Film photography captures images with a rich, organic texture and unique grain that digital cameras often struggle to replicate, offering an artistic depth prized by enthusiasts. Digital photography provides instant feedback, extensive editing possibilities, and greater convenience, making it a favored choice for modern pet portraits. Both methods hold distinct aesthetic values, influencing how the personality and character of pets are artistically portrayed.
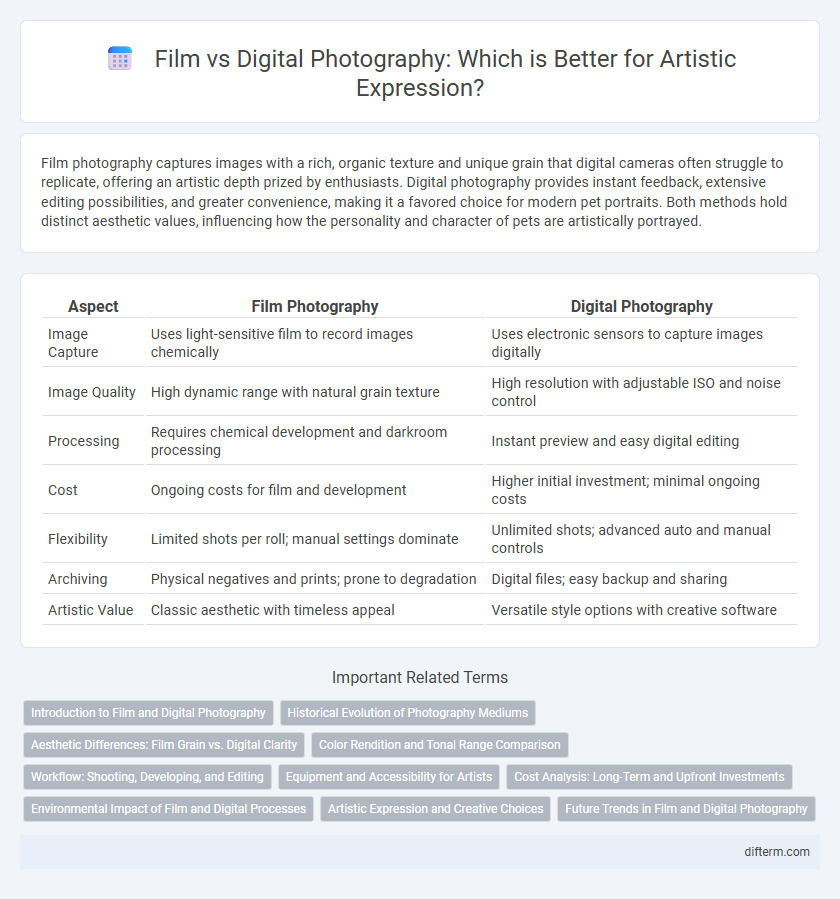
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Film Photography | Digital Photography |
|---|---|---|
| Image Capture | Uses light-sensitive film to record images chemically | Uses electronic sensors to capture images digitally |
| Image Quality | High dynamic range with natural grain texture | High resolution with adjustable ISO and noise control |
| Processing | Requires chemical development and darkroom processing | Instant preview and easy digital editing |
| Cost | Ongoing costs for film and development | Higher initial investment; minimal ongoing costs |
| Flexibility | Limited shots per roll; manual settings dominate | Unlimited shots; advanced auto and manual controls |
| Archiving | Physical negatives and prints; prone to degradation | Digital files; easy backup and sharing |
| Artistic Value | Classic aesthetic with timeless appeal | Versatile style options with creative software |
Introduction to Film and Digital Photography
Film photography captures images using chemical-coated film that reacts to light, producing tangible negatives or slides which require developing and printing processes. Digital photography employs electronic sensors to record images as digital files, enabling instant review, editing, and sharing without physical development. Both mediums influence artistic expression, with film offering a distinct grain and tonal quality, while digital provides versatility and convenience for contemporary visual storytelling.
Historical Evolution of Photography Mediums
Film photography emerged in the late 19th century, revolutionizing visual documentation with its chemical process and physical negatives, dominating the art and commercial sectors for over a century. The digital photography era began in the late 20th century, leveraging semiconductor sensors and digital storage to enable instant image review and manipulation, rapidly becoming the preferred medium worldwide. The historical evolution reflects shifts in technology, accessibility, and artistic expression, with each medium influencing photographic style, technique, and cultural impact distinctly.
Aesthetic Differences: Film Grain vs. Digital Clarity
Film photography offers a distinctive aesthetic characterized by organic film grain, which adds texture and a nostalgic ambiance to images. In contrast, digital photography emphasizes sharp clarity and detail, producing cleaner, more precise visuals without the natural imperfections found in film. The choice between film grain and digital clarity significantly influences artistic expression, mood, and the emotional impact of photographic works.
Color Rendition and Tonal Range Comparison
Film photography typically offers a richer, more nuanced color rendition with a natural warmth and subtle gradations that appeal to artists aiming for a classic aesthetic. Digital photography excels in capturing a broader tonal range with higher dynamic flexibility, enabling precise adjustments in post-processing to enhance color vibrancy and contrast. The choice between film and digital often hinges on whether the desired outcome favors the organic texture and depth of film or the technical precision and versatility of digital imaging.
Workflow: Shooting, Developing, and Editing
Film photography demands a slower, more deliberate workflow, involving manual shooting, chemical development, and physical editing through techniques like dodging and burning in the darkroom. Digital photography streamlines the process with instant image capture, rapid post-processing using software like Adobe Lightroom, and flexible non-destructive editing options. Workflow efficiency in digital photography allows photographers to experiment freely and iterate quickly, while film emphasizes craftsmanship and tactile control from exposure to print.
Equipment and Accessibility for Artists
Film photography relies on analog cameras, film rolls, and darkroom equipment, requiring artists to master manual settings and chemical development processes. Digital photography utilizes electronic sensors, memory cards, and computer software, offering instant image review and easier editing, which broadens accessibility for artists at various skill levels. The cost and availability of film materials and processing labs often pose barriers, while digital technology continues to become more affordable and widely accessible.
Cost Analysis: Long-Term and Upfront Investments
Film photography involves higher upfront costs due to the need for purchasing film rolls and developing chemicals, alongside ongoing expenses for processing and scanning. Digital photography requires a significant initial investment in camera equipment and storage devices, but offers lower long-term costs since images can be edited and stored without physical materials. Over time, digital photography provides cost efficiency through reusable memory cards and software updates, contrasting with the recurring expenses typical in film development.
Environmental Impact of Film and Digital Processes
Film photography generates significant environmental waste through chemical processing, including hazardous silver and developer chemicals that require careful disposal to prevent soil and water contamination. Digital photography reduces chemical use but involves electronic waste from devices and energy consumption during manufacturing and data storage, contributing to carbon emissions. Sustainable practices in both mediums, such as recycling film materials and using energy-efficient digital equipment, can mitigate their environmental footprints.
Artistic Expression and Creative Choices
Film photography offers a tactile, grain-rich aesthetic that encourages deliberate composition and mastery of light, fostering unique analog textures difficult to replicate digitally. Digital photography provides instant feedback and extensive post-processing flexibility, enabling artists to experiment with color manipulation, exposure adjustments, and creative effects in real-time. Both mediums empower photographers to express vision and emotion, but film emphasizes process and unpredictability while digital prioritizes versatility and precision.
Future Trends in Film and Digital Photography
Future trends in film photography indicate a resurgence driven by nostalgia and analog aesthetics, with artists and collectors valuing the unique grain and color rendition of film. Digital photography continues to evolve rapidly through advancements in sensor technology, AI-powered image processing, and enhanced connectivity for instant sharing and editing. Hybrid approaches integrating film's tactile qualities with digital enhancements are emerging, blending traditional techniques with cutting-edge innovations to appeal to a diverse creative audience.
Film Photography vs Digital Photography Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com