Analog art captures the tactile essence of materials, offering a unique, textured experience that engages the senses in a way digital art often can't replicate. Digital art provides unmatched flexibility and precision, allowing artists to experiment with infinite variations and easily correct mistakes. The choice between analog and digital mediums influences the creative process, artistic expression, and final aesthetic of a piece.
Table of Comparison
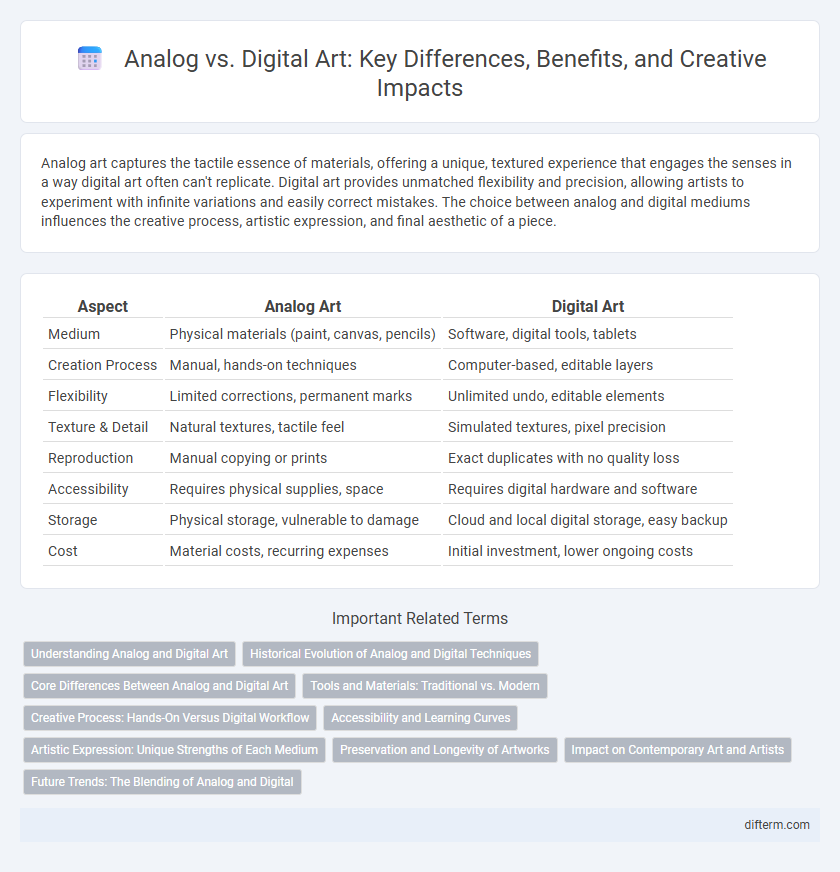
| Aspect | Analog Art | Digital Art |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Physical materials (paint, canvas, pencils) | Software, digital tools, tablets |
| Creation Process | Manual, hands-on techniques | Computer-based, editable layers |
| Flexibility | Limited corrections, permanent marks | Unlimited undo, editable elements |
| Texture & Detail | Natural textures, tactile feel | Simulated textures, pixel precision |
| Reproduction | Manual copying or prints | Exact duplicates with no quality loss |
| Accessibility | Requires physical supplies, space | Requires digital hardware and software |
| Storage | Physical storage, vulnerable to damage | Cloud and local digital storage, easy backup |
| Cost | Material costs, recurring expenses | Initial investment, lower ongoing costs |
Understanding Analog and Digital Art
Analog art involves traditional methods such as painting, drawing, and sculpting, relying on physical materials like canvas, paper, and clay to create tangible artworks. Digital art utilizes software, tablets, and computers to produce images that can be easily edited, duplicated, and shared across digital platforms. Understanding the strengths of analog's tactile texture and digital's versatility helps artists choose the best medium for their creative vision.
Historical Evolution of Analog and Digital Techniques
Analog art techniques, rooted in traditions like painting and sculpture, evolved over centuries through manual craftsmanship and direct material interaction. The digital revolution began in the mid-20th century, introducing pixel-based creation and computer-aided design, transforming artistic processes with software tools and digital media. This shift enabled new forms of expression, merging traditional aesthetics with advanced technology to expand creative possibilities.
Core Differences Between Analog and Digital Art
Analog art involves traditional methods using tangible materials like paint, canvas, and brushes, emphasizing tactile texture and physical presence. Digital art relies on software and electronic devices, enabling infinite editing, layering, and the use of digital tools such as tablets and styluses. Core differences include the permanence of physical mediums in analog art versus the versatility and reproducibility of digital formats.
Tools and Materials: Traditional vs. Modern
Traditional art relies on physical tools and materials such as brushes, canvas, charcoal, and oil paints, offering tactile control and unique texture effects. Digital art utilizes software programs like Adobe Photoshop and Procreate, alongside hardware like graphics tablets and styluses, enabling precise editing and infinite color palettes. Both mediums influence creative processes, with analog requiring manual skills while digital incorporates technology-driven flexibility and experimentative potential.
Creative Process: Hands-On Versus Digital Workflow
The creative process in analog art emphasizes tactile engagement with materials such as paint, clay, or charcoal, fostering intuitive experimentation and physical connection to the medium. Digital workflows streamline creation through software tools like Adobe Photoshop or Procreate, offering features like undo, layering, and infinite color palettes that enhance precision and efficiency. Both analog and digital methods influence artistic expression uniquely, shaping the concept, technique, and final output of the artwork.
Accessibility and Learning Curves
Analog art techniques offer tactile engagement and intuitive control, making them accessible to beginners who prefer hands-on experiences, though mastering precision can require extensive practice. Digital art provides versatile tools and immediate feedback, lowering initial learning barriers while enabling complex adjustments that streamline the creative process. Both mediums cater to diverse learning preferences, shaping accessibility through either physical interaction or user-friendly software interfaces.
Artistic Expression: Unique Strengths of Each Medium
Analog art offers tactile textures and spontaneous imperfections, allowing artists to physically engage with materials and create one-of-a-kind pieces rich in emotional depth. Digital art provides precision, versatility, and infinite editing possibilities with tools like layers, filters, and digital brushes, enabling complex compositions and seamless experimentation. Both mediums contribute uniquely to artistic expression, with analog emphasizing materiality and digital enhancing creative flexibility.
Preservation and Longevity of Artworks
Analog artworks, such as paintings and sculptures, often benefit from physical durability and historical authenticity, but they are susceptible to environmental damage like fading, mold, and physical wear. Digital artworks offer ease of replication and backup, ensuring longevity through multiple storage options and cloud preservation, yet face challenges including technological obsolescence and data corruption. Preservation strategies increasingly combine high-resolution digitization of analog pieces with digital archiving to balance authenticity and long-term accessibility.
Impact on Contemporary Art and Artists
The impact of analog versus digital mediums on contemporary art fundamentally shapes creative expression and artistic innovation, with analog techniques offering tactile authenticity and digital tools enabling expansive multimedia experimentation. Artists leveraging digital platforms gain unprecedented reach and interactive possibilities, transforming audience engagement and enabling dynamic, evolving artworks. Meanwhile, analog art preserves traditional craftsmanship, emphasizing materiality and physical presence that continue to influence contemporary aesthetics and artistic discourse.
Future Trends: The Blending of Analog and Digital
Future trends in art reveal a seamless blending of analog and digital techniques, where traditional mediums like painting and sculpture integrate with augmented reality and AI-driven processes. Artists increasingly leverage digital tools to enhance tactile experiences while preserving the authenticity of analog textures and materials. This fusion fosters innovative expressions that redefine creativity, pushing boundaries between physical art and immersive digital environments.
Analog vs Digital Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com