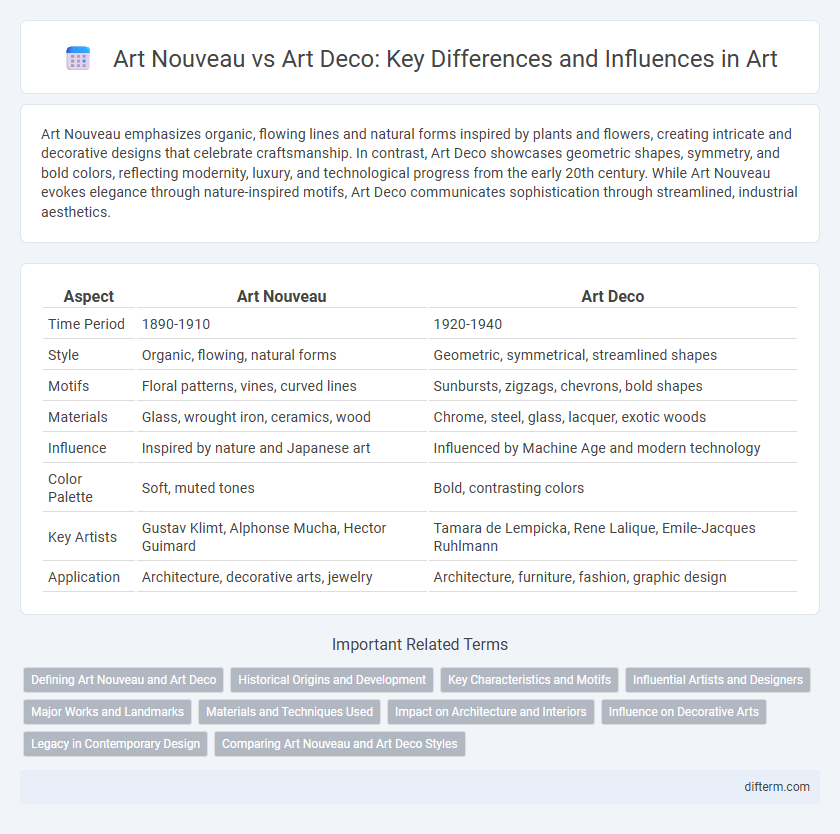
Art Nouveau emphasizes organic, flowing lines and natural forms inspired by plants and flowers, creating intricate and decorative designs that celebrate craftsmanship. In contrast, Art Deco showcases geometric shapes, symmetry, and bold colors, reflecting modernity, luxury, and technological progress from the early 20th century. While Art Nouveau evokes elegance through nature-inspired motifs, Art Deco communicates sophistication through streamlined, industrial aesthetics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Art Nouveau | Art Deco |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | 1890-1910 | 1920-1940 |
| Style | Organic, flowing, natural forms | Geometric, symmetrical, streamlined shapes |
| Motifs | Floral patterns, vines, curved lines | Sunbursts, zigzags, chevrons, bold shapes |
| Materials | Glass, wrought iron, ceramics, wood | Chrome, steel, glass, lacquer, exotic woods |
| Influence | Inspired by nature and Japanese art | Influenced by Machine Age and modern technology |
| Color Palette | Soft, muted tones | Bold, contrasting colors |
| Key Artists | Gustav Klimt, Alphonse Mucha, Hector Guimard | Tamara de Lempicka, Rene Lalique, Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann |
| Application | Architecture, decorative arts, jewelry | Architecture, furniture, fashion, graphic design |
Defining Art Nouveau and Art Deco
Art Nouveau emphasizes organic, flowing lines inspired by natural forms, featuring intricate floral patterns and asymmetrical shapes that create a decorative, elaborate aesthetic. Art Deco contrasts this with streamlined, geometric designs, bold colors, and symmetrical patterns reflecting modernity and luxury from the 1920s and 1930s. Both movements influenced architecture, jewelry, and graphic design, but Art Nouveau showcases fluidity and nature, while Art Deco highlights industrial elegance and symmetry.
Historical Origins and Development
Art Nouveau originated in the late 19th century, emerging primarily in Europe as a reaction against academic art and industrialization, characterized by organic, flowing lines inspired by natural forms. In contrast, Art Deco developed in the 1920s and 1930s, reflecting the era's fascination with modernity, technology, and luxury through geometric shapes, symmetry, and bold colors. Both movements significantly influenced decorative arts, architecture, and design, with Art Nouveau emphasizing craftsmanship and Art Deco embracing industrial materials and streamlined aesthetics.
Key Characteristics and Motifs
Art Nouveau features organic, flowing lines inspired by natural forms such as plants and flowers, emphasizing intricate, asymmetrical designs with curves and whiplash patterns. Art Deco contrasts with strong geometric shapes, symmetry, and streamlined forms, incorporating motifs like sunbursts, zigzags, and stylized floral elements often rendered in metallic finishes. Both movements reflect their era's cultural shifts, with Art Nouveau focused on craftsmanship and nature, while Art Deco embraces modernity and luxury.
Influential Artists and Designers
Art Nouveau, characterized by flowing lines and organic motifs, prominently featured influential artists like Gustav Klimt and designers such as Hector Guimard, who revolutionized architectural ornamentation. In contrast, Art Deco emphasized geometric shapes and modern materials, with notable figures including Tamara de Lempicka and Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann, pioneers in painting and furniture design respectively. Both movements significantly shaped 20th-century art and design, reflecting distinct cultural and technological shifts.
Major Works and Landmarks
Art Nouveau is characterized by organic, flowing lines and is exemplified by landmarks like Antoni Gaudi's Sagrada Familia and Hector Guimard's Paris Metro entrances. In contrast, Art Deco features geometric shapes and luxurious materials, with iconic works including the Chrysler Building in New York and the Palais de Chaillot in Paris. Both styles represent distinct eras of design, with Art Nouveau flourishing around 1890-1910 and Art Deco dominating the 1920s-1940s.
Materials and Techniques Used
Art Nouveau utilizes organic materials such as wood, glass, and wrought iron, emphasizing handcrafting techniques like intricate carving, stained glass work, and flowing, natural forms. In contrast, Art Deco incorporates industrial materials including chrome, stainless steel, and plastic, with techniques focusing on geometric patterns, streamlined shapes, and mass production methods like machine stamping and inlay work. These differences highlight Art Nouveau's artisanal craftsmanship versus Art Deco's embrace of modernity and mechanization.
Impact on Architecture and Interiors
Art Nouveau's organic lines and natural motifs transformed architecture and interiors by emphasizing fluidity and artisanal detail, creating spaces that felt immersive and ornamental. In contrast, Art Deco introduced a sleek, geometric approach characterized by bold symmetry, luxurious materials, and streamlined forms that reflected modernity and industrial progress in buildings and interior design. Both movements profoundly influenced 20th-century aesthetics, with Art Nouveau inspiring intricate craftsmanship and Art Deco promoting elegant, functional opulence.
Influence on Decorative Arts
Art Nouveau emphasizes organic, flowing lines and natural forms, influencing decorative arts with intricate floral motifs and sinuous curves in furniture, ceramics, and glassware. Art Deco, contrastingly, embraces geometric shapes, symmetry, and bold colors, shaping decorative arts through streamlined designs and luxurious materials like chrome, lacquer, and inlaid wood. These distinct styles profoundly impacted 20th-century decorative arts, reflecting cultural shifts from romanticism to modernity.
Legacy in Contemporary Design
Art Nouveau's organic forms and intricate details influence contemporary architecture and jewelry, emphasizing natural motifs and handcrafted aesthetics. Art Deco's geometric shapes and bold symmetry inspire modern graphic design and fashion, highlighting luxury and technological progress. Together, these styles shape a dynamic visual language that continues to redefine trends in interior design and urban landscapes.
Comparing Art Nouveau and Art Deco Styles
Art Nouveau features organic, flowing lines inspired by natural forms, emphasizing intricate floral patterns and asymmetry, while Art Deco embraces geometric shapes, bold colors, and streamlined symmetry, reflecting industrial progress and modernity. Both styles influenced architecture, interior design, and decorative arts during the early 20th century, but Art Nouveau emerged around the 1890s with a more romantic aesthetic, whereas Art Deco peaked in the 1920s and 1930s, showcasing luxury and exuberance. The contrast between Art Nouveau's fluid curves and Art Deco's angular motifs signifies the cultural transition from handcrafted elegance to machine-age sophistication.
art nouveau vs art deco Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com