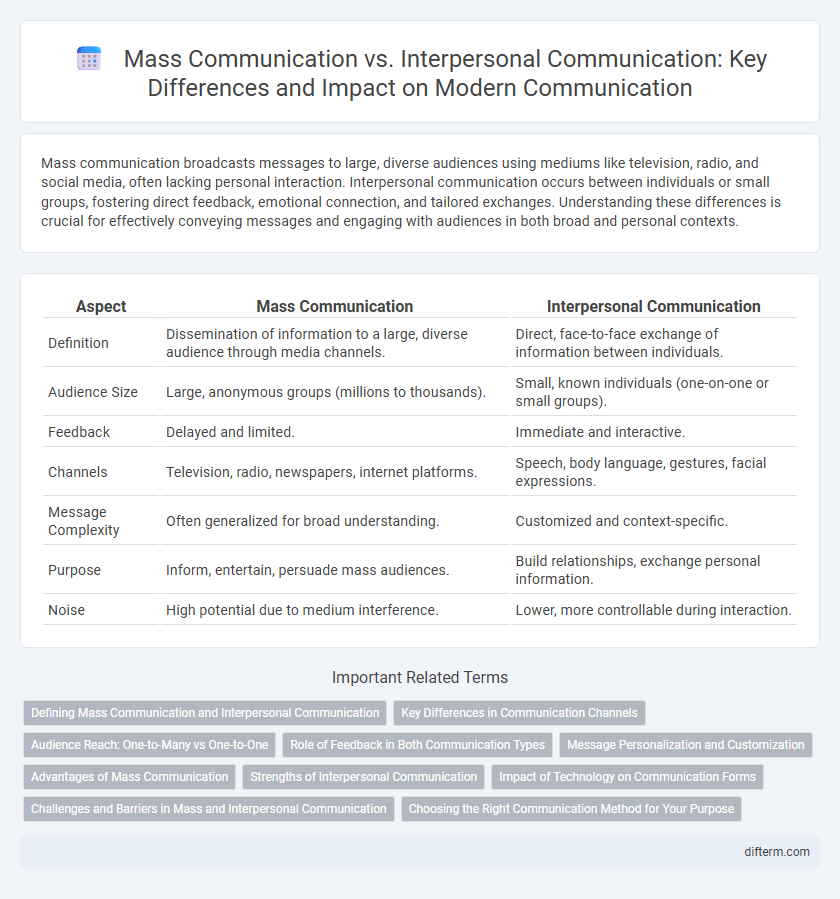
Mass communication broadcasts messages to large, diverse audiences using mediums like television, radio, and social media, often lacking personal interaction. Interpersonal communication occurs between individuals or small groups, fostering direct feedback, emotional connection, and tailored exchanges. Understanding these differences is crucial for effectively conveying messages and engaging with audiences in both broad and personal contexts.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mass Communication | Interpersonal Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dissemination of information to a large, diverse audience through media channels. | Direct, face-to-face exchange of information between individuals. |
| Audience Size | Large, anonymous groups (millions to thousands). | Small, known individuals (one-on-one or small groups). |
| Feedback | Delayed and limited. | Immediate and interactive. |
| Channels | Television, radio, newspapers, internet platforms. | Speech, body language, gestures, facial expressions. |
| Message Complexity | Often generalized for broad understanding. | Customized and context-specific. |
| Purpose | Inform, entertain, persuade mass audiences. | Build relationships, exchange personal information. |
| Noise | High potential due to medium interference. | Lower, more controllable during interaction. |
Defining Mass Communication and Interpersonal Communication
Mass communication involves the dissemination of information to large, diverse audiences through mediums such as television, radio, newspapers, and digital platforms, emphasizing one-to-many communication. Interpersonal communication refers to direct, face-to-face exchanges between individuals, characterized by personal interaction, feedback, and nonverbal cues. Understanding the distinctions between mass communication and interpersonal communication highlights differences in scale, channel, and interaction dynamics.
Key Differences in Communication Channels
Mass communication utilizes media platforms such as television, radio, and social networks to reach large, diverse audiences simultaneously, often resulting in one-way information flow. Interpersonal communication involves direct, face-to-face or digital interactions between individuals, allowing immediate feedback and personalized exchanges. The key differences in communication channels lie in the scale, interactivity, and feedback mechanisms, with mass communication favoring broad dissemination and interpersonal communication emphasizing intimate, two-way dialogue.
Audience Reach: One-to-Many vs One-to-One
Mass communication delivers messages from one sender to a large, diverse audience simultaneously through channels like television, radio, and social media, enabling widespread information dissemination. Interpersonal communication involves direct, face-to-face interaction between individuals, facilitating personalized, immediate feedback and deeper emotional connection. The distinction between one-to-many (mass communication) and one-to-one (interpersonal communication) defines their effectiveness based on audience reach and interaction quality.
Role of Feedback in Both Communication Types
Feedback in mass communication is typically delayed and indirect, limiting immediate adjustments and personalized responses, while in interpersonal communication, real-time feedback enables dynamic interaction and mutual understanding. The asynchronous nature of mass communication often leads to one-way information flow with limited audience engagement, contrasting with the continuous feedback loop that characterizes interpersonal exchanges. Effective feedback mechanisms in interpersonal communication foster trust and clarity, whereas mass communication relies on aggregated data and audience metrics to gauge effectiveness.
Message Personalization and Customization
Mass communication delivers standardized messages to broad audiences, limiting personalization and customization due to its one-to-many format. Interpersonal communication enables tailored messages based on individual preferences, feedback, and context, enhancing relevance and engagement. Effective communication strategies leverage personalization in interpersonal interactions to increase message impact and audience connection.
Advantages of Mass Communication
Mass communication enables the rapid dissemination of information to vast audiences, facilitating widespread awareness and education on critical issues. It offers cost-effective platforms such as television, radio, and social media to reach diverse demographic groups simultaneously. The ability to influence public opinion and promote cultural exchange on a large scale represents a significant advantage over interpersonal communication.
Strengths of Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication excels in fostering trust and emotional connection through direct, face-to-face interaction, enabling nuanced understanding via nonverbal cues such as facial expressions and tone of voice. It allows for immediate feedback and personalized messages, reducing misunderstandings and enhancing relationship building. Unlike mass communication, interpersonal communication adapts dynamically to the needs and reactions of individuals, promoting deeper engagement and effective problem-solving.
Impact of Technology on Communication Forms
Technology has revolutionized mass communication by enabling real-time information dissemination through digital platforms, social media, and broadcast networks, enhancing reach and immediacy. In contrast, interpersonal communication benefits from technological tools like video calls, instant messaging, and social media, which foster more personalized and context-rich interactions despite physical distances. The integration of AI-driven analytics further refines message targeting in mass media while enhancing contextual understanding in one-on-one communication, transforming how information is exchanged and perceived.
Challenges and Barriers in Mass and Interpersonal Communication
Mass communication faces challenges such as information distortion, limited feedback, and cultural differences that hinder message accuracy and audience engagement. Interpersonal communication struggles with barriers like emotional biases, language ambiguities, and physical distractions that reduce clarity and mutual understanding. Both communication types require overcoming noise and misinterpretation to ensure effective message transmission.
Choosing the Right Communication Method for Your Purpose
Selecting the appropriate communication method depends on the message's complexity and audience size; mass communication efficiently reaches large, diverse groups with generalized content, while interpersonal communication allows personalized, immediate feedback in more intimate settings. For real-time discussions or sensitive topics, interpersonal communication enhances understanding and relationship-building. When broadcasting information widely or shaping public opinion, mass communication delivers consistent messaging to vast audiences.
mass communication vs interpersonal communication Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com