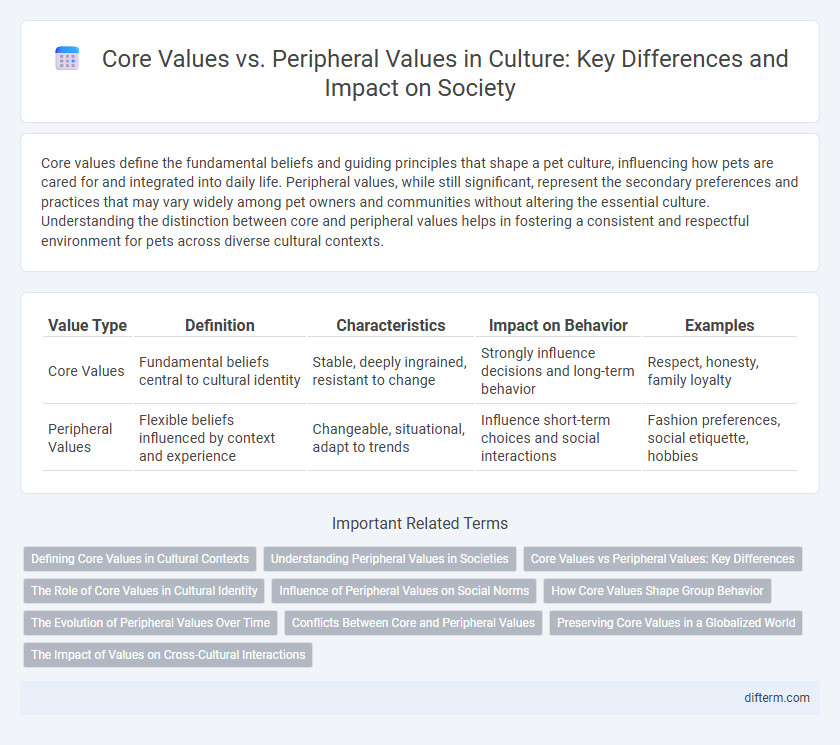
Core values define the fundamental beliefs and guiding principles that shape a pet culture, influencing how pets are cared for and integrated into daily life. Peripheral values, while still significant, represent the secondary preferences and practices that may vary widely among pet owners and communities without altering the essential culture. Understanding the distinction between core and peripheral values helps in fostering a consistent and respectful environment for pets across diverse cultural contexts.
Table of Comparison
| Value Type | Definition | Characteristics | Impact on Behavior | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Values | Fundamental beliefs central to cultural identity | Stable, deeply ingrained, resistant to change | Strongly influence decisions and long-term behavior | Respect, honesty, family loyalty |
| Peripheral Values | Flexible beliefs influenced by context and experience | Changeable, situational, adapt to trends | Influence short-term choices and social interactions | Fashion preferences, social etiquette, hobbies |
Defining Core Values in Cultural Contexts
Core values in cultural contexts are fundamental beliefs and principles that guide behavior and decision-making within a community, serving as the foundation for social norms and identity. These values are deeply embedded, enduring over time, and resistant to change, distinguishing them from peripheral values which are more adaptable and situational. Understanding core values enables insight into cultural cohesion and the mechanisms that sustain collective integrity and continuity.
Understanding Peripheral Values in Societies
Peripheral values in societies represent flexible, context-dependent norms that adapt to changing environments and cultural interactions, contrasting with core values that remain stable and foundational. These values influence everyday behavior and social practices, often acting as negotiable guidelines rather than rigid principles. Recognizing peripheral values enhances cross-cultural understanding and facilitates social cohesion amidst diversity.
Core Values vs Peripheral Values: Key Differences
Core values represent the fundamental beliefs and principles that shape an organization's identity and guide decision-making, while peripheral values are more flexible and adaptive, often influenced by external factors and situational demands. Core values remain consistent over time, fostering a strong organizational culture and cohesiveness, whereas peripheral values can evolve to accommodate changing environments and diverse teams. Understanding the distinction between core and peripheral values helps in aligning strategic goals with cultural integrity and operational flexibility.
The Role of Core Values in Cultural Identity
Core values serve as the foundational principles that shape and sustain a culture's identity, providing a stable framework for collective beliefs and behaviors. They influence social norms, traditions, and decision-making processes by reflecting what a community deeply prioritizes over time. Peripheral values, while flexible and varying across groups, often adapt around these unchanging core values, reinforcing cultural continuity and resilience.
Influence of Peripheral Values on Social Norms
Peripheral values subtly shape social norms by introducing flexibility and innovation within cultural frameworks, often acting as catalysts for gradual change. While core values maintain societal stability and identity, peripheral values influence evolving attitudes and behaviors, reflecting adaptive responses to new social conditions. The dynamic interplay between core and peripheral values drives cultural transformation and social cohesion.
How Core Values Shape Group Behavior
Core values serve as the fundamental principles guiding a group's behavior, influencing decision-making, communication patterns, and conflict resolution. These intrinsic values create cohesion and a shared sense of identity, distinguishing the group from others. Peripheral values, in contrast, offer flexibility and adaptability but do not significantly alter the group's core behavioral framework.
The Evolution of Peripheral Values Over Time
Peripheral values shift significantly as societies evolve, reflecting changing social norms and external influences more than core values do. These values adapt to historical events, technological advancements, and intercultural exchanges, demonstrating flexibility in cultural identity. Over time, peripheral values often serve as indicators of societal transformation while core values remain stable and foundational to cultural continuity.
Conflicts Between Core and Peripheral Values
Core values represent the fundamental beliefs that guide behavior and decision-making within a culture, while peripheral values are more flexible and situational. Conflicts between core and peripheral values often arise when peripheral values challenge or undermine the integrity of core values, leading to social tension or identity crises. Understanding these conflicts is essential for managing cultural cohesion and addressing issues of adaptation and change within societies.
Preserving Core Values in a Globalized World
Preserving core values in a globalized world requires prioritizing fundamental cultural beliefs that define identity and social cohesion over peripheral values susceptible to change. Core values such as respect, family integrity, and community responsibility serve as anchors amid cultural diffusion and globalization pressures. Emphasizing these enduring principles helps maintain cultural uniqueness while adapting to global interconnectedness.
The Impact of Values on Cross-Cultural Interactions
Core values, deeply ingrained and universally prioritized within a culture, serve as the foundation for behavior and decision-making during cross-cultural interactions, influencing trust, communication styles, and conflict resolution. Peripheral values, more flexible and situational, may vary significantly between cultures and often shape everyday social norms and etiquette, affecting first impressions and casual exchanges. Understanding the distinction between core and peripheral values enables individuals and organizations to navigate cultural differences effectively, fostering respect and collaboration in global environments.
core values vs peripheral values Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com