaches
Method acting emphasizes deep emotional authenticity by encouraging actors to draw from their personal experiences and emotions to fully inhabit a character's psyche. Classical acting relies on techniques such as voice modulation, physicality, and scripted interpretation to convey emotions convincingly without necessarily internalizing the character's feelings. Both approaches aim for truthful performances, but method acting prioritizes internal emotional truth, while classical acting balances external expression and technical precision.
Preparation Techniques: Immersion or Study?
Method acting emphasizes deep emotional immersion by encouraging actors to draw from personal experiences and fully inhabit their characters' psychological states. Classical acting relies on rigorous study of text, voice, and movement techniques to master precise control and deliver consistent performances. Both preparation techniques demand discipline but differ in approach: emotional authenticity in method acting versus technical proficiency in classical acting.
Notable Actors: Method Acting Legends
Method acting, championed by legends like Marlon Brando and Robert De Niro, emphasizes deep emotional immersion and psychological realism to create authentic performances. These actors train rigorously to embody their characters' experiences, often drawing from personal memories to evoke genuine emotions. Their groundbreaking techniques contrast sharply with classical acting's focus on external gestures and voice modulation.
Iconic Performers: Masters of Classical Acting
Masters of classical acting like Laurence Olivier and Dame Judi Dench have set benchmarks with their precise voice control, clear diction, and adherence to traditional techniques rooted in Shakespearean theater. Their performances emphasize a deep understanding of text and character psychology without relying on personal emotional experiences, making roles universally relatable across time. This approach contrasts with method acting but remains celebrated for its discipline, elegance, and enduring impact on the theatrical canon.
Training and Discipline: Schools and Influences
Method acting emphasizes immersive emotional experience through techniques pioneered by Lee Strasberg and the Actors Studio, requiring rigorous psychological training and deep character exploration. Classical acting relies on formal training in voice, movement, and textual analysis, often taught in conservatories inspired by classical theater traditions like those of Stanislavski and Meisner. Both methods demand disciplined practice, but method acting prioritizes internal sensation while classical acting focuses on external technique and vocal precision.
On-Set Experiences: Method versus Classical
Method acting immerses actors deeply into their characters' emotions and experiences on set, often leading to intense, raw performances that blur the line between actor and role. Classical acting relies on technical skill, structured rehearsal, and external techniques such as voice modulation and physicality to deliver controlled, consistent portrayals. The on-set dynamic for method actors can involve spontaneous improvisation and emotional vulnerability, whereas classical actors typically adhere to precise direction and scripted cues.
Impact on Modern Cinema and Theatre
Method acting, pioneered by Lee Strasberg, revolutionized modern cinema by encouraging actors to deeply embody their characters' emotions, creating more authentic and emotionally resonant performances. Classical acting, rooted in precise voice control and physicality from traditions like Shakespearean theatre, remains essential for stage productions demanding clarity and projection. The fusion of these techniques has expanded the range of expressive tools available, enhancing storytelling in both contemporary film and theatre.
Choosing Your Path: Which Acting Technique is Right for You?
Method acting immerses performers in their characters' emotional experiences, fostering authentic and deeply personal portrayals by drawing on past memories and emotions. Classical acting emphasizes vocal projection, physicality, and adherence to scripted text, providing actors with a structured approach rooted in tradition and discipline. Deciding between these techniques depends on your emotional depth, adaptability, and the specific demands of your roles within contemporary or classical theater and film.
method acting vs classical acting Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com