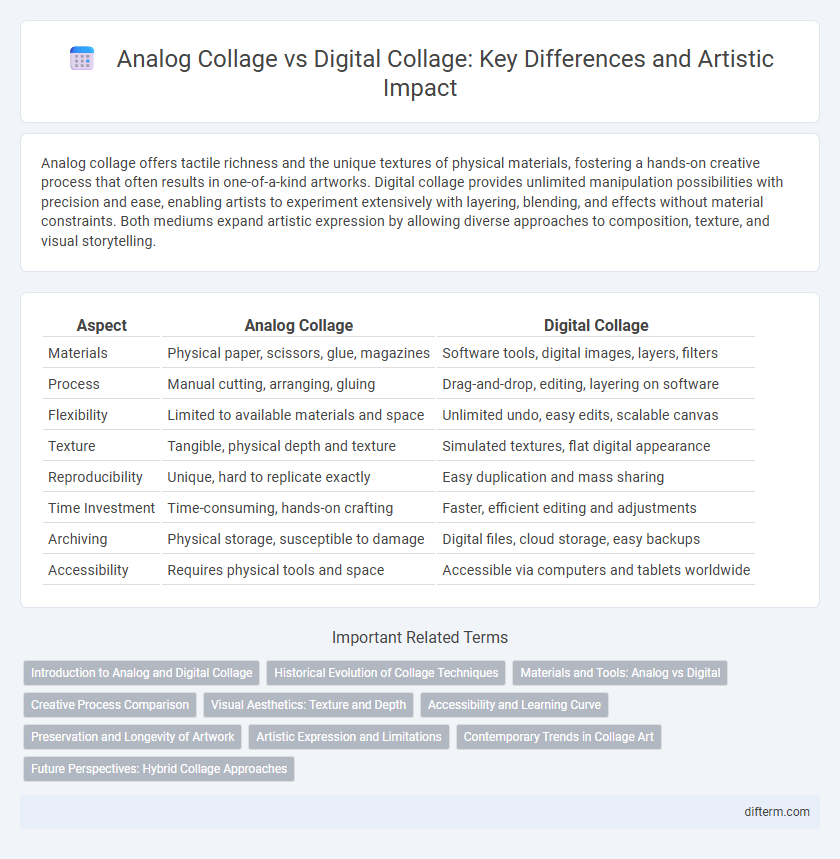
Analog collage offers tactile richness and the unique textures of physical materials, fostering a hands-on creative process that often results in one-of-a-kind artworks. Digital collage provides unlimited manipulation possibilities with precision and ease, enabling artists to experiment extensively with layering, blending, and effects without material constraints. Both mediums expand artistic expression by allowing diverse approaches to composition, texture, and visual storytelling.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Analog Collage | Digital Collage |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | Physical paper, scissors, glue, magazines | Software tools, digital images, layers, filters |
| Process | Manual cutting, arranging, gluing | Drag-and-drop, editing, layering on software |
| Flexibility | Limited to available materials and space | Unlimited undo, easy edits, scalable canvas |
| Texture | Tangible, physical depth and texture | Simulated textures, flat digital appearance |
| Reproducibility | Unique, hard to replicate exactly | Easy duplication and mass sharing |
| Time Investment | Time-consuming, hands-on crafting | Faster, efficient editing and adjustments |
| Archiving | Physical storage, susceptible to damage | Digital files, cloud storage, easy backups |
| Accessibility | Requires physical tools and space | Accessible via computers and tablets worldwide |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Collage
Analog collage involves physically assembling different materials like paper, fabric, and photographs to create a tactile, textured artwork, emphasizing hands-on creativity and original materiality. Digital collage employs software tools such as Adobe Photoshop or Procreate to manipulate and layer images digitally, allowing for infinite adjustments, ease of replication, and integration of multimedia elements. Both techniques offer unique artistic possibilities, blending traditional craft methods with modern technology to expand the boundaries of visual storytelling.
Historical Evolution of Collage Techniques
Analog collage originated in the early 20th century with artists like Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, who pioneered Cubism by assembling torn paper and everyday objects to create new visual narratives. Digital collage emerged in the late 20th century, leveraging advanced software such as Adobe Photoshop, enabling artists to manipulate images with precision and layers previously impossible in traditional methods. The historical evolution of collage techniques reflects a shift from tactile, manual assembly to dynamic, computer-aided composition, expanding creative possibilities and accessibility in contemporary art.
Materials and Tools: Analog vs Digital
Analog collage relies on physical materials such as paper, fabric, magazines, and adhesives combined with traditional tools like scissors, glue, and cutting mats, offering tactile texture and organic layering. Digital collage utilizes software like Adobe Photoshop or Procreate, leveraging virtual brushes, layers, and image manipulation tools that allow for infinite editing flexibility and precise control over blending and composition. The choice between analog and digital tools significantly impacts the creative process, material interaction, and the final artwork's texture and dimensionality.
Creative Process Comparison
Analog collage involves a tactile, hands-on approach using physical materials like paper, fabric, and found objects, which fosters spontaneity and unique texture in the creative process. Digital collage leverages software tools such as Adobe Photoshop and Procreate, enabling extensive experimentation, layering, and easy revisions without material constraints. Both methods demand artistic intuition and composition skills, but digital collage offers greater flexibility and efficiency in manipulating imagery and effects.
Visual Aesthetics: Texture and Depth
Analog collage offers tactile textures and layered depth through physical materials like paper, fabric, and found objects, creating a multidimensional visual experience that engages the viewer's sense of touch and sight. Digital collage achieves texture and depth by manipulating pixels, shadows, and blending modes, allowing for precise control over visual elements and seamless integration of diverse images. The choice between analog and digital collage significantly influences the artwork's tangible feel and visual complexity, shaping the overall aesthetic impact.
Accessibility and Learning Curve
Analog collage requires physical materials such as magazines, scissors, and glue, making it less accessible due to cost and space constraints. Digital collage offers greater accessibility through software tools and online resources, enabling easier experimentation and editing without physical mess. The learning curve for analog collage is generally straightforward, relying on manual skills, whereas digital collage involves mastering software interfaces and digital techniques, which can be more complex for beginners.
Preservation and Longevity of Artwork
Analog collage relies on physical materials such as paper, fabric, and adhesives, which are vulnerable to environmental factors like light, humidity, and pests, potentially causing deterioration over time. Digital collage offers enhanced preservation and longevity by storing artwork in high-resolution digital formats, resistant to physical degradation and easily duplicated for archival purposes. However, the longevity of digital files depends on regular data migration and technological compatibility, necessitating proactive maintenance to prevent data loss.
Artistic Expression and Limitations
Analog collage offers tactile engagement, allowing artists to physically manipulate materials like paper, fabric, and found objects, which fosters unique textures and unforeseen juxtapositions integral to artistic expression. Digital collage provides expansive creative possibilities through software tools that enable layering, resizing, and color manipulation with precision, yet may lack the tangible spontaneity and imperfections that characterize analog work. Both mediums impose limitations: analog collages are constrained by physical materials and spatial dimensions, whereas digital collages rely on screen resolution and digital format constraints that can influence the final output's authenticity and sensory impact.
Contemporary Trends in Collage Art
Contemporary collage art increasingly blurs the lines between analog and digital techniques, with artists integrating traditional cut-and-paste methods alongside digital manipulation software such as Adobe Photoshop and Procreate. The resurgence of analog collage emphasizes tactile textures, physical layering, and found materials, while digital collage offers limitless possibilities for scale, color adjustment, and precision editing. Current trends show a hybrid approach dominating galleries and online platforms, reflecting a dynamic dialogue between materiality and virtual creativity in modern art practices.
Future Perspectives: Hybrid Collage Approaches
Hybrid collage approaches combine analog and digital techniques, offering artists enhanced creative flexibility and expanded aesthetic possibilities. The integration of tactile textures from traditional collage with the precision and scalability of digital tools fosters innovative artworks that can be easily modified and reproduced. Emerging technologies such as augmented reality and AI-driven design are further transforming hybrid collages, pushing the boundaries of artistic expression for future generations.
analog collage vs digital collage Infographic
 difterm.com
difterm.com