Pigments are solid, finely ground particles that provide color by reflecting light and are typically insoluble in the medium, making them ideal for use in paints and coatings due to their durability and lightfastness. Dyes, on the other hand, are soluble substances that chemically bond with the material they color, resulting in vibrant hues but often less resistance to fading and environmental wear. Understanding the distinct properties of pigments versus dyes is essential for artists seeking specific effects and longevity in their artworks.
Table of Comparison
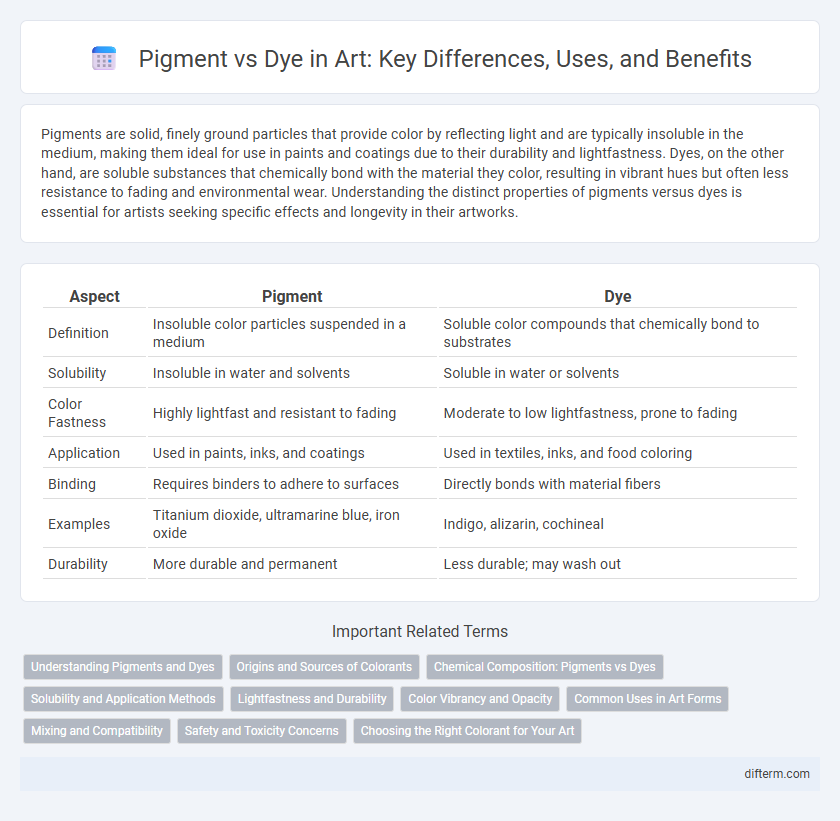
| Aspect | Pigment | Dye |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Insoluble color particles suspended in a medium | Soluble color compounds that chemically bond to substrates |
| Solubility | Insoluble in water and solvents | Soluble in water or solvents |
| Color Fastness | Highly lightfast and resistant to fading | Moderate to low lightfastness, prone to fading |
| Application | Used in paints, inks, and coatings | Used in textiles, inks, and food coloring |
| Binding | Requires binders to adhere to surfaces | Directly bonds with material fibers |
| Examples | Titanium dioxide, ultramarine blue, iron oxide | Indigo, alizarin, cochineal |
| Durability | More durable and permanent | Less durable; may wash out |
Understanding Pigments and Dyes
Pigments are finely ground particles that provide color by reflecting specific wavelengths of light and are insoluble in their medium, making them ideal for use in paints and coatings due to their permanence and opacity. Dyes, on the other hand, are soluble substances that chemically bond with the material they color, offering vibrant hues but often less lightfastness compared to pigments. Understanding the distinct properties of pigments and dyes is crucial for artists and manufacturers to select appropriate materials for desired color effects and durability in artworks.
Origins and Sources of Colorants
Pigments originate from naturally occurring minerals, earths, and synthetic compounds that provide opacity and permanence to artworks, often sourced from substances like ochre, ultramarine, and titanium dioxide. Dyes derive from organic materials such as plants, insects, and mollusks, including indigo, cochineal, and tyrian purple, which absorb into fibers for vivid, transparent coloration. The distinction between pigments and dyes lies in their molecular structure and light interaction, affecting their application and durability in artistic mediums.
Chemical Composition: Pigments vs Dyes
Pigments consist of insoluble particles made from minerals or synthetic compounds that provide color by reflecting light, whereas dyes are typically organic molecules that dissolve in a medium and impart color through absorption. The chemical composition of pigments includes stable, inorganic compounds such as titanium dioxide or iron oxide, making them more resistant to fading and chemical reactions. Dyes, composed mainly of complex carbon-based molecules like azo or anthraquinone structures, are more susceptible to degradation due to their solubility and interaction with fibers or surfaces.
Solubility and Application Methods
Pigments are insoluble particles that remain suspended in a medium, providing opacity and durability when applied in materials like paint or ink. Dyes, in contrast, dissolve completely in a solvent, penetrating the substrate to impart vibrant, translucent color ideal for textiles and inks. The differences in solubility dictate application methods, with pigments requiring binders for adhesion and dyes relying on chemical or physical bonding during fabric dyeing processes.
Lightfastness and Durability
Pigments provide superior lightfastness and durability compared to dyes, making them ideal for long-lasting artwork exposed to sunlight. While dyes tend to fade quickly due to their water-soluble molecular structure, pigments consist of insoluble particles that remain stable and retain color vibrancy over time. High-quality artist pigments, such as cadmium red and ultramarine blue, are renowned for their resistance to UV degradation and chemical breakdown.
Color Vibrancy and Opacity
Pigments offer superior color vibrancy and opacity due to their particulate nature, which allows them to reflect more light and provide richer, more saturated hues. Unlike dyes, pigments do not dissolve but rather suspend in a medium, resulting in better coverage and less translucency on surfaces. This makes pigments ideal for artwork requiring intense, long-lasting color with high opacity.
Common Uses in Art Forms
Pigments are commonly used in painting, sculpture, and printmaking due to their opacity and durability, providing vibrant, long-lasting colors in mediums like oil, acrylic, and watercolor. Dyes are frequently utilized in textile art, fabric design, and paper-based crafts because they penetrate fibers for rich, translucent hues and enhanced colorfastness. Both pigments and dyes play essential roles in mixed media and contemporary art, adapting to various surfaces and artistic techniques.
Mixing and Compatibility
Pigments and dyes differ significantly in their mixing properties and compatibility with mediums; pigments are finely ground solid particles that remain suspended in binders, ensuring better stability and opacity in paint mixtures. Dyes, being soluble substances, dissolve within solvents and often exhibit superior color intensity but can suffer from lower lightfastness and bleed when mixed. Compatibility with various mediums like oil, acrylic, or watercolor depends on the pigment's inertness and particle size, while dyes require careful solvent selection to prevent separation or fading in artistic applications.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Pigments are generally safer than dyes due to their insoluble nature, which reduces skin absorption and toxicity risks in art materials. Many dyes contain synthetic chemicals or heavy metals that pose higher toxicity and allergen hazards when inhaled or ingested. Proper ventilation and protective equipment are essential when handling any art pigment or dye to minimize health risks associated with toxic compounds.
Choosing the Right Colorant for Your Art
Pigments provide excellent lightfastness and opacity, making them ideal for artworks requiring longevity and vibrancy. Dyes, while offering intense and transparent colors, often lack permanence and can fade over time when exposed to light. Understanding the chemical composition and intended use of pigments versus dyes is crucial for artists aiming to achieve desired colorfastness and texture in their creations.
pigment vs dye Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com