The background score in entertainment pets enhances emotional engagement by subtly supporting scenes without overpowering the visuals, while the soundtrack consists of selected songs or instrumental pieces that define the overall mood and identity of the production. A well-crafted background score creates atmosphere and continuity, often composed specifically to match the narrative flow. In contrast, the soundtrack may include popular music tracks that resonate with audiences and elevate memorable moments.
Table of Comparison
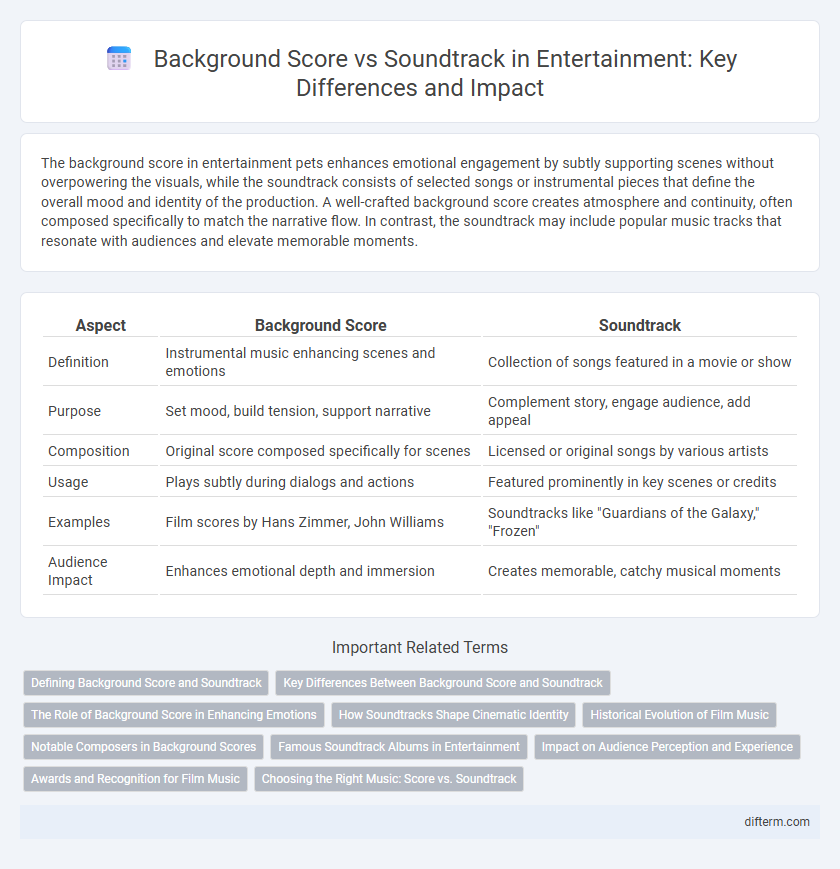
| Aspect | Background Score | Soundtrack |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instrumental music enhancing scenes and emotions | Collection of songs featured in a movie or show |
| Purpose | Set mood, build tension, support narrative | Complement story, engage audience, add appeal |
| Composition | Original score composed specifically for scenes | Licensed or original songs by various artists |
| Usage | Plays subtly during dialogs and actions | Featured prominently in key scenes or credits |
| Examples | Film scores by Hans Zimmer, John Williams | Soundtracks like "Guardians of the Galaxy," "Frozen" |
| Audience Impact | Enhances emotional depth and immersion | Creates memorable, catchy musical moments |
Defining Background Score and Soundtrack
Background score refers to the instrumental music composed specifically to enhance the mood, emotion, and atmosphere of a film or TV show, playing subtly beneath the scenes. Soundtrack encompasses all the music featured in a production, including background scores, songs performed by characters, and licensed tracks that contribute to the overall audio experience. These elements are crucial in shaping audience engagement, with the background score driving emotional responses and the soundtrack providing thematic or cultural context.
Key Differences Between Background Score and Soundtrack
The background score consists of instrumental music composed to enhance the emotional atmosphere and narrative flow of scenes in films or TV shows, often played subtly without vocals. The soundtrack includes all_audio elements of a film's music, encompassing songs performed by artists, licensed tracks, and the background score, frequently released as an album. Key differences lie in purpose and composition: the background score supports the story dynamically, while the soundtrack delivers memorable songs that may stand independently of the visual media.
The Role of Background Score in Enhancing Emotions
The background score plays a critical role in enhancing emotions by subtly guiding the audience's feelings and heightening the narrative impact without distracting from the visuals. Unlike the soundtrack, which consists of songs that can define a film's identity, the background score dynamically supports character development and scene tension through instrumental music and motifs. Composers like Hans Zimmer and John Williams exemplify how powerful scores evoke emotional responses, making scenes more immersive and memorable.
How Soundtracks Shape Cinematic Identity
Soundtracks play a pivotal role in shaping a film's cinematic identity by weaving together songs and instrumental pieces that reflect the narrative's mood and cultural context. Unlike background scores, which primarily underscore scenes to evoke emotions subtly, soundtracks create memorable moments through curated tracks that resonate with audiences and enhance storytelling. Iconic soundtracks often become synonymous with their films, influencing audience perceptions and contributing to the movie's lasting legacy.
Historical Evolution of Film Music
Film music evolved through distinct phases, beginning with silent film era live accompaniments to synchronized soundtracks in the late 1920s. The background score developed as orchestral compositions tailored to enhance narrative and emotional depth, while soundtracks expanded to include pre-existing songs and popular music integrated into film scenes. This historical evolution reflects technological advancements and changing audience preferences, shaping how music functions within cinematic storytelling.
Notable Composers in Background Scores
Notable composers in background scores like Hans Zimmer, John Williams, and Howard Shore have transformed cinematic experiences by creating emotionally immersive music that enhances storytelling without overshadowing dialogue. These scores differ from soundtracks, which often feature pre-existing songs used to establish mood or era; background scores are original compositions tailored to the film's narrative flow. Their ability to evoke tension, joy, or sorrow through instrumental themes remains a critical element in film production and audience engagement.
Famous Soundtrack Albums in Entertainment
Famous soundtrack albums like "The Bodyguard" and "Purple Rain" have become cultural milestones, blending iconic background scores with chart-topping songs that define movies' identities. Background scores, typically instrumental, enhance the emotional tone and atmosphere, while soundtracks often feature popular tracks sung by notable artists, driving both narrative and commercial success. These albums frequently top music charts, showcasing the powerful synergy between film and the music industry in entertainment.
Impact on Audience Perception and Experience
Background scores create an emotional atmosphere that subtly influences the audience's feelings and heightens tension, immersion, or empathy within scenes. Soundtracks, featuring songs chosen for their lyrical content or mood, actively engage viewers by reinforcing themes and enhancing memorability through recognizable music. Both elements significantly shape audience perception, with scores driving emotional undercurrents and soundtracks providing cultural or narrative context that enriches the overall entertainment experience.
Awards and Recognition for Film Music
Background scores and soundtracks play pivotal roles in film music, each earning distinct awards and recognition. The Academy Award for Best Original Score honors composers for their background music that enhances the narrative, while the Grammy Awards often celebrate soundtracks, spotlighting collections of songs featured in a film. Notable examples include Hans Zimmer's Oscar-winning background score for "Dune" and the Grammy-winning soundtrack of "The Greatest Showman," highlighting industry appreciation for both musical elements in entertainment.
Choosing the Right Music: Score vs. Soundtrack
Selecting the right music for a film or game hinges on understanding the distinct roles of background score and soundtrack; the background score typically consists of instrumental compositions tailored to enhance the emotional tone and narrative flow, while the soundtrack includes pre-existing songs that resonate with the story's setting or characters. A background score offers seamless emotional guidance without distracting from the visuals, whereas a soundtrack injects cultural or thematic authenticity through recognizable tracks. Choosing between them depends on whether the project requires subtle emotional layering or impactful, mood-defining music to strengthen audience connection.
background score vs soundtrack Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com