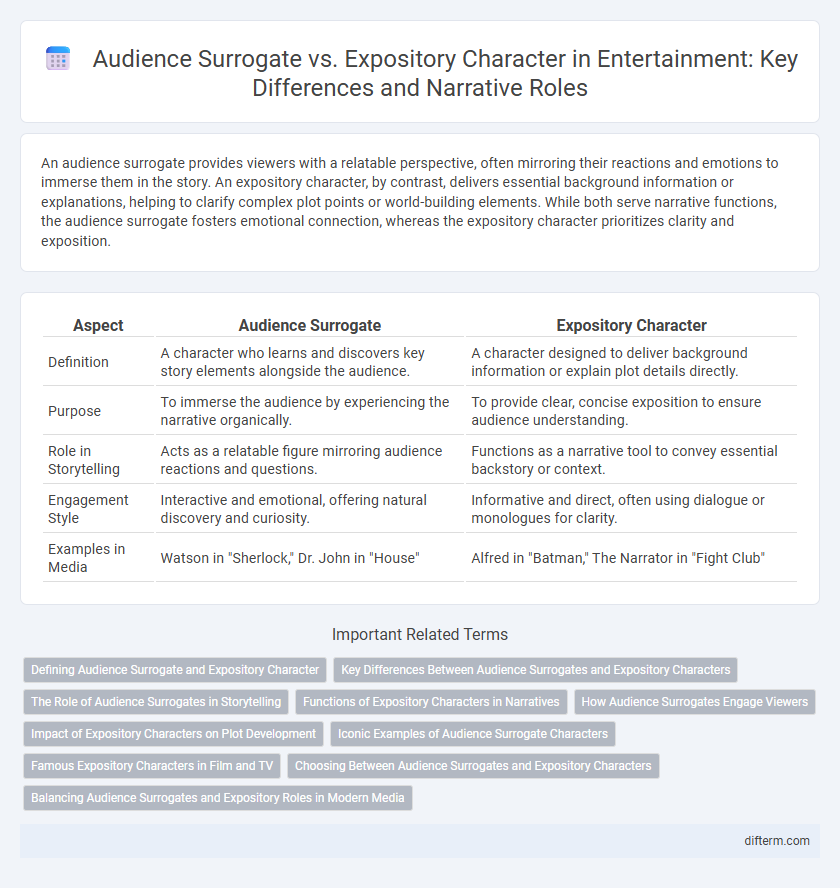
An audience surrogate provides viewers with a relatable perspective, often mirroring their reactions and emotions to immerse them in the story. An expository character, by contrast, delivers essential background information or explanations, helping to clarify complex plot points or world-building elements. While both serve narrative functions, the audience surrogate fosters emotional connection, whereas the expository character prioritizes clarity and exposition.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Audience Surrogate | Expository Character |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A character who learns and discovers key story elements alongside the audience. | A character designed to deliver background information or explain plot details directly. |
| Purpose | To immerse the audience by experiencing the narrative organically. | To provide clear, concise exposition to ensure audience understanding. |
| Role in Storytelling | Acts as a relatable figure mirroring audience reactions and questions. | Functions as a narrative tool to convey essential backstory or context. |
| Engagement Style | Interactive and emotional, offering natural discovery and curiosity. | Informative and direct, often using dialogue or monologues for clarity. |
| Examples in Media | Watson in "Sherlock," Dr. John in "House" | Alfred in "Batman," The Narrator in "Fight Club" |
Defining Audience Surrogate and Expository Character
An audience surrogate is a character in entertainment who represents the viewer's perspective, asking questions and reacting in ways that guide the audience's understanding of the story. An expository character primarily serves to deliver background information or exposition necessary to advance the plot or clarify the narrative. While both characters facilitate storytelling, the audience surrogate engages emotionally with the audience, making the story more relatable, whereas the expository character focuses on providing essential context.
Key Differences Between Audience Surrogates and Expository Characters
Audience surrogates immerse viewers by experiencing the story through their perspective, fostering empathy and emotional connection. Expository characters primarily serve to convey background information, plot details, or world-building elements through dialogue or narration. The key difference lies in audience surrogates driving engagement by embodying the audience's curiosity, while expository characters function as informational tools essential for narrative clarity.
The Role of Audience Surrogates in Storytelling
Audience surrogates serve as relatable characters who guide viewers through complex narratives, allowing them to experience the story's events and emotions firsthand. These characters often ask questions and react authentically, bridging the gap between the audience and the fictional world without disrupting immersion. Unlike expository characters who primarily convey information, audience surrogates drive engagement by embodying the audience's perspective throughout the storytelling process.
Functions of Expository Characters in Narratives
Expository characters function primarily to convey essential information, background, and plot details crucial for narrative progression, often serving as a bridge between the story and the audience. Unlike audience surrogates, who experience the story firsthand and embody viewers' perspectives, expository characters explicitly articulate context through dialogue or narration, enhancing comprehension. Their role is pivotal in clarifying complex story elements, motivating character decisions, and revealing hidden motivations without disrupting narrative flow.
How Audience Surrogates Engage Viewers
Audience surrogates immerse viewers by embodying the typical audience perspective, allowing them to experience the story's world through relatable emotions and reactions. Unlike expository characters who primarily convey information and background, audience surrogates actively drive narrative curiosity and emotional investment. This engagement technique enhances viewer identification, making plot developments more impactful and fostering deeper connection with the story.
Impact of Expository Characters on Plot Development
Expository characters facilitate plot development by delivering essential background information and clarifying complex story elements, which helps the audience understand motivations and conflicts. Their presence often advances the narrative by explaining key events or character intentions that might otherwise remain ambiguous. Unlike audience surrogates, who experience the story firsthand, expository characters strategically guide the viewer's comprehension, ensuring smoother progression and deeper engagement with the plot.
Iconic Examples of Audience Surrogate Characters
Audience surrogate characters serve as the viewers' or readers' entry point into a fictional world, embodying the audience's questions and reactions in narratives like Dr. John Watson in Sherlock Holmes. Unlike expository characters who primarily deliver background information, audience surrogates actively explore and respond to the story's mystery or conflict, making complex plots more accessible. Iconic examples include Nick Carraway in The Great Gatsby and Ron Weasley in the Harry Potter series, both offering relatable perspectives that bridge the audience with the narrative experience.
Famous Expository Characters in Film and TV
Famous expository characters in film and TV, such as Watson from Sherlock Holmes and Ron Weasley from Harry Potter, serve to reveal crucial plot details and background information to the audience through their interactions and inquiries. Unlike audience surrogates who primarily experience the story firsthand, expository characters articulate complex narrative elements and world-building in digestible dialogue. Their presence enhances storytelling clarity, making intricate storylines accessible and engaging for viewers.
Choosing Between Audience Surrogates and Expository Characters
Choosing between audience surrogates and expository characters depends on narrative goals and audience engagement. Audience surrogates offer immersive viewpoints by experiencing the story firsthand, facilitating emotional connection and relatability. Expository characters efficiently convey essential background and information, enhancing plot understanding without interrupting story flow.
Balancing Audience Surrogates and Expository Roles in Modern Media
Balancing audience surrogates and expository characters in modern media involves crafting relatable figures who naturally introduce key information without overwhelming the narrative. Audience surrogates engage viewers by experiencing the story's world alongside them, while expository characters provide necessary background and context through dialogue. Effective storytelling integrates these roles seamlessly to maintain pacing and immersion, ensuring that exposition feels organic rather than forced.
Audience surrogate vs Expository character Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com