Cross-cultural culture pet studies compare differences and similarities between distinct cultural groups, highlighting how traditions influence pet care and human-animal relationships. Transcultural approaches transcend individual cultures, emphasizing shared experiences and hybrid practices that emerge from cultural interactions in pet ownership. Understanding both perspectives enriches insights into how global connectivity shapes evolving cultural norms around pets.
Table of Comparison
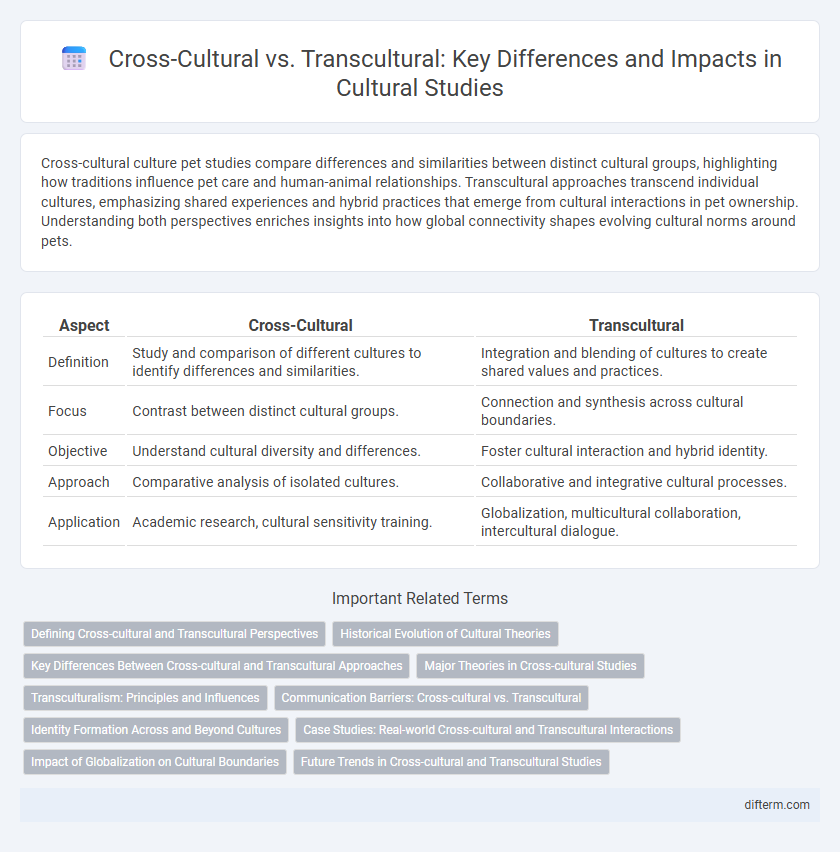
| Aspect | Cross-Cultural | Transcultural |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study and comparison of different cultures to identify differences and similarities. | Integration and blending of cultures to create shared values and practices. |
| Focus | Contrast between distinct cultural groups. | Connection and synthesis across cultural boundaries. |
| Objective | Understand cultural diversity and differences. | Foster cultural interaction and hybrid identity. |
| Approach | Comparative analysis of isolated cultures. | Collaborative and integrative cultural processes. |
| Application | Academic research, cultural sensitivity training. | Globalization, multicultural collaboration, intercultural dialogue. |
Defining Cross-cultural and Transcultural Perspectives
Cross-cultural perspectives analyze differences and similarities between distinct cultural groups, emphasizing comparative studies to understand cultural norms and behaviors. Transcultural perspectives go beyond comparison by exploring the blending and merging of cultural elements, highlighting interconnectedness and cultural transformation. Both approaches provide valuable insights for navigating global diversity and fostering intercultural communication.
Historical Evolution of Cultural Theories
The historical evolution of cultural theories highlights the distinction between cross-cultural and transcultural approaches, where cross-cultural studies compare cultural differences to identify patterns, while transcultural theories emphasize cultural interconnectedness and blending beyond boundaries. Early anthropological research primarily fostered cross-cultural methodologies to classify and contrast societies, evolving over time into transcultural perspectives that recognize fluid identities and global interactions. These shifts reflect broader historical changes, including globalization and increased intercultural communication, reshaping how culture is understood and studied in social sciences.
Key Differences Between Cross-cultural and Transcultural Approaches
Cross-cultural approaches analyze differences and similarities between distinct cultural groups to understand their unique behaviors, values, and communication styles. Transcultural approaches emphasize the blending and merging of cultural elements to create shared experiences and foster intercultural understanding beyond traditional boundaries. Key differences lie in cross-cultural studies maintaining distinct cultural perspectives, while transcultural approaches seek integration and synthesis of cultures.
Major Theories in Cross-cultural Studies
Major theories in cross-cultural studies include Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions Theory, which identifies key values influencing behavior across societies; Edward T. Hall's theory of high-context and low-context communication styles, highlighting differences in communication patterns; and Schwartz's Theory of Basic Human Values, which categorizes universal values shaping cultural norms. These frameworks facilitate understanding of cultural variability by analyzing specific cultural traits and their impact on interpersonal and organizational interactions. Cross-cultural approaches emphasize comparing distinct cultures, whereas transcultural perspectives seek to integrate and transcend cultural boundaries for a more holistic understanding.
Transculturalism: Principles and Influences
Transculturalism emphasizes the dynamic exchange and integration of cultural elements across diverse societies, fostering mutual respect and understanding beyond mere coexistence. Principles of transculturalism include openness to cultural dialogue, adaptability, and the recognition of shared human experiences that transcend specific cultural boundaries. Influences shaping transculturalism originate from globalization, migration patterns, and increasing interconnectivity through technology, which together promote hybrid identities and inclusive cultural narratives.
Communication Barriers: Cross-cultural vs. Transcultural
Communication barriers in cross-cultural contexts often arise from differences in language, nonverbal cues, and cultural norms, leading to misunderstandings and misinterpretations. Transcultural communication emphasizes shared values and hybrid identities, reducing barriers by fostering empathy and collaborative meaning-making across cultures. This approach facilitates smoother interactions by focusing on commonalities rather than cultural distinctions.
Identity Formation Across and Beyond Cultures
Cross-cultural identity formation examines how individuals navigate and integrate multiple distinct cultural frameworks, emphasizing comparison and interaction between cultures. Transcultural identity extends beyond cultural boundaries by fostering fluid, hybrid identities that merge elements from diverse cultural origins into a cohesive self-concept. Both perspectives explore the dynamic process of self-construction amid cultural diversity, highlighting adaptation, negotiation, and the evolving nature of personal and communal identities.
Case Studies: Real-world Cross-cultural and Transcultural Interactions
Cross-cultural interactions involve examining differences between distinct cultures to improve communication and collaboration, exemplified by corporate mergers where teams from Japan and the United States navigate contrasting work ethics. Transcultural interactions transcend cultural boundaries, fostering hybrid identities and shared practices, as seen in global art projects blending Indigenous Australian and European techniques. Case studies such as international healthcare partnerships reveal how transcultural approaches enhance patient care by integrating multiple cultural perspectives.
Impact of Globalization on Cultural Boundaries
Globalization has blurred cultural boundaries, intensifying interactions that highlight differences in cross-cultural contexts while promoting shared values in transcultural exchanges. Cross-cultural encounters emphasize understanding diverse cultural norms and practices, often requiring negotiation and adaptation. Transcultural processes go beyond mere interaction by fostering hybrid cultural identities and facilitating the flow of ideas, customs, and innovations across global communities.
Future Trends in Cross-cultural and Transcultural Studies
Future trends in cross-cultural and transcultural studies emphasize integration of digital communication technologies to facilitate global dialogue and understanding. Emerging research prioritizes hybrid identities, exploring how cultural boundaries blur through migration and virtual interactions. Artificial intelligence and big data analytics are increasingly used to analyze cultural dynamics, predicting shifts in societal values and intercultural competence development.
Cross-cultural vs Transcultural Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com