Mediated communication leverages technology to connect individuals across distances, enabling instant sharing of messages through text, video, or audio platforms. Face-to-face communication offers the advantage of direct interaction, allowing for richer nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, tone, and body language that enhance understanding and emotional connection. While mediated communication provides convenience and accessibility, face-to-face interactions often result in deeper rapport and more effective conflict resolution.
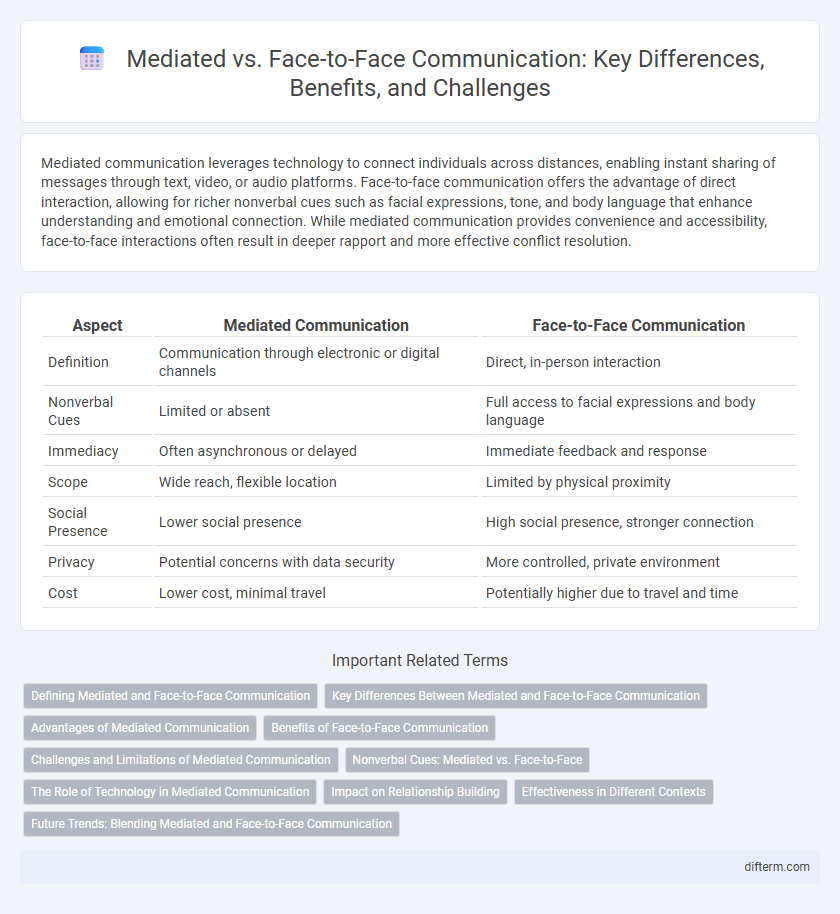
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mediated Communication | Face-to-Face Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Communication through electronic or digital channels | Direct, in-person interaction |
| Nonverbal Cues | Limited or absent | Full access to facial expressions and body language |
| Immediacy | Often asynchronous or delayed | Immediate feedback and response |
| Scope | Wide reach, flexible location | Limited by physical proximity |
| Social Presence | Lower social presence | High social presence, stronger connection |
| Privacy | Potential concerns with data security | More controlled, private environment |
| Cost | Lower cost, minimal travel | Potentially higher due to travel and time |
Defining Mediated and Face-to-Face Communication
Mediated communication involves exchanging messages through digital platforms, such as email, social media, and video calls, allowing interaction without physical presence. Face-to-face communication occurs in real-time, directly between individuals in the same physical space, enabling immediate feedback and nonverbal cue recognition. Understanding the differences between these modes is essential for effective interpersonal communication strategies.
Key Differences Between Mediated and Face-to-Face Communication
Mediated communication relies on technology such as phones, social media, or video conferencing, enabling interaction across distances but often lacking nonverbal cues present in face-to-face communication. Face-to-face interactions provide immediate feedback, rich emotional context, and body language, enhancing understanding and relationship-building. The absence of physical presence in mediated communication can lead to misunderstandings, but it offers flexibility and accessibility unavailable in traditional face-to-face settings.
Advantages of Mediated Communication
Mediated communication offers significant advantages such as increased accessibility, allowing individuals to connect across vast geographical distances in real-time through platforms like video calls and instant messaging. It provides enhanced convenience and flexibility by enabling asynchronous interactions, giving users control over response timing and reducing scheduling conflicts. Additionally, mediated communication supports multimodal data sharing, including text, images, and audio, enriching the communication experience beyond the limitations of face-to-face exchanges.
Benefits of Face-to-Face Communication
Face-to-face communication enhances nonverbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice, improving message clarity and emotional connection. This mode fosters trust and rapport more effectively than mediated communication by enabling immediate feedback and reducing misunderstandings. In professional and personal settings, the direct interaction of face-to-face conversation promotes stronger relationships and collaboration.
Challenges and Limitations of Mediated Communication
Mediated communication often faces challenges such as reduced nonverbal cues, which limits emotional expression and can lead to misunderstandings. Technological issues like connectivity problems and platform constraints further hinder message clarity and timeliness. The absence of immediate feedback in mediated interactions decreases conversational fluidity compared to face-to-face communication.
Nonverbal Cues: Mediated vs. Face-to-Face
Nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, body language, and eye contact play a crucial role in face-to-face communication by enhancing message clarity and emotional connection. Mediated communication, particularly through text-based platforms, often lacks these nonverbal signals, which can lead to misunderstandings or reduced emotional depth. Video calls partially restore nonverbal interaction, but subtle cues like microexpressions and physical gestures remain limited compared to in-person encounters.
The Role of Technology in Mediated Communication
Technology enhances mediated communication by enabling real-time interaction across vast distances through platforms like video calls, instant messaging, and social media, overcoming geographical barriers. Digital tools support diverse communication modalities, including text, audio, and visual content, enriching message clarity and emotional expression compared to traditional face-to-face interactions. The integration of AI-driven features such as chatbots and translation services further personalizes and streamlines mediated communication, optimizing user experience and connectivity.
Impact on Relationship Building
Mediated communication often limits nonverbal cues such as facial expressions and body language, which are essential for building trust and emotional connection in relationships. Face-to-face interactions allow for immediate feedback and richer social presence, enhancing empathy and understanding between participants. These differences result in mediated communication typically leading to less depth and slower development in relationship building compared to direct, in-person communication.
Effectiveness in Different Contexts
Mediated communication, such as emails and video calls, excels in contexts requiring documentation and asynchronous interaction, enhancing clarity and accessibility across distances. Face-to-face communication proves more effective in settings demanding immediate feedback, emotional nuance, and complex problem-solving due to real-time verbal and nonverbal cues. The choice between mediated and face-to-face communication depends on factors like urgency, message complexity, and relationship dynamics to maximize effectiveness in diverse professional and social contexts.
Future Trends: Blending Mediated and Face-to-Face Communication
Future communication trends emphasize the integration of mediated and face-to-face interactions, leveraging advancements in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to create immersive, hybrid environments. These technologies enable real-time, context-rich exchanges that maintain nonverbal cues, enhancing understanding and emotional connection. Organizations increasingly adopt these blended communication models to improve collaboration, flexibility, and inclusivity across geographically dispersed teams.
mediated vs face-to-face Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com