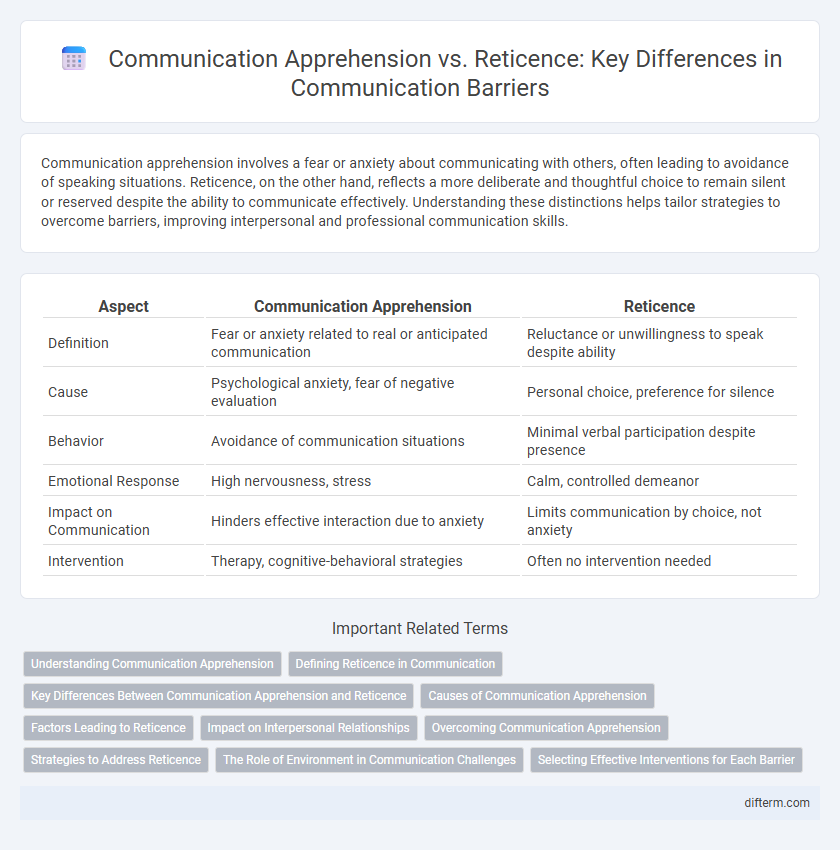
Communication apprehension involves a fear or anxiety about communicating with others, often leading to avoidance of speaking situations. Reticence, on the other hand, reflects a more deliberate and thoughtful choice to remain silent or reserved despite the ability to communicate effectively. Understanding these distinctions helps tailor strategies to overcome barriers, improving interpersonal and professional communication skills.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Communication Apprehension | Reticence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fear or anxiety related to real or anticipated communication | Reluctance or unwillingness to speak despite ability |
| Cause | Psychological anxiety, fear of negative evaluation | Personal choice, preference for silence |
| Behavior | Avoidance of communication situations | Minimal verbal participation despite presence |
| Emotional Response | High nervousness, stress | Calm, controlled demeanor |
| Impact on Communication | Hinders effective interaction due to anxiety | Limits communication by choice, not anxiety |
| Intervention | Therapy, cognitive-behavioral strategies | Often no intervention needed |
Understanding Communication Apprehension
Communication apprehension involves the fear or anxiety associated with either real or anticipated communication with others, often leading to avoidance behaviors. It is a psychological barrier that affects an individual's ability to express themselves clearly in public or group settings. Understanding communication apprehension requires recognizing its cognitive, affective, and behavioral components that influence how messages are sent and received.
Defining Reticence in Communication
Reticence in communication refers to an individual's deliberate choice to withhold verbal expression due to personal preference or situational factors rather than fear or anxiety. Unlike communication apprehension, which stems from anxiety about speaking, reticent individuals may simply prefer listening over speaking, exhibiting reluctance without distress. This distinction highlights reticence as a behavioral tendency characterized by silent engagement rather than avoidance caused by apprehension.
Key Differences Between Communication Apprehension and Reticence
Communication apprehension refers to the fear or anxiety experienced during communication situations, often manifesting as physical symptoms like sweating or trembling, whereas reticence is the deliberate choice to remain silent or avoid communication despite the absence of fear. Apprehension is typically rooted in psychological factors impacting an individual's willingness to engage, while reticence stems from personal preferences or social norms influencing communication behavior. Understanding these distinctions helps in designing targeted interventions for improving communication effectiveness in various contexts.
Causes of Communication Apprehension
Communication apprehension primarily stems from fear of negative evaluation, lack of communication skills, and previous negative experiences during interactions. Biological factors such as genetic predisposition and temperament also significantly contribute to heightened anxiety in communication settings. Environmental influences like unfamiliar audiences and high-pressure situations exacerbate the intensity of communication apprehension.
Factors Leading to Reticence
Communication reticence often stems from fear of negative evaluation, lack of confidence, and previous adverse communication experiences. Social anxiety and perceived communication skill deficits contribute significantly to an individual's reluctance to engage in conversations. Environmental factors, such as unsupportive audiences or high-stakes settings, further exacerbate reticence in communication contexts.
Impact on Interpersonal Relationships
Communication apprehension significantly hinders interpersonal relationships by creating anxiety that limits open expression and mutual understanding. Reticence, characterized by a deliberate choice to remain silent, may reduce conflict but often leads to misunderstandings and weakened emotional connections. Both behaviors impair effective exchange, but communication apprehension tends to evoke more distress, while reticence fosters emotional distance.
Overcoming Communication Apprehension
Overcoming communication apprehension requires targeted strategies such as systematic desensitization, cognitive restructuring, and skill enhancement through repeated practice and positive reinforcement. Research shows that gradual exposure to speaking situations coupled with anxiety management techniques significantly reduces the fear associated with public speaking. Building confidence through preparation and supportive feedback fosters effective communication and diminishes communication apprehension over time.
Strategies to Address Reticence
Communication apprehension involves fear or anxiety about communicating, while reticence refers to a deliberate choice to remain silent or withdrawn. Effective strategies to address reticence include creating a supportive environment that encourages open dialogue, promoting active listening to validate the speaker's perspective, and gradually increasing participation through small group discussions or one-on-one interactions. Tailoring interventions to individual comfort levels helps reduce communication barriers and fosters more confident expression.
The Role of Environment in Communication Challenges
Communication apprehension arises from an individual's anxiety about speaking in various environments, impacting their ability to convey messages effectively. Reticence, often linked to personal disposition, can be exacerbated by unsupportive or intimidating settings that inhibit participation. Understanding the role of environmental factors, such as audience size, setting formality, and perceived judgment, is crucial in addressing communication challenges and fostering more inclusive interactions.
Selecting Effective Interventions for Each Barrier
Communication apprehension requires interventions such as systematic desensitization, cognitive restructuring, and skills training to reduce anxiety and build confidence. Reticence, characterized by deliberate silence or social withdrawal, benefits from gradual exposure, encouragement of self-disclosure, and fostering supportive communication environments. Tailoring interventions to address the unique psychological and behavioral aspects of each barrier enhances overall communication effectiveness and personal growth.
communication apprehension vs reticence Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com