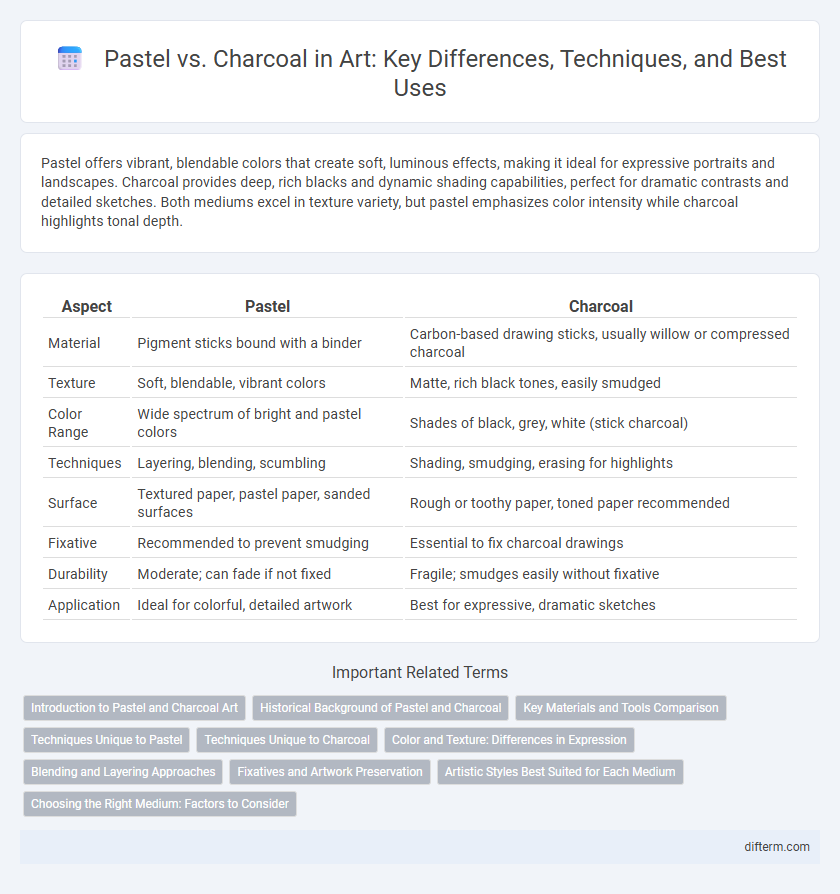
Pastel offers vibrant, blendable colors that create soft, luminous effects, making it ideal for expressive portraits and landscapes. Charcoal provides deep, rich blacks and dynamic shading capabilities, perfect for dramatic contrasts and detailed sketches. Both mediums excel in texture variety, but pastel emphasizes color intensity while charcoal highlights tonal depth.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pastel | Charcoal |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Pigment sticks bound with a binder | Carbon-based drawing sticks, usually willow or compressed charcoal |
| Texture | Soft, blendable, vibrant colors | Matte, rich black tones, easily smudged |
| Color Range | Wide spectrum of bright and pastel colors | Shades of black, grey, white (stick charcoal) |
| Techniques | Layering, blending, scumbling | Shading, smudging, erasing for highlights |
| Surface | Textured paper, pastel paper, sanded surfaces | Rough or toothy paper, toned paper recommended |
| Fixative | Recommended to prevent smudging | Essential to fix charcoal drawings |
| Durability | Moderate; can fade if not fixed | Fragile; smudges easily without fixative |
| Application | Ideal for colorful, detailed artwork | Best for expressive, dramatic sketches |
Introduction to Pastel and Charcoal Art
Pastel and charcoal are versatile media in fine art, each offering unique textures and expressive qualities. Pastels provide vibrant, blendable pigments ideal for rich color layering and smooth transitions, while charcoal delivers bold, intense blacks and soft grays suited for dramatic contrasts and detailed shading. Both materials excel in figure drawing and portraiture, enabling artists to achieve depth and emotion through varied pressure and stroke techniques.
Historical Background of Pastel and Charcoal
Pastels originated in the 15th century, prized by Renaissance artists like Leonardo da Vinci for their vibrant pigments and ease of blending, allowing delicate color transitions and detailed work. Charcoal, dating back to prehistoric times, was among the first drawing materials used by humans, valued for its deep blacks and expressive, bold strokes seen in ancient cave paintings such as those at Lascaux. Both mediums have historically influenced artistic techniques, with pastels often associated with soft, luminous portraits and charcoal favored for dynamic, high-contrast sketches.
Key Materials and Tools Comparison
Pastel and charcoal art both utilize distinct materials that influence texture and color vibrancy, with pastels composed of pigment and a binder creating bright, blendable strokes, while charcoal is made from burnt wood offering deep blacks and a matte finish. Tools for pastels typically include soft, hard, and oil variants along with blending stumps and fixatives for layering and preserving work, whereas charcoal artists rely on vine, compressed charcoal sticks, erasers, and blending tools to manipulate shading and contrast. The choice between pastels and charcoal affects the artistic outcome through differences in material composition, ease of blending, and the achievable tonal range.
Techniques Unique to Pastel
Pastel techniques emphasize blending and layering vibrant pigments directly on paper, allowing artists to achieve smooth gradients and subtle color transitions unique to this medium. Unlike charcoal, pastel enables rich color saturation with minimal smudging, often employing tools such as fingers, blending stumps, or soft cloth to create soft edges and delicate textures. The dry, powdery consistency of pastel facilitates techniques like scumbling and feathering, which contribute to its distinct luminous quality in artwork.
Techniques Unique to Charcoal
Charcoal enables artists to achieve deep, velvety blacks and a wide range of tonal values through blending and layering that are difficult to replicate with pastels. Its friable nature allows for expressive, textured strokes and effortless smudging, creating dynamic contrast and atmospheric depth. Techniques unique to charcoal include subtractive drawing, where artists erase highlights for dramatic effects, and the use of compressed versus vine charcoal for varied hardness and shading precision.
Color and Texture: Differences in Expression
Pastel offers vibrant, rich colors with a smooth, blendable texture that creates soft transitions and luminous effects, ideal for capturing delicate light and vibrant scenes. Charcoal provides deep, intense blacks and a rough, grainy texture, lending dramatic contrasts and expressive, bold strokes perfect for dynamic and moody compositions. The choice between pastel and charcoal significantly influences the artwork's emotional tone and visual depth through their distinct color qualities and tactile surfaces.
Blending and Layering Approaches
Pastels offer smooth blending with a soft, velvety texture that allows for seamless color transitions, making them ideal for subtle gradients and delicate shading. Charcoal, on the other hand, excels in layering through bold, expressive marks and rich tonal contrasts, providing depth and intensity to compositions. The powdery nature of both media supports smudging, but pastel tends to retain vibrant hues, whereas charcoal layers often build dramatic shadows and highlights.
Fixatives and Artwork Preservation
Charcoal artworks benefit significantly from fixatives, which prevent smudging and preserve the integrity of the pigment on paper, ensuring longevity and vibrancy over time. Pastel fixatives are formulated to maintain the delicate texture and colors without altering the artwork's matte finish or brightness, protecting the fragile pastel particles from environmental damage. Using quality fixatives designed specifically for charcoal or pastel is essential for long-term preservation, preventing deterioration caused by handling, moisture, and dust.
Artistic Styles Best Suited for Each Medium
Pastel excels in creating vibrant, soft transitions ideal for impressionistic and portrait art, allowing artists to blend colors smoothly for delicate skin tones and atmospheric effects. Charcoal lends itself to expressive, bold lines and deep contrasts, making it well-suited for dramatic sketches, figure drawing, and chiaroscuro techniques that emphasize light and shadow. Both mediums support distinct artistic styles, with pastel favoring subtle color modulation and charcoal emphasizing strong textural dynamics.
Choosing the Right Medium: Factors to Consider
Choosing between pastel and charcoal depends on desired texture and blending capabilities, with pastels offering vibrant color intensity and smooth transitions, while charcoal provides deep, rich blacks and expressive lines. Artists should consider the permanence and fixative requirements; pastels are more stable when fixed, whereas charcoal may smudge easily without proper sealing. The subject matter and style also influence the choice, as pastels suit soft, colorful portraits, and charcoal excels in dramatic, monochromatic sketches.
pastel vs charcoal Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com