Monoculturalism emphasizes the dominance of a single culture, often leading to limited perspectives and reduced social diversity. In contrast, multiculturalism promotes the coexistence of multiple cultures, enriching societies through diverse traditions, languages, and worldviews. Embracing multiculturalism fosters inclusivity and innovation by encouraging intercultural dialogue and understanding.
Table of Comparison
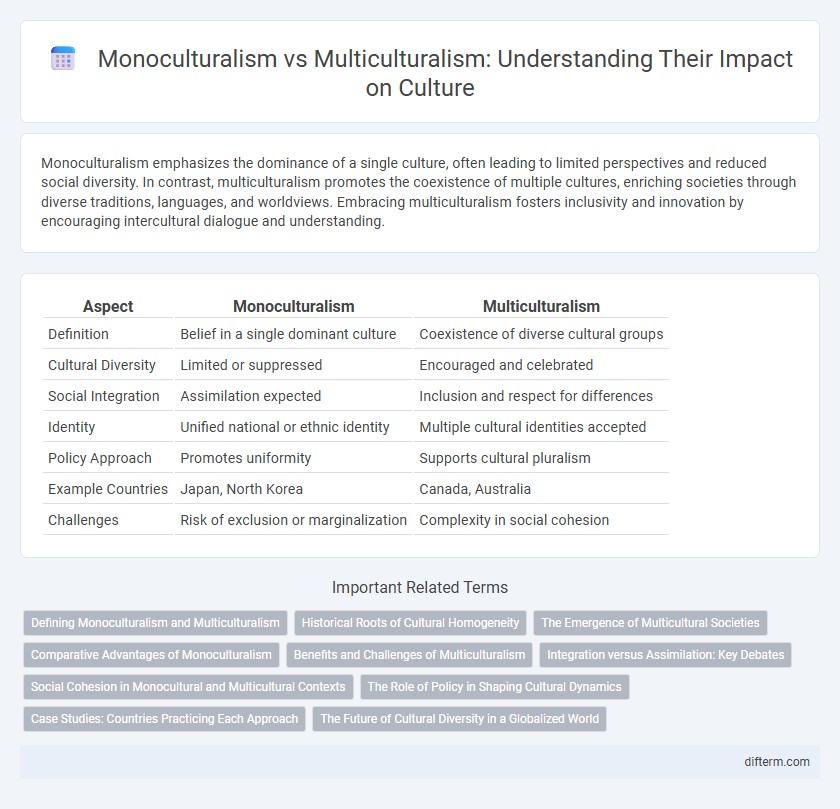
| Aspect | Monoculturalism | Multiculturalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief in a single dominant culture | Coexistence of diverse cultural groups |
| Cultural Diversity | Limited or suppressed | Encouraged and celebrated |
| Social Integration | Assimilation expected | Inclusion and respect for differences |
| Identity | Unified national or ethnic identity | Multiple cultural identities accepted |
| Policy Approach | Promotes uniformity | Supports cultural pluralism |
| Example Countries | Japan, North Korea | Canada, Australia |
| Challenges | Risk of exclusion or marginalization | Complexity in social cohesion |
Defining Monoculturalism and Multiculturalism
Monoculturalism refers to the dominance of a single cultural framework within a society, emphasizing uniformity in language, traditions, and values. Multiculturalism embraces the coexistence of diverse cultural backgrounds, promoting inclusivity, cultural exchange, and respect for pluralism. Understanding these concepts is essential for analyzing social cohesion, identity formation, and policy-making in increasingly diverse populations.
Historical Roots of Cultural Homogeneity
Monoculturalism's historical roots stem from societies that developed isolationist policies to preserve ethnic uniformity and social cohesion, often through language, religion, and shared traditions that reinforced a singular cultural identity. In contrast, multiculturalism emerged prominently in colonial and post-colonial contexts where migration, trade, and imperial expansion facilitated cultural exchanges, blending diverse ethnicities and belief systems. Historical examples include the homogeneous nation-states of Japan and Iceland versus the multicultural mosaics of the Ottoman Empire and modern-day Canada.
The Emergence of Multicultural Societies
The emergence of multicultural societies reflects a shift from monoculturalism, where a single cultural framework dominates, to diverse cultural landscapes shaped by immigration, globalization, and urbanization. Multiculturalism fosters social inclusion and cultural exchange, enriching communities with varied traditions, languages, and worldviews. This transformation challenges traditional national identities and promotes policies that celebrate cultural pluralism and integration.
Comparative Advantages of Monoculturalism
Monoculturalism offers streamlined communication and cohesive social norms, fostering strong group identity and unity. Homogeneous cultural environments can reduce misunderstandings and conflicts, enabling efficient decision-making and collaboration. Economic and organizational structures often benefit from shared values and practices that promote stability and predictability.
Benefits and Challenges of Multiculturalism
Multiculturalism enriches societies by fostering cultural diversity, promoting inclusivity, and enhancing global awareness, which stimulates creativity and economic growth. Challenges include potential social fragmentation, communication barriers, and conflicts arising from differing cultural norms and values. Effective policies and intercultural dialogue are essential to harness the benefits of multicultural societies while addressing integration and cohesion issues.
Integration versus Assimilation: Key Debates
Monoculturalism emphasizes assimilation, expecting individuals to abandon their cultural identities to fully integrate into the dominant culture, often leading to the loss of cultural diversity. In contrast, multiculturalism advocates for integration, encouraging the coexistence of multiple cultures while respecting and preserving distinct cultural identities within a society. Key debates revolve around the balance between social cohesion and cultural pluralism, highlighting the challenges of maintaining unity without eroding minority cultural expressions.
Social Cohesion in Monocultural and Multicultural Contexts
Monoculturalism fosters social cohesion through shared values, traditions, and language, creating a unified collective identity that strengthens community bonds. Multiculturalism, while promoting diversity, requires active intercultural dialogue and inclusive policies to bridge differences and build mutual trust among diverse groups. Social cohesion in multicultural contexts depends heavily on cross-cultural understanding and equitable participation in societal institutions.
The Role of Policy in Shaping Cultural Dynamics
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping cultural dynamics by either promoting monoculturalism or encouraging multiculturalism. Monocultural policies often emphasize cultural homogeneity, prioritizing a singular national identity, whereas multicultural policies support cultural diversity, fostering inclusion and equal representation of various ethnic groups. The effectiveness of these policies impacts social cohesion, cultural preservation, and integration outcomes within societies.
Case Studies: Countries Practicing Each Approach
Japan exemplifies monoculturalism through its emphasis on ethnic homogeneity and cultural preservation, fostering social cohesion but facing challenges in immigration integration. Canada represents multiculturalism by actively promoting diversity and inclusion policies, enabling ethnic communities to maintain distinct cultural identities while contributing to a unified national identity. These case studies reveal how differing cultural frameworks influence social dynamics, policy-making, and nation-building strategies worldwide.
The Future of Cultural Diversity in a Globalized World
Monoculturalism limits societal growth by preserving a single cultural identity, while multiculturalism fosters inclusivity and innovation through diverse perspectives. In a globalized world, the rise of transnational migration and digital connectivity accelerates cultural exchange, enhancing social cohesion and economic resilience. Embracing multiculturalism is essential for addressing global challenges and promoting sustainable development in increasingly interconnected societies.
monoculturalism vs multiculturalism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com