Multiculturalism celebrates the coexistence of diverse cultures within a society, encouraging the preservation of individual cultural identities while fostering mutual respect and understanding. In contrast, the melting pot concept advocates for the blending of different cultures into a single, cohesive identity, often emphasizing assimilation. Embracing multiculturalism allows cultural pet owners to maintain unique traditions and values, enriching the collective cultural tapestry without losing their distinctiveness.
Table of Comparison
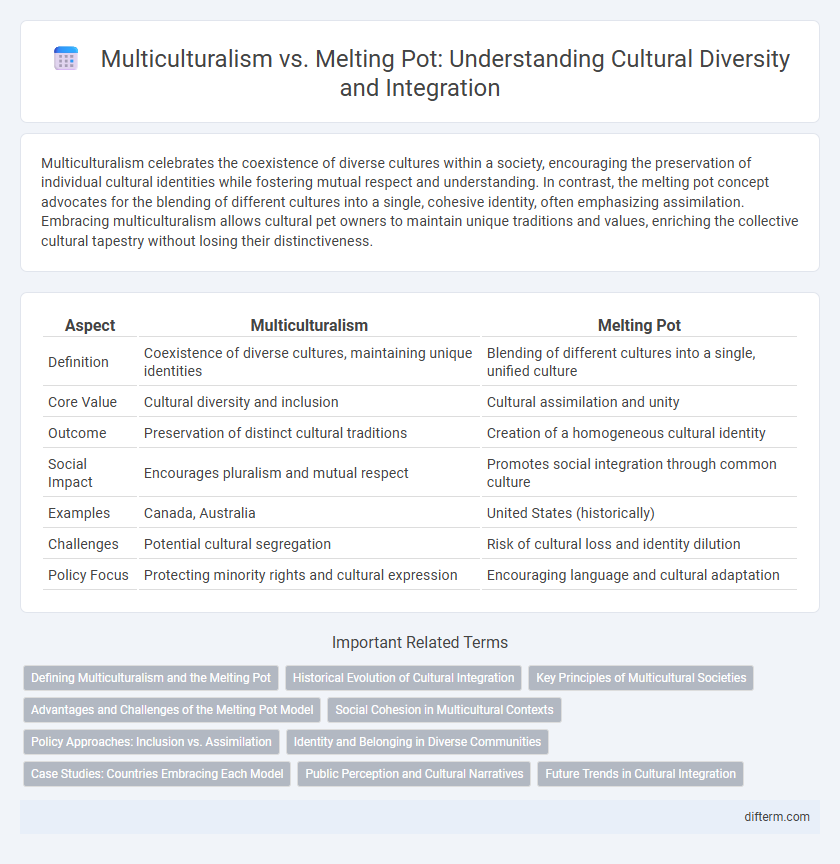
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Melting Pot |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultures, maintaining unique identities | Blending of different cultures into a single, unified culture |
| Core Value | Cultural diversity and inclusion | Cultural assimilation and unity |
| Outcome | Preservation of distinct cultural traditions | Creation of a homogeneous cultural identity |
| Social Impact | Encourages pluralism and mutual respect | Promotes social integration through common culture |
| Examples | Canada, Australia | United States (historically) |
| Challenges | Potential cultural segregation | Risk of cultural loss and identity dilution |
| Policy Focus | Protecting minority rights and cultural expression | Encouraging language and cultural adaptation |
Defining Multiculturalism and the Melting Pot
Multiculturalism embraces the coexistence of diverse cultures, promoting equal respect and preservation of distinct identities within a society. The melting pot concept advocates for blending various cultural backgrounds into a single unified identity, often emphasizing assimilation. These differing approaches shape national policies on integration, social cohesion, and cultural expression.
Historical Evolution of Cultural Integration
The historical evolution of cultural integration reveals that multiculturalism promotes the preservation of distinct cultural identities within a society, while the melting pot concept emphasizes the blending of diverse cultures into a single, unified identity. Early American history favored the melting pot ideal, encouraging immigrants to assimilate and create a cohesive national culture. In contrast, contemporary cultural policies increasingly support multiculturalism, recognizing the value of cultural diversity and the coexistence of multiple cultural narratives within a nation.
Key Principles of Multicultural Societies
Multicultural societies emphasize the coexistence of diverse cultural identities, promoting mutual respect, inclusivity, and equal recognition of all ethnic groups. They foster cultural pluralism by supporting language preservation, religious freedom, and social equity, contrasting with the assimilation focus of melting pot models. Key principles include cultural autonomy, anti-discrimination policies, and active engagement in intercultural dialogue to maintain social cohesion and mutual understanding.
Advantages and Challenges of the Melting Pot Model
The melting pot model fosters social cohesion by encouraging cultural assimilation and creating a unified national identity, which can enhance mutual understanding and reduce ethnic divisions. Challenges include the risk of cultural homogenization, where minority traditions and languages may be marginalized or lost, potentially causing resistance and social tensions. Promoting inclusive policies that respect cultural diversity while encouraging integration is essential to balance the advantages and mitigate the drawbacks of the melting pot approach.
Social Cohesion in Multicultural Contexts
Social cohesion in multicultural contexts thrives when diverse cultural identities are recognized and valued rather than assimilated into a single norm, as seen in multiculturalism models. Unlike the melting pot approach that emphasizes homogenization, multiculturalism fosters inclusivity by promoting equal participation and mutual respect among different cultural groups. This dynamic strengthens community bonds and enhances social stability by allowing cultural diversity to coexist with shared societal values.
Policy Approaches: Inclusion vs. Assimilation
Multiculturalism policy approaches emphasize inclusion by recognizing and celebrating diverse cultural identities within a society, promoting equal participation and respect for minority groups. In contrast, the melting pot model advocates assimilation, expecting individuals from different backgrounds to adopt a dominant culture, often at the expense of their original identities. These contrasting policies directly impact social cohesion, identity preservation, and the extent to which cultural pluralism is institutionalized in national frameworks.
Identity and Belonging in Diverse Communities
Multiculturalism fosters the coexistence of diverse cultural identities, encouraging individuals to maintain their distinct heritage while participating in a shared community. The melting pot concept emphasizes the blending of different backgrounds into a unified identity, promoting social integration through cultural assimilation. Both frameworks impact individuals' sense of belonging by shaping how cultural identity is expressed and valued within diverse societies.
Case Studies: Countries Embracing Each Model
Canada exemplifies multiculturalism by promoting official bilingualism and protecting cultural heritage through policies like the Multiculturalism Act, fostering inclusive identity. Conversely, the United States traditionally represents the melting pot model, encouraging assimilation while blending diverse cultures into a unified national identity. Australia demonstrates a hybrid approach, combining multicultural policies with integration initiatives to balance cultural diversity and social cohesion.
Public Perception and Cultural Narratives
Public perception of multiculturalism often highlights the value of preserving distinct cultural identities within a society, promoting inclusivity and mutual respect among diverse groups. In contrast, the melting pot narrative emphasizes assimilation, encouraging individuals to merge into a unified culture, sometimes at the expense of individual cultural expression. These differing cultural narratives shape national identity and influence policies on immigration, social integration, and community cohesion.
Future Trends in Cultural Integration
Emerging future trends in cultural integration highlight a shift towards multiculturalism, emphasizing the preservation of diverse identities within a unified society over the traditional melting pot model, which promotes assimilation and cultural blending into a single homogeneous culture. Advances in technology and global connectivity facilitate cross-cultural exchanges and multilingualism, supporting inclusive policies that celebrate cultural pluralism. Demographic changes and increased migration patterns further encourage governance frameworks that recognize and institutionalize cultural diversity as a key asset for social cohesion and economic innovation.
multiculturalism vs melting pot Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com