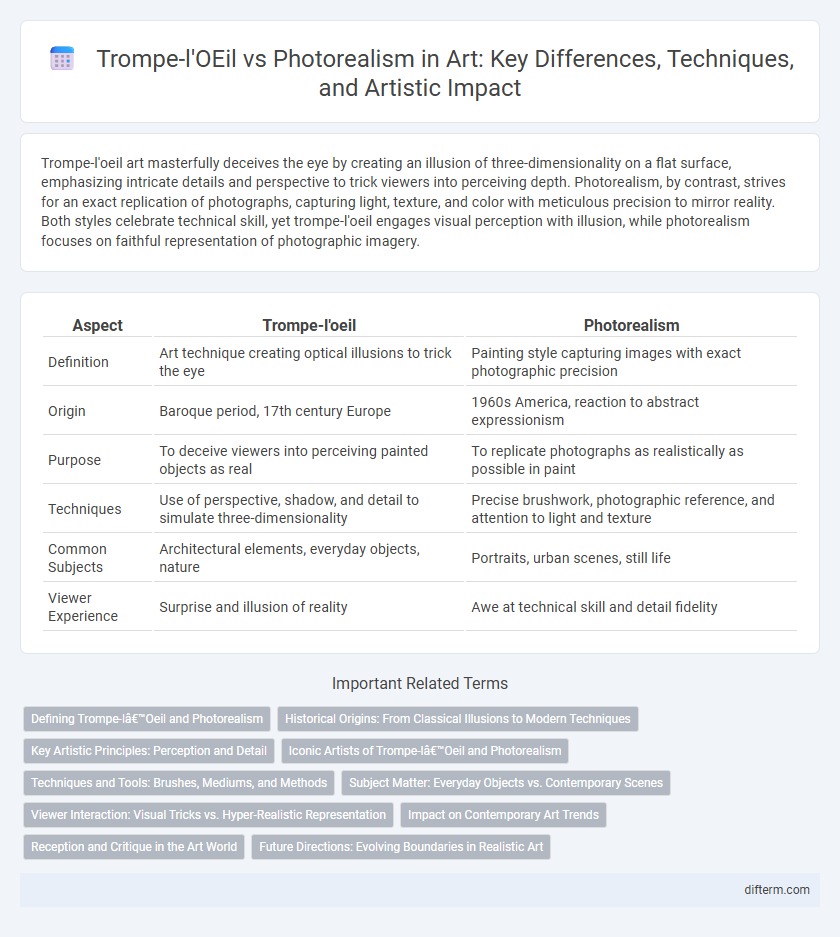
Trompe-l'oeil art masterfully deceives the eye by creating an illusion of three-dimensionality on a flat surface, emphasizing intricate details and perspective to trick viewers into perceiving depth. Photorealism, by contrast, strives for an exact replication of photographs, capturing light, texture, and color with meticulous precision to mirror reality. Both styles celebrate technical skill, yet trompe-l'oeil engages visual perception with illusion, while photorealism focuses on faithful representation of photographic imagery.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Trompe-l'oeil | Photorealism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art technique creating optical illusions to trick the eye | Painting style capturing images with exact photographic precision |
| Origin | Baroque period, 17th century Europe | 1960s America, reaction to abstract expressionism |
| Purpose | To deceive viewers into perceiving painted objects as real | To replicate photographs as realistically as possible in paint |
| Techniques | Use of perspective, shadow, and detail to simulate three-dimensionality | Precise brushwork, photographic reference, and attention to light and texture |
| Common Subjects | Architectural elements, everyday objects, nature | Portraits, urban scenes, still life |
| Viewer Experience | Surprise and illusion of reality | Awe at technical skill and detail fidelity |
Defining Trompe-l’Oeil and Photorealism
Trompe-l'oeil is an artistic technique that creates the optical illusion of three-dimensionality by meticulously rendering objects to trick the viewer's eye into perceiving painted detail as tangible reality. Photorealism, originating in the late 1960s, involves painting highly detailed imagery that closely resembles high-resolution photographs, emphasizing precision and surface texture to replicate photographic effects. Both styles challenge perceptions of reality, but trompe-l'oeil focuses on illusionistic spatial deception, while photorealism emphasizes faithful photographic replication.
Historical Origins: From Classical Illusions to Modern Techniques
Trompe-l'oeil originated in ancient Greece and Rome, using meticulous perspective and shadow to create optical illusions that trick the eye into perceiving painted details as three-dimensional objects. Photorealism emerged in the late 1960s as a reaction to abstract expressionism, employing photographic techniques and airbrushing to achieve hyper-detailed, lifelike images that mimic high-resolution photos. Both styles emphasize intense visual realism but differ in their historical contexts and methods, with trompe-l'oeil rooted in classical illusionism and photorealism grounded in modern technology and media.
Key Artistic Principles: Perception and Detail
Trompe-l'oeil masterfully exploits perception by creating an optical illusion that deceives viewers into believing painted objects exist in three-dimensional space, emphasizing meticulous detail to achieve this effect. Photorealism focuses on replicating photographic detail with precision, capturing surface textures, light reflections, and intricate nuances to evoke realism. Both art forms prioritize detail but diverge in intent: trompe-l'oeil manipulates spatial perception, while photorealism aims for faithful representation of visual reality.
Iconic Artists of Trompe-l’Oeil and Photorealism
Iconic artists of trompe-l'oeil such as Giovanni Battista Piranesi and William Harnett masterfully created illusions that deceive the viewer's eye by rendering objects with hyper-realistic detail and spatial depth. In photorealism, prominent figures like Chuck Close and Ralph Goings emphasize meticulous, camera-like precision to replicate photographs on canvas with extraordinary accuracy. Both movements highlight different artistic approaches to realism, where trompe-l'oeil focuses on three-dimensional illusion and photorealism strives for photographic exactness.
Techniques and Tools: Brushes, Mediums, and Methods
Trompe-l'oeil employs meticulous layering and glazing techniques using fine brushes and oil mediums to create an illusion of three-dimensionality on flat surfaces. Photorealism relies on airbrushes, photographic references, and sometimes digital tools to achieve precise detail and smooth gradients that mimic high-resolution photographs. Both genres demand mastery of brush control and surface preparation, yet trompe-l'oeil emphasizes texture and depth, while photorealism prioritizes exact replication of light and shadow effects.
Subject Matter: Everyday Objects vs. Contemporary Scenes
Trompe-l'oeil art centers on meticulously painted everyday objects designed to deceive the viewer's eye through hyper-realistic detail and precise perspective. Photorealism, however, captures contemporary scenes with photographic accuracy, emphasizing urban environments, people, and modern life moments. The contrast lies in trompe-l'oeil's focus on individual objects as illusions, while photorealism portrays broader narrative contexts within contemporary settings.
Viewer Interaction: Visual Tricks vs. Hyper-Realistic Representation
Trompe-l'oeil captivates viewers through visual tricks that create optical illusions, making two-dimensional surfaces appear three-dimensional and encouraging active perception to distinguish reality from artifice. Photorealism offers hyper-realistic representation, immersing viewers in meticulously detailed scenes that mimic high-resolution photographs, fostering an appreciation of technical precision and authenticity. Both styles engage audiences differently: trompe-l'oeil challenges perceptual boundaries, while photorealism emphasizes accurate imitation of the visual world.
Impact on Contemporary Art Trends
Trompe-l'oeil challenges viewers by creating optical illusions that blur reality and art, influencing contemporary artists to explore perception and spatial deception. Photorealism emphasizes meticulous detail and accuracy, pushing the boundaries of technical skill and redefining realism in modern art. Both movements have deeply impacted contemporary art trends by inspiring hybridity in visual experiences and elevating the dialogue on authenticity and representation.
Reception and Critique in the Art World
Trompe-l'oeil garners acclaim for its extraordinary illusionistic skill, often praised for challenging viewers' perception and engaging them in a visual puzzle that blurs reality and artifice. Photorealism receives mixed critiques, with admirers lauding its meticulous attention to detail and technical prowess, while detractors argue it sometimes lacks emotional depth or conceptual innovation compared to other contemporary art movements. The art world debates both genres' contributions to visual culture, emphasizing trompe-l'oeil's historical roots and photorealism's commentary on media saturation and photographic influence.
Future Directions: Evolving Boundaries in Realistic Art
Trompe-l'oeil and photorealism continue to push the boundaries of visual perception by integrating emerging technologies such as augmented reality and AI-driven image synthesis. These advancements enable artists to create immersive, hyper-realistic experiences that blur the lines between illusion and reality, challenging traditional definitions of authenticity in art. Future directions emphasize dynamic interactions and multisensory engagement, expanding realistic art beyond static visual representation into experiential realms.
trompe-l’oeil vs photorealism Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com