Appropriation in art involves borrowing elements from existing works often without permission, raising questions about originality and ethical boundaries. Homage, unlike appropriation, respectfully acknowledges and celebrates the influence of another artist or style, creating a dialogue between past and present. Understanding the distinction helps viewers appreciate the intent behind artistic creations and the cultural conversations they provoke.
Table of Comparison
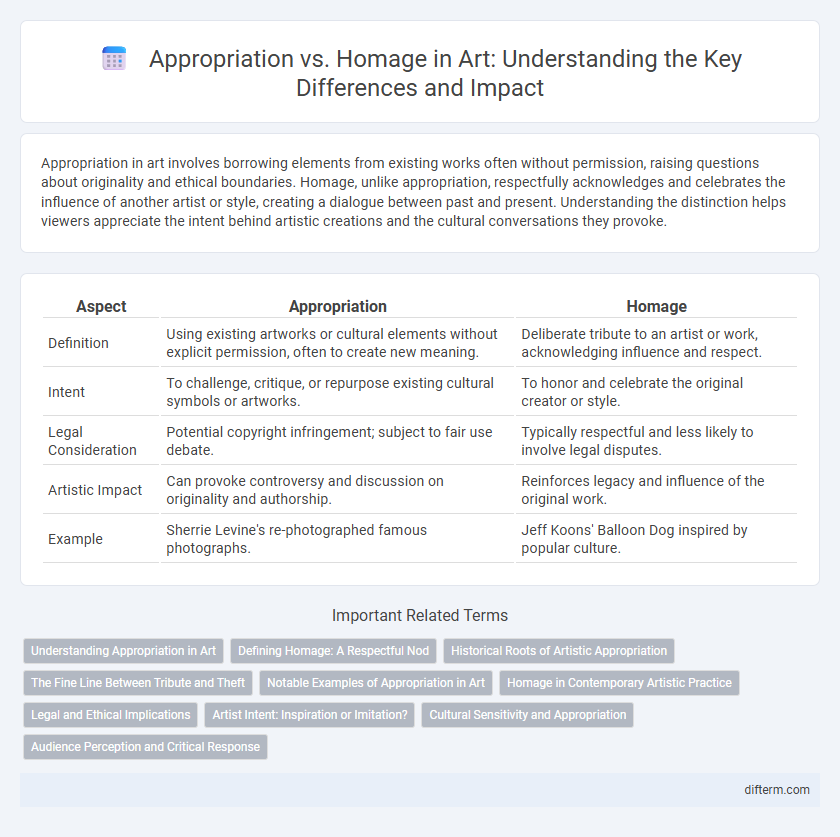
| Aspect | Appropriation | Homage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using existing artworks or cultural elements without explicit permission, often to create new meaning. | Deliberate tribute to an artist or work, acknowledging influence and respect. |
| Intent | To challenge, critique, or repurpose existing cultural symbols or artworks. | To honor and celebrate the original creator or style. |
| Legal Consideration | Potential copyright infringement; subject to fair use debate. | Typically respectful and less likely to involve legal disputes. |
| Artistic Impact | Can provoke controversy and discussion on originality and authorship. | Reinforces legacy and influence of the original work. |
| Example | Sherrie Levine's re-photographed famous photographs. | Jeff Koons' Balloon Dog inspired by popular culture. |
Understanding Appropriation in Art
Appropriation in art involves the deliberate borrowing or reuse of existing images, styles, or cultural elements to create new works that challenge originality and authorship concepts. This practice often raises critical questions about intellectual property, cultural sensitivity, and the boundaries between influence and exploitation. Understanding appropriation requires analyzing the intent behind the work, the context of borrowed material, and the dialogue it creates between past and present artistic expressions.
Defining Homage: A Respectful Nod
Homage in art signifies a respectful nod to an original work or artist, incorporating recognizable elements while honoring the source's significance. Unlike appropriation, homage emphasizes admiration and acknowledgment rather than unauthorized use or critique. This practice fosters creative dialogue, connecting contemporary creators with historical influences through intentional tribute.
Historical Roots of Artistic Appropriation
Artistic appropriation traces back to Renaissance artists who borrowed classical motifs to innovate new styles, reflecting a continuum of cultural dialogue. The practice evolved as artists in the 20th century recontextualized images and objects to challenge notions of originality and authorship. Understanding these historical roots highlights how appropriation serves as a transformative process rather than mere replication, distinguishing it from homage, which typically honors and preserves the integrity of source material.
The Fine Line Between Tribute and Theft
Appropriation in art involves using existing objects or images with little transformation, raising concerns about originality and intellectual property rights. Homage pays respectful tribute to an artist or style, often adding personal interpretation or context that honors the source. The fine line between tribute and theft hinges on intent, originality, and cultural sensitivity, with legal frameworks like copyright laws providing boundaries.
Notable Examples of Appropriation in Art
Notable examples of appropriation in art include Sherrie Levine's re-photographing of Walker Evans's images, which challenges notions of originality and authorship, and Jeff Koons's reproduction of banal objects such as balloon animals, questioning consumer culture and artistic value. Richard Prince's re-photography of Marlboro ads sparked debates on copyright and artistic expression by transforming commercial images into fine art. These works exemplify how appropriation recontextualizes existing images to critique cultural norms and redefine creative ownership.
Homage in Contemporary Artistic Practice
Homage in contemporary artistic practice serves as a deliberate and respectful nod to influential artists or movements, often reinterpreting classic themes through a modern lens. This practice enriches cultural dialogues by bridging historical and current artistic expressions, fostering deeper appreciation rather than replication. Artists employ homage to celebrate legacy while asserting their unique creative voices within evolving art narratives.
Legal and Ethical Implications
Appropriation in art involves using existing works or cultural elements without permission, often raising legal issues such as copyright infringement and moral rights violations. Homage respects the original creator by crediting source material and transforming it in a way that acknowledges its influence while avoiding direct replication. Ethical considerations emphasize intention, cultural sensitivity, and the impact on original communities, distinguishing respectful homage from exploitative appropriation.
Artist Intent: Inspiration or Imitation?
Artist intent plays a crucial role in distinguishing appropriation from homage, as genuine homage reflects inspiration and respect for the original work, while appropriation often implies imitation without acknowledgment. In art, homage preserves the original creator's significance, enhancing meaning through reinterpretation, whereas appropriation risks diminishing authenticity by repurposing elements primarily for personal gain. Understanding the nuanced intentions behind an artwork helps viewers discern whether it contributes to cultural dialogue or merely copies existing creative expressions.
Cultural Sensitivity and Appropriation
Appropriation in art often involves the unauthorized use of cultural symbols, styles, or meanings, leading to potential misrepresentation and disrespect of marginalized communities. Homage respects the source culture by acknowledging its significance and context, fostering appreciation rather than exploitation. Artists must prioritize cultural sensitivity to avoid perpetuating stereotypes and ensure ethical creative expression.
Audience Perception and Critical Response
Audience perception of appropriation in art often hinges on the perceived intent and originality, with critics scrutinizing whether the work exploits or respectfully references the source material. Homage tends to be viewed more favorably, fostering appreciation for influences and cultural continuity, while appropriation can provoke debates about authorship, cultural sensitivity, and ethical boundaries. Critical response frequently evaluates the artist's ability to transform the appropriated elements, emphasizing creative innovation versus mere replication.
Appropriation vs Homage Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com