The sender initiates communication by encoding and transmitting a message, while the receiver decodes and interprets it. Effective communication depends on clarity in the sender's message and active listening skills of the receiver. Feedback from the receiver helps ensure that the intended meaning is accurately understood.
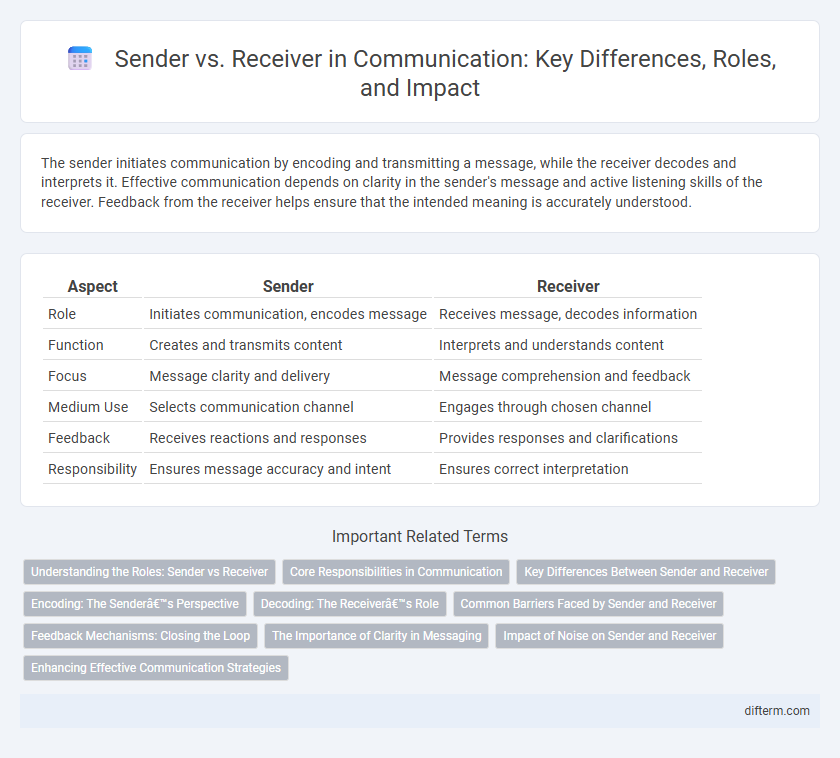
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sender | Receiver |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Initiates communication, encodes message | Receives message, decodes information |
| Function | Creates and transmits content | Interprets and understands content |
| Focus | Message clarity and delivery | Message comprehension and feedback |
| Medium Use | Selects communication channel | Engages through chosen channel |
| Feedback | Receives reactions and responses | Provides responses and clarifications |
| Responsibility | Ensures message accuracy and intent | Ensures correct interpretation |
Understanding the Roles: Sender vs Receiver
The sender initiates communication by encoding and transmitting a message using a chosen channel, while the receiver decodes and interprets the message to derive meaning. Effective communication depends on the sender's clarity and the receiver's ability to accurately understand, minimizing potential noise or misinterpretation. Understanding the distinct roles enhances message accuracy, feedback quality, and overall interaction success.
Core Responsibilities in Communication
The sender's core responsibility in communication is to encode clear, concise messages that effectively convey the intended information. The receiver's primary duty involves accurately decoding and interpreting the message to ensure mutual understanding. Both roles require active engagement to minimize miscommunication and enhance message clarity.
Key Differences Between Sender and Receiver
The sender initiates the communication by encoding and transmitting a message, while the receiver's role is to decode and interpret the message's content accurately. Senders control the message format and delivery channel, whereas receivers provide feedback that influences message clarity and understanding. Effective communication depends on the sender's clarity and the receiver's ability to comprehend and respond appropriately.
Encoding: The Sender’s Perspective
Encoding from the sender's perspective involves transforming thoughts into clear, concise messages using language and symbols tailored to the receiver's understanding. Effective encoding requires consideration of cultural context, tone, and medium to ensure the message's meaning is preserved and accurately interpreted. Misencoding can lead to misunderstandings, making the sender's skill in selecting appropriate words and formats crucial for successful communication.
Decoding: The Receiver’s Role
Decoding is the process by which the receiver interprets and makes sense of the sender's message, relying heavily on their cognitive skills and contextual understanding. Effective decoding requires the receiver to accurately translate symbols, language, or signals into meaningful information, minimizing misunderstandings. The receiver's background, experiences, and cultural context play crucial roles in how messages are perceived and understood during communication.
Common Barriers Faced by Sender and Receiver
Common barriers faced by both sender and receiver in communication include language differences, which cause misunderstandings and misinterpretations of messages. Psychological factors such as stress, emotions, or preconceived notions can distort the intended meaning and reduce message clarity. Physical distractions and environmental noise interfere with effective transmission and reception of information, lowering overall communication effectiveness.
Feedback Mechanisms: Closing the Loop
Feedback mechanisms are essential in communication, acting as the bridge that closes the loop between the sender and receiver. By providing timely responses, they ensure the message is understood correctly, allowing the sender to adjust or clarify as needed. Effective feedback enhances mutual understanding, promotes active engagement, and improves overall communication efficiency.
The Importance of Clarity in Messaging
Clarity in messaging ensures the sender's ideas are accurately interpreted by the receiver, minimizing misunderstandings and enhancing effective communication. Precise vocabulary, structured sentences, and unambiguous expressions contribute to clear messages, facilitating smoother information exchange. When the receiver clearly understands the intended message, engagement improves and the overall communication process becomes more efficient.
Impact of Noise on Sender and Receiver
Noise disrupts the accuracy of messages sent by the sender, leading to distorted information before it reaches the receiver. The receiver's ability to interpret the message correctly is compromised by various types of noise, such as physical, psychological, or semantic interference. Effective communication depends on minimizing noise to preserve the clarity and intent of the sender's original message.
Enhancing Effective Communication Strategies
Effective communication strategies prioritize the clarity and accuracy of the sender's message to minimize misunderstandings and ensure the intended meaning reaches the receiver. Active listening and feedback mechanisms empower the receiver to interpret and respond appropriately, fostering a two-way exchange that enhances mutual understanding. Leveraging nonverbal cues and context analysis further bridges communication gaps between sender and receiver, optimizing message delivery and reception.
sender vs receiver Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com